Unit (II): Producer’s Behaviour and Supply.
advertisement

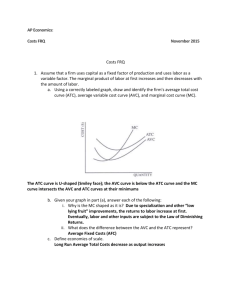
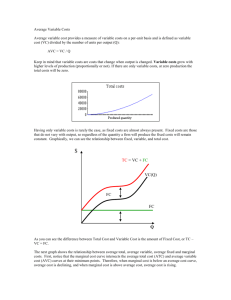
Unit (II): Producer’s Behaviour and Supply. Very Short Answer Type Questions carrying (1 mark) Q1. Define fixed cost. Q2. Define marginal cost. Q3. What causes a downward movement along a supply curve? Q4. Give one reason for a rightward shift in supply curve. Q5. Why is average total cost greater than average variable cost? Q6. Define production function. Q7. What is market supply? Q8. Give the meaning of opportunity cost. Q9. What does cost mean in economics? Q10. Define revenue. Q11. Define marginal physical product. Q12. When the supply of a commodity is called ‘elastic’? Q13. Define marginal revenue. Q14. Price elasticity of supply of a good is 0.8. Is the supply ‘elastic’ or ‘inelastic’? Q15. What is meant by producer’s equilibrium? Q16. Draw AR curve of a firm under perfect competition. Q17. What is meant by transfer earnings of a factor of production? Q18. When TP increases at an increasing rate, what happens to MP? Q19. When TP increases at a decreasing rate, what happens to MP? Q20. Define explicit and implicit cost. Short Answer Type Questions carrying (3 and 4 mark) Q1. Explain the meaning of increase in supply and increase in quantity supplied. Give example. Q2. Explain the effect of fall in prices of other goods on the supply of a given good. Q3. Complete the following table: Output (units) AVC (Rs.) 1 2 18 3 4 20 5 22 Q4. Complete the following table: Output (units) 4 5 6 7 8 Price (RS.) 9 6 - TC (Rs.) 60 120 - MC (Rs.) 20 18 - TR (Rs.) 36 42 40 MR (Rs.) 4 - Q5. Commodity X and Y have equal price elasticity of supply. The supply of X rises from 400 units to 500 units due to a 20 percent rise in its price. Calculate the percentage fall in supply of Y if its price falls by 8%. Q6. From the following schedule find out the level of output at which the producer is in equilibrium. Give reasons for your answer. Output (units) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Q7. Complete the following table: Output (Rs.) 1 2 3 4 Q8. Explain the law of supply. Price (Rs.) 24 24 24 24 24 24 24 TR (Rs.) 12 8 Total Cost (Rs.) 26 50 72 92 115 139 165 MR (Rs.) 4 - AV (Rs.) 8 4 2 Q9. Distinguish between ‘increase’ and ‘extension’ of supply. Q10. Distinguish between ‘decrease’ and ‘contraction’ of supply. Q11. Show with the help of a supply curve Es=1. (HOTS) Q12. Draw two supply curves out of which one is elastic and other is inelastic throughout. (HOTS) Q13. Explain briefly any four factors determining supply. Q14. When one input is increased while others kept fixed TP increases at increasing rate in the beginning. Why? Q15. Explain the reasons behind the three phases of the law of variable proportions. Q16. Complete the following table: Variable input (units) 0 1 2 3 4 5 TP (units) 0 66 - AP (units) 0 19 - MP (units) 0 20 26 4 Q17. Distinguish between short run and long run in terms of cost. Q18. Draw ATC, AVC and MC curves on a single diagram.(HOTS) Q19. Explain the relationship between AVC and ATC curves. (HOTS) Q20. Explain the behaviour of AR and MR of a firm when more sale is possible at a given price. Use diagram. (HOTS) Q21. What is economic profit? State the conditions of profit maximisation in terms of MC and MR. Q22. Explain producer’s equilibrium in terms of total cost and total revenue. Use diagram. Long Answer Type Questions carrying (6 mark) Q1. Give reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false: A) When there are diminishing returns to a factor, total product always decreases. B) Total product will increase only when marginal product increases, C) When marginal revenue is zero, average revenue will be constant. Q2. Distinguish between returns to a factor and returns to scale. Explain the reasons for increasing returns to a factor. Q3. State the factors that cause a rightward shift of the supply curve of a commodity. When will there be a movement along the given supply curve? Q4. Define Elasticity of supply. Explain the %age method of measuring elasticity of supply. Q5. Give reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false: A) Average cost falls only when marginal cost falls. B) The difference between average total cost average variable cost is constant. C) When total revenue is maximum, marginal revenue is also maximum. Q6. State the phases of the law of variable proportions in terms of total physical product. Use diagram. Q7. Define production function. Distinguish between long run and short run production. Q8. Calculate TFC, TVC, AFC, AVC and ATC from the following table: Output (units) Total cost (Rs.) 0 60 1 100 2 120 3 150 4 200 5 280 Q9. Assuming that TFC is Rs. 12, calculate TC, TVC, ATC and AVC from the following: Output (units) 1 2 3 4 Q10. Identify fixed costs and variable costs: 1. Salary of permanent staff. 2. Interest payment 3. Wages to daily wage workers 4. Expenditure on raw material 5. Depreciation 6. Licence fee 7. Excise duty Marginal cost (Rs.) 20 10 15 25