What is temperature?
advertisement

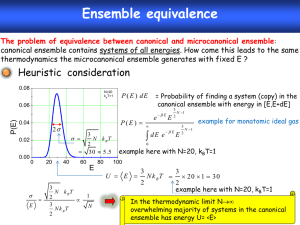
What is temperature? 1. Temperature (T) measures the tendency of an object to spontaneously give up/absorb energy to/from its surroundings. 2. Most likely macrostate the system will find itself in is the one with the maximum number of microstates. E1 E2 1(E1) 2(E2) d ln 1 d ln 2 1 dE1 dE2 k BT Ensemble a complete costume of harmonizing or complementary clothing and accessories a group of people or things that make up a complete unit (such as a musical group, a group of actors or dancers, or a set of clothes) Microcanonical ensemble: An ensemble of snapshots of a system with the same N, V, and E Microcanonical ensemble: An ensemble of snapshots of a system with the same N, V, and E Canonical ensemble: An ensemble of snapshots of a system with the same N, V, and T E1 1(E1) E2 2(E2) Canonical ensemble: An ensemble of snapshots of a system with the same N, V, and T (red box with energy << E. E- (E-) I( ) Boltzmann Factor (canonical ensemble) P ( ) e k BT clear all; s = 100; e = 11; et = 40; for n = 1:e i=n-1; x(n)=n-1; y(n)=factorial(s-1)./(factorial(et-i).*factorial((s-1)-(et-i))); end plot(x,y,'b--o') pause z = log(y); plot(z,x,'b--o')