MSE 308 Thermodynamics of Materials Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering

MSE 308
Thermodynamics of Materials
Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering
Spring 2005/Bill Knowlton
Problem Set 5 Solutions
1.
Develop a state function for pressure for a system in which changes in Helmholtz free energy and temperature. Simplify your answer to receive full credit.
MSE 308
Thermodynamics of Materials
Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering
Spring 2005/Bill Knowlton
2.
Develop a state function for Gibb’s free energy for a system that undergoes a change in volume and entropy. Simplify your answer to receive full credit.
MSE 308
Thermodynamics of Materials
Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering
Spring 2005/Bill Knowlton
MSE 308
Thermodynamics of Materials
Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering
Spring 2005/Bill Knowlton
3.
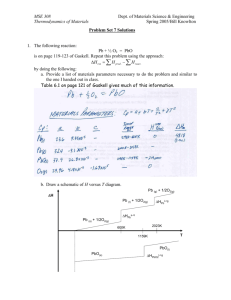
Compute the change in internal energy when 12 liters of argon gas at 273 K and 1 atm is compressed to 6 liters with the final pressure is equal to 10 atm. Solve this problem in two different ways: a.
Apply the general procedure to evaluate U = U ( P,V ) and integrate from initial to final ( P,V ).
MSE 308
Thermodynamics of Materials
Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering
Spring 2005/Bill Knowlton
MSE 308
Thermodynamics of Materials
Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering
Spring 2005/Bill Knowlton
MSE 308
Thermodynamics of Materials
Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering
Spring 2005/Bill Knowlton b.
Use the information to compute the final temperature of the gas and apply the general relation
δ
U = Cv
∆
T.
72 atm L x()
4.
MSE 308
Thermodynamics of Materials
Evaluate the partial derivative: in terms of experimental variables.
Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering
Spring 2005/Bill Knowlton
⎛ ∂
H
⎞
⎜
∂
G
⎟
S
MSE 308
Thermodynamics of Materials
Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering
Spring 2005/Bill Knowlton
5.
Derive the relationship that describes the dependence of Helmholtz free energy on entropy and temperature.