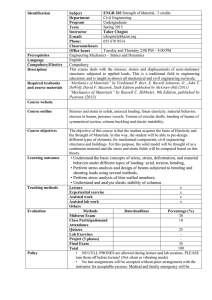
MECH-212: Mechanics of Materials Required core course
advertisement

MECH-212: Mechanics of Materials Prof. Arnaldo Mazzei – amazzei@kettering.edu ; www.kettering.edu/~amazzei Required core course 2010 Catalog Data: Credit: 4-0-0-4; Prerequisite: MECH-210: Statics (previously, Mechanics I) The fundamental topics of this course include: normal and shear stress and strain, Hooke’s law, Poisson’s ratio, generalized Hooke’s law, axial deformation, torsion of circular bars, angle of twist, bending of beams, flexure formula, flexural shear stress, beam deflections, combined stresses, transformation of stresses, Mohr’s circle (principal stresses), statically indeterminate problems, and columns. Homework will be assigned. Design related projects may also be assigned. Textbook(s): “Mechanics of Materials”, By F. P. Beer, E.R. Johnston, and J.T DeWolf, McGrawHill, 5th Edition, 2008, ISBN 978-0-07-352938-7 ,"Mechanics of Materials"; by W. Riley, L. Sturges and D. Morris; Wiley, 6th ed.,2007,ISBN 978-0-471-70511-6 Course Learning Objectives: Objective 1: Apply the principles of Statics to determine the forces and moments on load carrying members. [ME PO’s a (35%), c (30%), e (30%), and i (5%)] Objective 2: Analyze the stresses in load carrying members due to axial forces, bearing forces, torsional moments, bending moments and shear forces. [ME PO’s a (35%), c (30%), e (30%), and k (5%)] Objective 3: Analyze the combined stresses in load carrying members due to axial forces, torsional moments, and bending moments acting together. [ME PO’s a (35%), c (25%), e (30%), and k (10%)] Objective 4: Determine the deflection of load carrying, members due to axial loads, torsional moments and bending moments. [ME PO’s a (35%), c (30%), e (30%), and k (5%)] Objective 5: Objective 5: Apply the principles learned from the objectives 1 through 4 to perform basic analysis and sizing of different structural members. [ME PO’s a (25%), c (25%), d (10%), e (25%), k(5%, p(10%)] Prerequisites by topic: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Rigid body equilibrium and free body diagrams Centroids, Center of Gravity Internal forces in structural members Moments of inertia Basic computer skills Topics: • • • Review of Statics – Internal Forces Concepts of Stress and Strain: Hooke’s Law Concepts of Stress, Deformation and safety factor as applied to: o Axial Loading (uniform and stepped bars), and • • • o Torsion Loading (uniform and stepped bars) o Horse power calculations o Applications Statically Indeterminate Problems as applied to: o Axial loading (uniform and stepped bars) o Effect of temperature (thermal stresses) in axial loading o Applications Concepts of Bending Stress, deflection and safety factor as applied to: o Transverse Loading (Pure Bending) (uniform section bars with concentrated as well as distributed loads) o Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams for the above o Deflection of beams for simple loading by superposition (using deflection tables) o Applications Transformations of stresses and Combined Loading: o Mohr’s circle for plane stress and determination of principal stresses o Equivalent stress using yield criterion o Applications (thin-walled cylinders, crankshaft example) Optional topics: • • • • • • • Effects of Stress Concentration in axial, torsion and transverse loadings o Applications Statically Indeterminate Problems as applied to: o Torsion loading (uniform and stepped bars) o Applications Transverse (Flexural) Shear effect o Applications Strain analysis by Mohr’s principle and strain rosettes o Applications Euler Buckling (long slender rods) o Applications Simple failure theory Other topics Grading Policy: Homework/Classwork Midterms Common hour final exam 20% (HW – 10%, CW – 10%) 50% (test 01 and – 05/06/10, test 02 06/04/10) test 01 test 02 (date to–be determined) 30% (date to be determined) Schedule: Two sessions per week of 120 minutes Computer usage: Basic Computer Skills (MathCAD/Working Model/Excel/MS-Word/or equivalent program) Laboratory projects: May include computer based design projects Relationship to professional component: Four credits of 100% Engineering Science.
![Applied Strength of Materials [Opens in New Window]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/009007576_1-1087675879e3bc9d4b7f82c1627d321d-300x300.png)
![Strength of Materials [Opens in New Window]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009980952_1-af573ee3f319ca71dbd5b53d99fdf436-300x300.png)