Note that the periodic table is arranged based on the... nucleus of an atom (to differ from the idea that...
advertisement

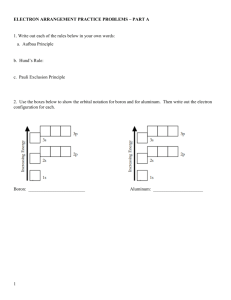
Note that the periodic table is arranged based on the way electrons arrange themselves around the nucleus of an atom (to differ from the idea that elements are solely based on atomic number). For example, elements in Group 1 exhibit many similar physical properties including reactivity in water. The Bohr-Rutherford Diagram is useful for the first 20 elements. The quantum model does give us a better understanding of atoms and their chemical properties. For any atom, there are three ways in which energy contributes: (1) (2) (3) Multi-electronic atomic orbitals have the same general shape as orbitals of the hydrogen atom, but there are obvious size and energy differences. Much has to do with the varying levels of attraction and repulsion between subatomic particles in the atom. For multi-electronic atoms, the energies of orbitals within the same energy level, n, are different. For example: < < < ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM The electronic structure of atoms can be represented by both electron configurations and energy level diagrams which show the relative energies of the electrons in an atom. The Aufbau Principle states: ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATIONS We can represent the and of atoms and ions in an easier way. Note that electron configurations represent electrons in the (lowest energy). OR ENERGY LEVEL (ORBITAL) DIAGRAMS The diagram to the right is a convention to show the relative energies of electrons in an atom. It takes into consideration the quantum numbers for each individual electron. Draw an energy level diagram for a nickel atom? Hund’s Rule - In order for electrons to have the lowest energy configuration, they must occupy the energy orbital with spins before adding electrons with spins. Basically, GUIDELINES FOR WRITING ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS: Example 1: Write the electron configuration for the element manganese, Mn? Example 2: Write the electron configuration for the aluminum ion? Write the electron configuration for the phosphide ion? CONDENSED ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS • There is a more shortened version for electron configuration, where the is represented in square brackets and is followed by the remaining electrons in their appropriate configuration. This is generally used for elements beyond Example: The electron configuration for Mg is 1s22s22p63s2 The condensed electron configuration for Mg is [Ne]3s2 Example 3: Write the condensed electron configuration for bromine? . ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS AND TRANSITION METALS • For transition metals, additional electrons begin to occupy the . There are two exceptions to the Aufbau principle: and . They prefer a low energy half-filled 4s orbital. • According to experimental evidence, it is more stable for electrons to have a low energy state Element Z Electron Confign Scandium 21 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d Titanium 22 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d Vanadium 23 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d Chromium 24 Manganese 25 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d Iron 26 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d Cobalt 27 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d Nickel 28 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d Copper 29 Zinc 30 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d Gallium 31 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d Short Electron Confign Important Points to Remember with Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table: 1. (n+1)s orbitals fill before nd orbitals. For example (3+1)s = 4s orbital fills before 3d orbitals 2. There are 14 elements. They correspond to the filling of the orbitals. There are 14 elements. They correspond to the filling of the orbitals 3. In certain cases, there is more stability with within the lanthanides and actinides 4. The atoms of every member element in each group have the configuration (we usually do not count the d orbital electrons) EXPLAINING IONIC CHARGES What do we know about transition metals? Example 4: What is the electron configuration of Cadmium? What is the electron configuration of the cadmium ion (Cd2+)? Cd: Cd2+: Example 5: What is the electron configuration of Lead? What are the multiple ions that lead can form? What is the electron configuration of these ions? Pb: Pb Ion ( ): Pb Ion ( ): EXPLAINING MAGNETISM Elements that are regarded as magnetic have the following properties: • They generally tend to have • Possess (small dense packs of atoms) which align themselves randomly (The atoms in a domain however are aligned in the same direction) Magnetic Field Absent Presence of a Magnetic Field FERROMAGNETISM • A property that certain elements possess • An external magnet causes the domains within a metal to align in the _____________________. They _______________________ when the magnet is removed. This is a very strong magnet. • Examples: __________________ PARAMAGNETISM • A property caused by unpaired electrons with the ___________ The spinning creates a _______ ___________________________ • The property is discovered when the element is brought close to a strong magnetic field. • They are ___________________ when the magnet is removed • Examples: __________________ Homework: Read Pages 160-172 - Practice Questions #1-4 on Page 166 - Practice Questions #1-2 on Page 170 - Review Questions #1-10 on Page 172


![6) cobalt [Ar] 4s 2 3d 7](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009918562_1-1950b3428f2f6bf78209e86f923b4abf-300x300.png)