Combined Effects of Optimism Level and Caffeine Intake on QEEG... A Pilot Study Befor Afte
advertisement

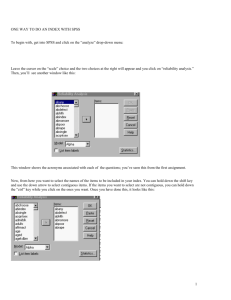
Combined Effects of Optimism Level and Caffeine Intake on QEEG Alpha Wave Power: Melissa Lenert & Dr. Luis Aguerrevere A Pilot Study Stephen F. Austin State University Mean AlphaResults Activity vs Location Introduction Caffeine has a general effect on alpha brain waves (Diukova, 2010). Heavy caffeine users experienced increased neural activity compared to vasoconstriction (Gilbert et al., 2000) Purpose of the pilot study is to assess the effects of caffeine intake and optimism levels on alpha wave activity in heavy caffeine users. Z-Scored Alpha Activity Example Befor e 16.0000 Absolute Power 14.0000 12.0000 Relative Power Average Alpha Vales 10.0000 Method 8.0000 Amplitude Asymmetry 6.0000 Participants Six participants: three males and three females All participants are heavy caffeine users – defined as daily consumption of more than one cup of coffee Materials and Methods Participants abstained from caffeine for 12 hours prior to assessment Assessments occurred between 8am and 11am Standard QEEG assessments using the 10-20 system First assessment prior to coffee Participants drank one cup of black coffee Second assessment 20 minutes after coffee Afte r 4.0000 Coherence 2.0000 0.0000 F3 AF3 F4 AF4 C3 AC3 C4 AC4 P3 AP3 P4 AP4 T3 AT3 T4 Skull Locations AT4 Phase Lag Results Strong correlations between absolute power and optimism in frontal (before R=-0.345; after R=-0.447) Greater caffeine activity correlated with optimism in frontal (R=0.413) and central (R=0.359) locations Interhemispheric differences in temporal areas (Mean before=1.54; Mean after=1.46) Human Neuroscience Lab Conclusion Caffeine has a general effect on alpha wave activity and optimism scores in heavy users. Although the sample size is small, the trend is significant enough to warrant further study. Poster Presented at the Undergraduate Research Conference March 31, 2016, 4:00 PM - 7:30 PM, Nacogdoches, TX