How Does WFC3 Geometric Distortion Vary with Time ? Kozhurina-Platais
advertisement

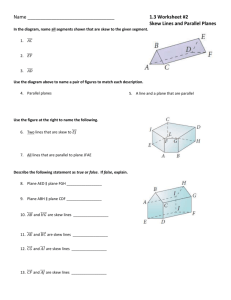
How Does WFC3 Geometric Distortion Vary with Time ? Kozhurina-Platais Observations Ω Cen observed with the WFC3/UVIS and IR F606W & F160W filters Wide Range PA_V3 and Large POSTARG ±40” L_Flat and Distortion Cal Programs: POSTARG ±40” & wide range PA_V3 Special Cal Program (12094) Δ(PA_V3) = ±10° Reduction Multidrizzled UVIS and IR images: correcting for distortion correcting for velocity aberration (VAFACTOR) Measured X,Y positions on all drizzled UVIS/IR images Defined u,v reference system from X,Y on first UVIS/IR drizzled image (2009) reducing the epoch difference ~ 4-5 years reducing scatter in measured positions due to μα = -4.9mas/yr , μδ = -3.5mas/yr internal velocity dispersion ~1 mas/yr Defined X,Y measured system from positions on all other UVIS/IR drizzled images Definition of Skew Y v Ouv - standard orthogonal system MXY - measured system Y u = X0 + A×X + B×Y v = Y0 + C×X + D×Y vo u Yo O uo X0 Y0 - offset between Ouv and MXY A,B,C,D - linear terms M Xo X 90° + X TAN( ) = B / D - rotation between Ouv and MXY TAN( ) = - (A×B + C×D) / (A×D − C×B) - skew term Kiselev A.A., 1989, “Nayka”, St.Petersburg, Russia UVIS Skew () Variation UVIS skew variation over 2 years : UVIS skew variation over 3 consecutive orbits Δ(PA_V3) = ±10° Yellow – target occultation Green – orbital target visibility Blue – orbital night All compared w.r.t first epoch (2009) Purple - linear fit f(t) = ao+ a1 Red - constant f(t) = ao Skew () = 1.7“ +/- 0.4” 1.7” scaled by 2048 ~0.02pix or 0.8mas UVIS skew variation over 3 consecutive orbits PA_V3 no changed, POSTARG ±40” Yellow – target occultation Green – orbital target visibility Blue – orbital night UVIS Skew () Variation and HST Focus? UVIS skew variation over 3 consecutive orbits (~7.5 h), July, 2010 Blue – temperature-based model of the UVIS focus Red – calculated skew UVIS measured focus and UVIS temperature based focus model Blue – temperature-based focus model Red – measured UVIS focus Difference between measured and its model due to e.g: - combination of Sun angle; - off-nominal HST roll-angle; - difference in temperature on different part of HST Variation of Skew on a orbital time scale is related to focus variations (e.g. orbital breathing) Focus variation effects PSF centroid changes skew (astrometric scale) Deviation of skew ±8” scaled by 2048 pixel ≈ 0.05 pixels or 2mas Effect is too complex to model astrometric scale change on HST orbital time scale ACS/WFC & WFC3/UVIS Skew Anderson, J., “Variation of the Distortion Solution of the WFC”, 2007, ACS-ISR-07-08 u = X0 + A×X + B×Y v = Y0 + C×X + D×Y (A − D) / 2 (B + C) / 2 - on - axis skew - off - axis skew ACS/WFC skew linearly changed vs time Off-axis skew ~0.3 WFC pixels (15mas) over 5-6 yr Kozhurina-Platais, V., and Petro, L., 2012 , WFC3-ISR-12-03 On-axis skew ~0 Off-axis skew < 0.02 pix or (0.4mas) WFC3/IR Skew () Variation IR skew () variation over 2 years time scale : All compared w.r.t first epoch i.e.2009 (top) Average skew per epoch (bottom) Purple - linear fit f(t)=ao+a1 Red - constant f(t)=ao Skew () = -3.6“ +/- 1.2” -3.6” scaled by 512 ~0.02pix (~2mas) On-axis skew < 0.02 pix (2mas) Off-axis skew ~0 Conclusions WFC3/UVIS and IR geometric distortion is stable on the 2-year time scale WFC3/UVIS and IR skew linearly changes over short time interval of orbital target visibility Deviation of UVIS skew ±8” scaled by 2048 pixel ~ 2mas Deviation of IR skew ±20” scaled by 512 pixel ~7mas Short term variation of UVIS and IR skew are likely due to the orbital breathing Acknowledgments Larry Petro and Knox Long - suggestions and comments on ISR Bill Januszewski - help on design two special calibration programs CAL-12094 & CAL-12353 George Chapman – discussion on orbital target occultation and target visibility Matt Lallo – discussion on HST focus model Matt Bourque – comments on slides UVIS XY residuals wrt 47Tuc and LMC Standard Catalog IR XY residuals wrt 47Tuc Standard Catalog UVIS XY residuals wrt Omega Cen Standard Catalog