1
advertisement

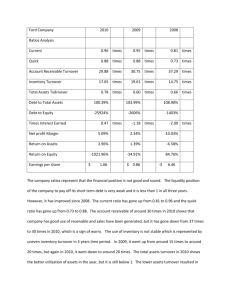
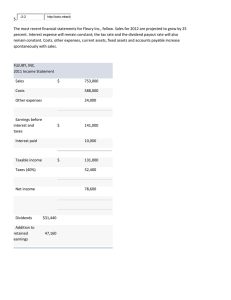
1 • • • • • • Computing Liquidity Ratios Current Ratio = CA / CL 708 / 540 = 1.31 times Quick Ratio = (CA ­ Inventory) / CL (708 ­ 422) / 540 = .53 times Cash Ratio = Cash / CL 98 / 540 = .18 times 2 • • • • • • Computing Leverage Ratios Total Debt Ratio = (TA ­ TE) / TA (3588 ­ 2591) / 3588 = 28% Debt/Equity = TD / TE (3588 ­ 2591) / 2591 = 38.5% Equity Multiplier = TA / TE = 1 + D/E 1 + .385 = 1.385 3 4 5 • • • • Computing Coverage Ratios Times Interest Earned = EBIT / Interest 691 / 141 = 4.9 times Cash Coverage = (EBIT + Depreciation) / Interest (691 + 276) / 141 = 6.9 times 6 • • • • Computing Inventory Ratios Inventory Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold / Inventory 1344 / 422 = 3.2 times Days’ Sales in Inventory = 365 / Inventory Turnover 365 / 3.2 = 114 days 7 • • • • Computing Receivables Ratios Receivables Turnover = Sales / Accounts Receivable 2311 / 188 = 12.3 times Days’ Sales in Receivables = 365 / Receivables Turnover 365 / 12.3 = 30 days 8 Computing Total Asset Turnover • Total Asset Turnover = Sales / Total Assets • 2311 / 3588 = .64 times • It is not unusual for TAT < 1, especially if a firm has a large amount of fixed assets. 9 • • • • • • Computing Profitability Measures Profit Margin = Net Income / Sales 363 / 2311 = 15.7% Return on Assets (ROA) = Net Income / Total Assets 363 / 3588 = 10.1% Return on Equity (ROE) = Net Income / Total Equity 363 / 2591 = 14.0% 10 • • • • • • Computing Market Value Measures Market Price = $88 per share Shares outstanding = 33 million PE Ratio = Price per share / Earnings per share 88 / 11 = 8 times Market­to­book ratio = market value per share / book value per share 88 / (2591 / 33) = 1.12 times 11 • ROE = NI / TE 3.3 The Du Pont Identity 12 3.5 Long­Term Financial Planning • Investment in new assets ­ determined by capital budgeting decisions • Degree of financial leverage ­ determined by capital structure decisions • Cash paid to shareholders ­ determined by dividend policy decisions • Liquidity requirements ­ determined by net working capital decisions Financial Planning Ingredients • Sales Forecast ­ many cash flows depend directly on the level of sales (often estimate sales growth rate) • Pro Forma Statements ­ setting up the plan as projected (pro forma) financial statements allows for consistency and ease of interpretation • Asset Requirements ­ the additional assets that will be required to meet sales projections • Financial Requirements ­ the amount of financing needed to pay for the required assets • Plug Variable ­ determined by management decisions about what type of financing will be used (makes the balance sheet balance) • Economic Assumptions ­ explicit assumptions about the coming economic environment 13 Percent of Sales Approach • Some items vary directly with sales, others do not. • Income Statement • Costs may vary directly with sales ­ if this is the case, then the profit margin is constant • Depreciation and interest expense may not vary directly with sales ­ if this is the case, then the profit margin is not constant • Dividends are a management decision and generally do not vary directly with sales ­ this affects additions to retained earnings Percent of Sales Approach • Balance Sheet • Initially assume all assets, including fixed, vary directly with sales. • Accounts payable also normally vary directly with sales. • Notes payable, long­term debt, and equity generally do not vary with sales because they depend on management decisions about capital structure. • The change in the retained earnings portion of equity will come from the dividend decision. • External Financing Needed (EFN) The difference between the forecasted increase in assets and the forecasted increase in liabilities and equity 14 15 16 3.6 External Financing and Growth At low growth levels, internal financing (retained earnings) may exceed the required investment in assets. As the growth rate increases, the internal financing will not be enough, and the firm will have to go to the capital markets for financing. Examining the relationship between growth and external financing required is a useful tool in long­range planning. The Internal Growth Rate The internal growth rate tells us how much the firm can grow assets using retained earnings as the only source of financing. Using the information from the Hoffman Co. ROA = 66 / 500 = .132 b = 44/ 66 = .66700 The Sustainable Growth Rate The sustainable growth rate tells us how much the firm can grow by using internally generated funds and issuing debt to maintain a constant debt ratio. Using the Hoffman Co. ROE = 66 / 250 = .264 b = .667 Determinants of Growth Profit margin ­ operating efficiency Total asset turnover ­ asset use efficiency Financial leverage ­ choice of optimal debt ratio 17 Jessica’s Boutique has cash of $50, accounts receivable of $60, accounts payable of $200, and inventory of $150. What is the value of the quick ratio? A firm has a debt­equity ratio of .40. What is the total debt ratio? A firm has total debt of $1,200 and a debt­equity ratio of .30. What is the value of the total assets? A firm has sales of $3,600, costs of $2,800, interest paid of $100, and depreciation of $400. The tax rate is 34%. What is the value of the cash coverage ratio? Rosita’s Resources paid $250 in interest and $130 in dividends last year. The times interest earned ratio is 3.8 and the depreciation expense is $60. What is the value of the cash coverage ratio? Mario’s Home Systems has sales of $2,800, costs of goods sold of $2,100, inventory of $500, and accounts receivable of $400. How many days, on average, does it take Mario’s to sell its inventory? Syed’s Industries has accounts receivable of $700, inventory of $1,200, sales of $4,200, and cost of goods sold of $3,400. How long does it take Syed’s to both sell its inventory and then collect the payment on the sale? 18 Lee Sun’s has sales of $3,000, total assets of $2,500, and a profit margin of 5%. The firm has a total debt ratio of 40%. What is the return on equity? Jupiter Explorers has $6,400 in sales. The profit margin is 4%. There are 6,400 shares of stock outstanding. The market price per share is $1.20. What is the price­earnings ratio? Patti’s has net income of $1,800, a price­earnings ratio of 12, and earnings per share of $1.20. How many shares of stock are outstanding? A firm has 5,000 shares of stock outstanding, sales of $6,000, net income of $800, a price­earnings ratio of 10, and a book value per share of $.50. What is the market­to­book ratio? Frederico’s has a profit margin of 6%, a return on assets of 8%, and an equity multiplier of 1.4. What is the return on equity? 19 20 21