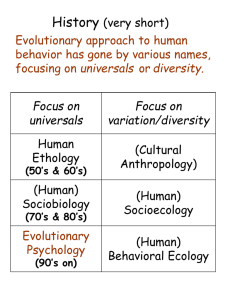
History universals diversity.
advertisement

• A very brief history • Problems humans present to the evolutionary approach to behavior History (very short) . Evolutionary approach to human behavior has gone by various names, focusing on universals or diversity. • Politics of the evolutionary approach & the ‘Naturalistic Fallacy’ Focus on universals • Robert Trivers – the 1st Evolutionary Psychologist Human Ethology • Genetic Determinism • Facultative Traits • Evolutionary Psychology – the basic approach Problems humans present to an evolutionary approach to behavior: • Individual differences • Learning/experience is everything. (What have genes got to do with it?) (50’s & 60’s) (Human) Sociobiology (70’s & 80’s) Evolutionary Psychology Focus on variation/diversity (Cultural Anthropology) (Human) Socioecology (Human) Behavioral Ecology Politics of Sociobiology (or Evolutionary Psychology) & the ‘Naturalistic Fallacy’ – Does the evolutionary viewpoint imply a particular political point of view? • Culture is everything. (What have genes got to do with it?) • Our psychology does not seem to be organized around inclusive fitness. • Many common human behaviors are patently non-adaptive (contraception, adoption, drug-taking, risk-taking, war, Mother Theresa, etc). • Evolutionary theory when applied to human behavior is considered morally repugnant (e.g., ‘Social Darwinism’). Social Darwinism: During the Industrial Revolution, many fat-cat capitalists justified their rewards in terms of “survival of the fittest”: given this ‘law of nature’, the fact that we are successful, and you are not implies that we deserve it and you do not. An example of the “naturalistic fallacy”. 1 The “Naturalistic Fallacy” Arguments which claim to draw ethical conclusions from the fact that something is "natural" or "unnatural". (Hume; Moore) Natural selection is a natural process that increases the frequency of certain genes and eliminates others, that yields some kinds of organisms rather than others; but it is not a process moral or immoral in itself or in its outcome, in the same way as gravity is not a morally laden force. In order to consider some evolutionary events as morally right and others wrong, we must introduce human values. ~ Francisco Ayala "The benefit of self-deception is the more fluid deception of others. The cost is an impaired ability to deal with reality.“ Robert Trivers 1971. The evolution of reciprocal altruism. Quarterly Review of Biology 46: 35-57. 1972. Parental investment and sexual selection. In Campbell, B. (ed.), Sexual Selection and the descent of man. 1975. Parent-offspring conflict. American Zoologist 14: 249-264. 1976. (with Hare, H.). Haplodiploidy and the evolution of the social insects. Science 191: 249-263. 1982. (with Newton, H.P). The crash of flight 90: doomed by self-deception? Science Digest 111: 66-67. 2011. The Folly of Fools: The Logic of Deceit and Self-Deception in Human Life. Basic Books. Time 1977 & Time 1995: Role of genes inferred from behavior (and theory) Time 2004: Key issue is a presumed gene-behavior correlation (Trivers/Newton 1982: 66) Robert Trivers the first evolutionary psychologist 2 Problems humans present to an evolutionary approach to behavior: Many of these ‘problems’ arise from assumption that evolutionary approach implies that all behavioral differences are due to genetic differences. developmental program. (Any trait difference can be due to a genetic difference or an environmental (experiential) difference. Obligate trait: Phenotypic difference is correlated with genetic difference. Term does not imply that environment (experience) has no effect in development or expression of the trait, only that the trait difference can be traced to a genetic difference. Facultative trait: Phenotypic diff. is The Fallacy of ‘Genetic Determinism’ correlated with environmental diff. Genotype ‘assumes’ and requires environmental difference to produce the phenotypic difference. Polyphenic development in spadefoot toad tadpole: A facultative trait Summary of Experiments: No (Any trait has its underlying genetic- Bluegill Sunfish Alternative Reproductive Strategies Potentially a Facultative Trait Yes 3