Forecasting Sample Problems: Finance & Accounting

Sample Problems--Forecasting
1.
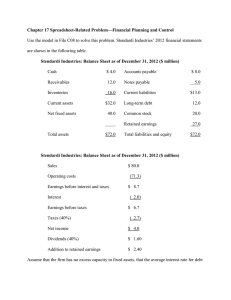
Jill's Wigs Inc. had the following balance sheet last year:
Cash $ 800 Accounts payable
Accts receivable
Inventory
450
950
Accrued wages
Notes payable
Net fixed assets 34,000
Total assets $36,200
Mortgage
Common stock
Retained earnings
Total liabilities and equity
$ 350
150
2,000
26,500
3,200
4,000
$36,200
Jill has just invented a non-slip wig for men which she expects will cause sales to double, increasing after-tax net income to $1,000. She feels that she can handle the increase without adding any fixed assets. (1)Will Jill need any external financing if she pays no dividends? (2) If so, how much?
2.
You are given the following information:
Taxes (at 34%)
Net income
$ 17
$ 33
Dividend payout ratio 30%
If costs maintain a constant percentage of sales, what is the addition to retained earnings resulting from a 10% increase in sales?
3.
You are the owner of a small business which has the following balance sheet last:
Current assets
Net fixed assets
$ 5,000
10,000
Accounts payable
Accruals
Long-term debt
Common equity
$1,000
1,000
5,000
8,000
Total assets $15,000
Total liabilities and equity $15,000
Fixed and currents assets are fully utilized. All assets as well as accounts payables and accruals will increase at the same rate as sales. Next year you expect sales to increase by 50 percent. You also expect to retain $2,000 of next year's earnings within the firm. What is next year's additional external funding requirement, i.e., what is your firm's
AFN?
4.
Jill's Wigs, Inc. had the following balance sheet last:
Cash
Accounts receivable
Inventory
$ 800
450
950
Accounts payable
Accrued wages
Notes payable
$ 350
150
2,000
Net fixed assets 34,000
Total assets $36,200
Mortgage
Common stock
Retained earnings
Total liabilities and equity
26,500
3,200
4,000
$36,200
Jill has just invented a non-slip wig for men which she expects will cause sales to double, increasing after-tax net income to $1,000. Jill's Wigs is currently operating at full capacity, so any increase in sales will have to be accompanied by an equivalent percentage increase in fixed assets. (1)Will Jill need any external financing if she pays no dividends? (2) If so, how much?
Use the following to answer questions 5 and 6:
Cash
Accounts receivable
Inventory
Current assets
Fixed assets
Total assets
($ in millions)
2001
$ 20,000
35,000
60,000
115,000
275,000
$390,000
Accounts payable
Notes payable
Current liabilities
Long-term debt
Common stock
Retained earnings
Total liab.& equity
AWOL Tours
2001
$50,000
5,000
55,000
120,000
15,000
200,000
$390,000
($ in millions)
Sales
Cost of goods sold
Earnings before interest and taxes
Interest paid
Taxes (35%)
Net income
$700,000
560,000
140,000
17,000
43,050
$ 79,950
Addition to retained earnings $47,970
5. AWOL Tours sales for 2002 are projected to grow by 20 percent. Interest expense will be the same as in 2001
($17,000). The tax rate will remain at 35% and the dividend payout ratio will remain at 40%. Cost of goods sold, all assets, and accounts payable increase are proportional to sales. If the firm is operating at full capacity, what is the external financing needed to support this 20 percent growth in sales?
6. Refer to problem 5 above. Suppose that AWOL was operating at only 80 percent of capacity in 2001, what is AFN now?
7. Use the following information for Rebel, Corp. to determine AFN. Rebel, Inc. has projected a 25 percent increase in sales for the coming year. Assume that total costs will continue to run at 80% of sales, that the company will pay out 1/3 of its Net Income as dividends, and that the company is operating at full capacity. What is AFN for Rebel, Inc.?
Sales
Costs
Rebel, Inc.
Income Statement
Original
$1,000
800
Cash
A/R
Inv
Rebel, Inc.
