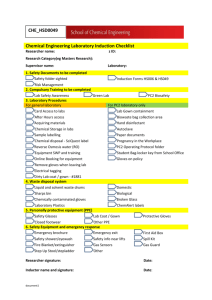
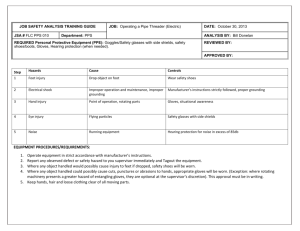
University of Colorado at Colorado Springs _________________________________________________________________________
advertisement

University of Colorado at Colorado Springs _________________________________________________________________________ Environmental Health and Safety Department of Public Safety 1420 Austin Bluffs Parkway Colorado Springs, Colorado 80918 719-255-3201 Animal Biosafety Level 2 (ABSL-2) Training Quiz Directions: Complete this Quiz and e-mail it to cnorton@uccs.edu or mail it to DPS-207. In order to receive credit for this training, you must provide the following contact information. Name: e-mail: Lab PI: Date: Status (Undergrad, Grad, PostDoc, Faculty): Phone #: Department: QUIZ SCORE: Risk Assessment & Risk Management 1. A Risk Assessment identifies risk factors associated with the work to be performed. ____ True ____ False 2. What is Risk Management? ____ a) manages lab activities that can be hazardous ____ b) manages the animal procedures ____ c) manages the biological and chemical agents used in animal procedures ____ d) manages the risks identified from the risk assessment 3. What are the common risk factors associated with the animal? ____ a) potential for bites and scratches, allergens, and animal facility ____ b) allergens and needle sticks ____ c) species, potential for bites and scratches, allergens, and zoonoses ____ d) species and the animal facility 4. What are the common risk factors associated with the agent studied? ____ a) agent’s stability and pathogenicity, dose used, potential to infect humans, and the manner and degree the animal sheds the agent ____ b) agent’s pathogenicity, potential to infect humans, and the manner and degree the sheds the agent ____ c) agent’s stability and pathogenicity ____ d) how the agent is being introduced into the animal and the dose used 5. What are the common risk factors associated with the research? ____ a) agent’s pathogenicity and dose used ____ b) what Risk Group the agent is in ____ c) agent’s concentration, procedures and/or equipment used, and the potential for transmission to humans (i.e. spill, needle stick, aerosolize agent) ____ d) how the agent is being introduced into the animal and the dose used animal 6. The following factor(s) must also be taken into account when performing a risk assessment: a) b) c) d) e) 7. immunization is available for this agent treatment is available if exposed to agent health status of lab personnel (i.e. immunocompromised) skill and expertise level of the lab personnel and animal care personnel performing the work all of the above A risk management plan must be specific to the agent(s) being used in describing the facility and biosafety containment level, the safety equipment, and the personal protective equipment and clothing required. ____ True ____ False Working at Animal Biosafety Level 2 (ABSL-2) 8. Work at ABSL-2 is suitable for work with animals infected with biological agents that are associated with human or animal disease. ____ True ____ False 9. For pathogens at ABSL-2, the risk of infection from inhalation of aerosols is typically greater than the risk of infection through cuts or breaks in the skin, ingestion and splashes to the eyes, nose or mouth. ____ True ____ False 10. The agents that typically fall into the ABSL-2 category are referred to as: a) Risk Group 2 pathogens b) Risk Group 3 pathogens c) Risk Group 1 pathogens d) Risk Group 4 pathogens 11. The air supply and exhaust system maintains the following pressure within the animal room relative to the adjoining spaces: ____ a) positive pressure ____ b) negative pressure ____ c) neutral pressure 12. A hand washing sink is not required to be in the immediate area of performing work with infected animals? ____ True ____ False 13. Work being performed in animals with Risk Group 2 agents can be done in the animal facility or lab where there is unrestricted access. ____ True ____ False 14. At a minimum, the following protective clothing must be worn when working at ABSL-2: a) gloves, lab coat, and other clothing to protect eyes, nose and mouth from splashes b) gloves, lab coat, shoe coverings c) lab coat, hair cover, surgical mask d) face shield, lab coat, hair cover 15. It is very important to conduct a risk assessment for each animal protocol to determine the appropriate personal protective clothing and equipment. ____ True ____ False 16. Individuals who have access to an ABSL-2 facility must have specialized training which is specific to the hazards associated with the work being performed. ____ True ____ False 17. If a risk assessment has been completed for the animal protocol, then no training is required prior to entering an ABSL-2 facility or working with animals at ABSL-2. ____ True ____ False 18. In order to properly disinfect all interior surfaces of the biosafety cabinet, it is acceptable to stick your head inside the cabinet as long as the cabinet blower is running. ____ True ____ False 19. A Class II biosafety cabinet or another physical containment device should always be used for aerosol generating procedures involving infectious agents. ____ True ____ False 20. Which of the following is an example of an aerosol generating procedure? a) harvesting tissues or fluids b) cage changing c) necropsy d) all of the above 21. Whenever injecting an animal with an infectious agent, it is important to wipe the injection site with a disinfectant after the injection to absorb any excess agent that may have been expelled by the animal or needle onto the animal’s fur. ____ True ____ False 22. Which of the following statements is correct for proper disinfection? a) use a 10% bleach solution b) use a disinfectant and sufficient contact time that is specific to the infectious organism(s) c) use a disinfectant that is specific to the infectious organism(s) d) use 70% ethanol solution 23. Items in the biosafety cabinet which have not come in contact with the animal or the biological agent may be removed from the cabinet without being decontaminated with an effective disinfectant for the appropriate contact time. ____ True ____ False 24. When exiting the animal room, in what order should protective clothing be removed? a) shoe covers, then outer gloves, then lab coat, then inner gloves, then hair cover and face protection last b) outer gloves, then lab coat, then shoe covers, then hair cover and face protection, then inner gloves last c) outer gloves, then lab coat, then shoe covers, then inner gloves, and then hair cover and face protection last d) shoe covers, then lab coat, then outer gloves, then hair cover and face protection, and inner gloves last 25. The best way to avoid contaminating areas of your skin while removing protective clothing is to turn the clothing and gloves inside-out as they are removed. ____ True ____ False