Phy 2053 Announcements I Phy 2053 Announcements II
advertisement

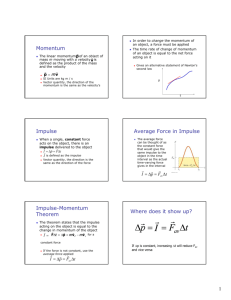
Phy 2053 Announcements I Exam 1 info 1. Please get there at least 10 minutes early, and preferably 20 minutes H-ITT clicker grades: 5. Up through and including gravitational potential energy – no springs!! Room assignments If your last name begins with A through P, you should go to Carleton 100 If your last name begins with R through Z, you should go to Pugh 170 You be allowed one handwritten formula sheet (both sides), 8 ½” x 11” paper In class review, Tuesday, Feb 17 2. Reitze will have special office hours Monday Feb 16 10 am 12 pm 4. Material from sections 1.1 – 5.3 of Serway/Vuille, 20 questions, multiple choice Chan back in town next week; normal office hours 3. Feb 18, 8:20 – 10:10 pm Phy 2053 Announcements II You may not receive any clicker grades this week; if not, don’t worry, your grades are still being recorded and they will resume when Prof. Chan returns HW set #5 is not due until Feb 25 6. Note: Exam 1 may include material that is covered in the HW set (problems 5.28, 5,40, 5.78, 5.80, 5.85, and 5.92), so you are strongly encouraged to complete this set before Exam 1 next week. Professor Biswas at the helm today Power Example #5-53 The rate at which energy transfer takes place Work F Δx P = = = Fv Δt Δt J kg m 2 =1 3 s s SI units are Watts: 1 W = Motors (US): 1 hp = 550 ft lb = 746 W 1 The electric motor of a model train accelerates the train from rest to 0.620 m/s in 21 ms. The total mass of the train is 875 g. Find the average power delivered to the train during the acceleration. (Assume the train is on a level track.) s KW-h is a unit of energy (check your electric bill!) http://www.poormansmodelrailroad.com/sites/cjackson/_files/Image/jflayoutlrg.jpg Center of Mass (Center of Gravity near Earth’s Surface) The point in the body which is used to measure the change in gravitational potential Try this at home 1 Why was energy a good concept to learn? From Schroedinger equation Because it was conserved. Conservation of energy equation in quantum mechanics Physicists love conservation (KE + PE) is conserved. PE is electrostatic (PHY2054) KE = Chapter 6 Momentum and Collisions Momentum The linear momentum of an object of mass m moving with a velocity is defined as the product of the mass and the velocity SI Units are kg m / s Vector quantity, the direction of the momentum is the same as the velocity’s In order to change the momentum of an object, a force must be applied The time rate of change of momentum of an object is equal to the net force acting on it Gives an alternative statement of Newton’s second law r Δp m(vf − v i ) r = = Fnet Δt Δt p t 2 Impulse Average Force in Impulse When a single, constant force acts on the object, there is an impulse delivered to the object r r r I = Δp = FΔt is defined as the impulse Vector quantity, the direction is the same as the direction of the force The average force can be thought of as the constant force that would give the same impulse to the object in the time interval as the actual time-varying force gives in the interval r r r I = Δp = Fav Δt Impulse-Momentum Theorem Where does it show up? The theorem states that the impulse acting on the object is equal to the change in momentum of the object r I = for a constant force If the force is not constant, use the average force applied If Δp is constant, increasing Δt will reduce Fav and vice versa r r r I = Δp = Fav Δt Deliberately increasing Δt to reduce Fav Large Fav, Small Δt 3 Good luck on your exam!!! 4