Balance Sheet
Original
$ 160
440
A/P
N/P
600
Original
$ 300
100
EBT
Taxes (34%)
200
68 Total $ 1,200 LTD 800
Net Income
Dividends
Add. To RE
$44
88
132 NFA
Total
1,800 C/S
$3,000
R/E
Total
800
1,000
$3,000
8.
Refer to problem 7 above. Now assume that Rebel, Inc. was operating at 90 percent capacity. What is
AFN in this case?
9.
Suppose a firm has net income of $100 and a profit margin equal to 14%. If the firm is working at 2/3 of capacity. What are full capacity sales?
10.
The most recent financial statements for 2 Doors Down, Inc. are shown below. Assets, costs, and current liabilities are proportional to sales. Long-term debt and equity are not. 2 Doors Down pays out 50% of its net income as dividends. Next year’s sales are projected to increase by 16%. What is the external financing needed (AFN)?
2 Doors Down, Inc.
Income Statement
Sales
Costs
Original
$3,100
2,600
EBT
Taxes (34%)
Net Income
500
170
330
Current assets
Fixed assets
Total
2 Doors Down Inc.
Balance Sheet
Original
$ 4,000
3,000
Current liabilities
Long-term debt
Equity
$7,000 Total
Original
$750
1,250
5,000
$7,000
11.
Brown & Sons recently reported sales of $100 million, and net income equal to $5 million. The company has
$70 million in total assets. Over the next year, the company is forecasting a 20 percent increase in sales.
Since the company is at full capacity, its assets must increase in proportion to sales. The company also estimates that if sales increase 20 percent, spontaneous liabilities will increase by $2 million. If the company’s sales increase its profit margin will remain at its current level. The company’s dividend payout ratio is 40%.
Based on the AFN formula, how much addition capital must the company raise in order to support the 20 percent in sales?
12.
Chicky Pen Corporation recently reported the following income statement for last year: The company forecasts that its sales will increase by 20 percent next year and its operating costs will increase in proportion to sales. The company’s interest expense is expected to remain at $300 million and the tax rate will remain at
40%. The company plans to pay out 30 percent of its net income as dividends, the other 70 percent will be added to retained earnings. What is the forecasted addition to retained earnings for next year?
Income Statement
Sales
Operating costs
EBIT
Interest
Earnings before taxes
Taxes (40%)
Net income available to common stockholders
$8,000
3,700
$4,300
300
$4,000
1,600
$2,400
13.
Suppose that in 2004 sales increase by 10 percent over 2003 sales and that the 2004 dividend payout ratio is 60%. Assume that the firm is operating at full capacity and that any external funds needed will come from Notes Payable. Construct the projected income statement and balance sheet for 2004—allowing the interest expense to remain at $20,280 for now.
Balance Sheet
Assets 2003
Cash
Accounts receivable
Inventories
$ 180,000
360,000
720,000
Income Statement
Total current assets
Net fixed assets
Total assets
$1,260,000
1,440,000
$2,700,000
2003
Sales
Operating costs
$3,600,000
3,279,720
Liabilities and equity
Accounts payables
Notes payable
Accrued liabilities
$360,000
156,000
180,000
EBIT
Interest
EBT
Taxes (40%)
Net Income
Total current liabilities
Common stock
$696,000
1,800,000
Retained earnings 204,000
Total liabilities and equity $2,700,000
$320,280
20,280
$300,000
120,000
$180,000
14.
Suppose that in 2005 sales increase by 10 percent over 2004 sales and that the 2005 dividend payout ratio is 46.7%. Assume that all assets, as well as accounts payables, accrued liabilities, operating costs, and depreciation grow at the same rate as sales. Construct the projected income statement and balance sheet for 2005 (go through the 2 nd
pass balance sheet). Assume that interest expense remains at $88 and that any external funds needed are financed by Notes payable.
