– 0.5 pts ea Section 17 fill-in-the-blank
advertisement

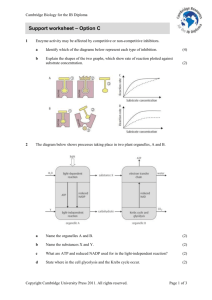
Section 17 fill-in-the-blank – 0.5 pts ea During stage III of cell respiration, reduced coenzymes are produced during the metabolic pathway known as Kreb’s cycle, which takes place in the matrix of the mitochondrion. During stage IV, a proton gradient is established across a membrane due to flow of electrons from 1 complex to next, with final oxidizing agent being O2. This gradient is dissipated during chemiosmosis, which is the diffusion of protons through ATP synthase, making ATP. In chloroplasts, the process is similar, except that the original source of electrons is H2O, and the final oxidizing agent in non-cyclic photophosphorylation is NADP. The light-independent reaction, or Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts. In C3 plants, such chloroplasts would be conducting this cycle in mesophyll cells; in C4 plants it would be done in bundle sheath cells. CAM plants, such as cactuses and bromeliads carry out the light and light-independent reaction at (during) daytime and fix CO2 at night. In these plants, the 1st stable product of fixation is 4-C compounds. The enzyme which carboxylates RuBP in these plants is RUBISCO.