Breakeven Analysis
advertisement

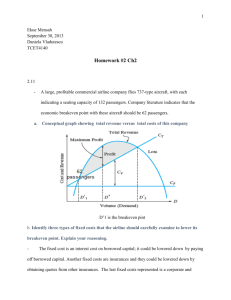
Breakeven Analysis Breakeven Analysis This is a technique used in budget planning and it provides information about expected future costs and revenues. Its key features are: 1. Fixed Costs: the costs that stay the same when extra units are produced. They are not linked directly to production, e.g. Rent, insurance premiums etc. 2. Marginal (or variable) Costs: the costs that increase when you produce extra units, i.e. the costs of production, e.g. Materials, labour, variable overheads such as energy, etc 3. The contribution is the difference between the selling price and the cost price of a unit. It goes towards covering the fixed costs and then becomes profit. 4. The Breakeven Point is the amount of goods at which the contribution equals the fixed costs. To find the Breakeven Point in units: Breakeven Point = Total Fixed Costs Contribution of a unit It can be expressed in money as well. Multiply the selling price by the breakeven point. 5. The Margin of Safety is the difference between the budgeted level of activity and the breakeven level. Example: A firm has the following estimates for its products Budgeted output 16,500 units Fixed Costs €52,000 Variable costs €5.80 Selling price €12.00 a) Find the breakeven point in units and euro. b) What is the margin of safety for this output? c) What profit would be made by producing and selling 14,800 units? Contribution: 12.00 – 5.80 = 6.20 Breakeven point: 52,000/6.20 = 8387.01 units In euro, the breakeven point is 8387.01 X €12 = €100,645, i.e. sales has to reach this figure before costs are covered. Margin of safety = 16,500 – 8387 = 8113 Profit = Total selling price – Total cost price – fixed costs = (14,800X12)(14,800X5.80) – (52,000) = 177,600 – 85,840 – 52,000 = €39,740 Walter Fleming Page 1 of 3 Breakeven Analysis Breakeven Chart This is a graph showing the total costs, the fixed costs and the total sales revenue. The breakeven point is where the total sales line crosses the total costs line. To draw a breakeven chart The money is on the Y axis and the number of units produced on the X axis The fixed costs is a horizontal line The total costs are a combination of the fixed costs and the variable costs. To draw it, add the fixed costs to the total variable costs for two values, at zero where the total variable cost is also zero, and at the budgeted output costs (cost price X budgeted output). The total sales revenue is plotted from (0, 0) to the sales revenue from the budgeted output (selling price X budgeted output) Example: A firm makes the following estimates of its products: Fixed costs €41,000 Variable Cost €6.50 per unit Budgeted output 7,000 units Selling price €15.00 per unit a) Find the breakeven point in units and euro b) Draw the breakeven chart c) Calculate the margin of safety at output of 10,000 d) If the selling price drops to €13.50 and the variable cost increases to €7.50 suggest a new breakeven point in units. Breakeven point = 41000/8.50 = 4824 units and (4824 X 15) = €72,360 Margin of safety at 10,000 units = 10000-4824 = 5176 New breakeven point = 41000/6 =6833 To draw the chart 1) The fixed costs line Draw a horizontal line across from 41,000 , 2) The total costs line first point = (0,41000) The second point = (7000, 86500) i.e. 7000X6.5 + 41000 3) The Total Sales Revenue line first point (0,0) the second point (7000, 105000) i.e. 7000X15 Limitations of Breakeven analysis 1) It only applies to a single product 2) It assumes that the fixed costs remain the same for all production values, which may not be the case 3) It also assumes that the variable cost stays the same 4) It assumes that the selling price is constant for all levels of output Walter Fleming Page 2 of 3 Breakeven Analysis Drawing a Breakeven Chart The scale on the X axis is determined by the Budgeted output while that on the Y axis is found by multiplying the Budgeted Output by the Selling Price. 1. Total Sales revenue Line Multiply the budgeted output by the selling price. Then plot the point opposite the budgeted output on the X axis and the answer on the Y axis. Join this point to the origin. 2. Fixed Costs Line Draw a horizontal line from the fixed cost value on the Y axis 3. Total Costs Line Multiply the budgeted output by the variable cost, then add the answer to the Fixed Costs. Plot the point opposite the budgeted output on the X axis and the answer on the Y axis. Join this point to the start of the fixed Cost Line ( the horizontal line) Walter Fleming Page 3 of 3