2004 Balance Sheet
Assets 2004
Cash
Accounts receivable
Inventories
Total current assets
Net fixed assets
Total assets
Liabilities and equity
Accounts payables
Notes payable
Accrued liabilities
Total current liabilities
Long-term bonds
Common stock
Retained earnings
Total liabilities and equity
$ 10
375
615
$1,000
1,000
$2,000
$60
110
140
$310
754
170
766
$2,000
Income Statement
Sales
Operating costs
Depreciation
EBIT
Interest
EBT
Taxes (40%)
Net Income
2004
$3,000
2,616
100
$284
88
$196
78
$118
15.
Kenny Corporation recently reported the following income statement for last year: The company forecasts that its sales will increase by 10 percent next year and its operating costs will increase in proportion to sales.
The company’s interest expense is expected to remain at $200 and the tax rate will remain at 40%. The company plans to pay out 50 percent of its net income as dividends and the other 50 percent will be added to retained earnings. What is the forecasted addition to retained earnings for next year?
Income Statement
Sales
Operating costs
EBIT
Interest
Earnings before taxes
Taxes (40%)
Net income available to common stockholders
$7,000
3,000
$4,000
200
$3,800
1,520
$2,280
16.
Actual 2003 sales were $2,000. 2004 sales are forecasted to grow at 30%--or to total $2,600.
The 1 st
pass forecasted balance sheet below assumes that the company was operating at full capacity and that all assets and accounts payables and accruals are proportional to sales Redo the problem below (re-project the 2004 balance sheet through the
2 nd
pass) assuming that the company was operating at 90 percent capacity in 2003. Assume also that any external financing needed (AFN) will be financed 50% by notes payable and 50 percent by long-term debt.
2003 2004
1st Pass
Projectd Projected
2004 2004
2nd Pass
Cash and securities
Accounts receivable
Inventories
Total current assets
Net fixed assets
Total assets
$ 100
120
140
360
640
130
156
182
468
832
1,000 $1,300
60
140
78
140
Liabilities and equity
Accounts payables & accruals
Notes payable
Total current liabilities
Long-term debt
Common stock
Retained earnings
Total liabilities and equity
200
200
10
590
1,000
218
200
10
761.6
1,189.6
17.
Patrick Star Corporation recently reported the following income statement for last year: The company forecasts that its sales will increase by 10 percent next year and its operating costs will increase in proportion to sales. The company’s interest expense is expected to remain at $400 and the tax rate will remain at 40%. The company plans to pay out 50 percent of its net income as dividends and the other 50 percent will be added to retained earnings. What is the forecasted addition to retained earnings for next year?
Income Statement
Sales
Operating costs
EBIT
Interest
Earnings before taxes
Taxes (40%)
$14,000
6,000
$8,000
400
$7,600
3,040
Net income available to common stockholders $4,560
18.
Carter Paint Company has plants in nine southern states. Sales for last year were $100 million. All assets
(including fixed assets) and current liabilities will vary directly with sales. Carter Paint has a profit margin of 5 percent and a retention ratio of 70 percent. Use the AFN formula to determine the Additional funds needed if sales grow by 10 percent next year.
Carter Paint.
Cash
Accounts receivable
Inventories
Current assets
Net fixed assets
Balance Sheet
$ 5
15
30
Accounts payable
Accruals wages
Accrued taxes
$ 50 Current liabilities
Notes payable
40 Total liabilities
Common stock
Retained earnings
$ 15
6
4
25
30
55
15
20
Total $90 Total $90
Cash
A/R
Inv
Total
NFA
Dividends
Add. To RE
$88
176
Futuroma, Inc.
Balance Sheet
Original
$ 320
880
1,200
A/P
N/P
$ 2,400
3,600
LTD
C/S
R/E
Total
19.
Use the following information for Futuroma, Inc. to determine AFN. Futuroma, Inc. has projected a 25 percent increase in sales for the coming year. Assume that total costs will continue to run at 80% of sales, that the company will pay out 1/3 of its Net Income as dividends, and that the company is operating at full capacity. What is AFN for Futuroma, Inc.?
Futuroma, Inc.
Income Statement
Sales
Costs
EBT
Taxes (34%)
Net Income
Original
$2,000
1,600
400
136
264
$6,000 Total
Original
$ 60
200
1,600
1,600
2,000
$6,000