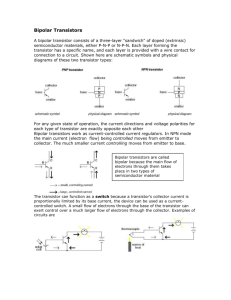
How will measure the common emitter mode input, output & transfer... transistor? Sketch the circuit diagram and charactaristics.
advertisement

How will measure the common emitter mode input, output & transfer charactaristics of a n-p-n transistor? Sketch the circuit diagram and charactaristics. Common Emitter Configuration: For the common-emitter configuration of Fig. 7.21a, the input terminals are the base and emitter terminals, but the output set is now the collector and emitter terminals. In addition, the emitter terminal is now common between the input and output ports of the amplifier. Substituting the re equivalent circuit for the npn transistor will result in the configuration of Fig. 7.21b. Note that the controlled-current source is still connected between the collector and base terminals and the diode between the base and Question: Sketch the circuit diagram of a common emmitter of npn transistor & hence explain the mechanics of current flow through the different parts. Emitter current: The above figure shows a biased transistor the minus (-) sign represents free electrons in the emitter region. The heavily doped emitter emits or injects free electron in the base when external voltage source . forward biases the emitter base junction. By convectional flow of current, the emitter current flows in the opposite direction of electron flow which has shown in the previous circuit. Base Current: When the forward bias is applied to the emitter base junction the electron in the emitter will not reach the biased region until the applied voltage overcomes the emitter base potential barrier. Once when is the greater than the emitter base barrier potential electrons will reach into the base region. Theoretically these electrons can flow in either or two directions. 1. They can flow to the left and out of the base through . to the positive terminal of source voltage 2. The free electrons can flow into the collector region. Collector Current: Almost all the electrons go into the collector as shown above. Once they are in the collector, the free electrons flow through the collector & through until they reach positive terminal of collector supply . The conventional flow of current has shown above. Question: Obtain expression for current gain, voltage gain, power gain, input resistance & output resistance for the common emitter configuration of a transistor. The current flowing between emitter and collector of a transistor is much greater than that flowing between base and emitter. Thus a small base current is controlling the emitter collector current. The ratio of the two currents, ICE/IBE is constant, provided that the collector emitter voltage is constant. Therefore, if the base current rises, so does collector current. This ratio is the CURRENT GAIN of the transistor and is given the symbol hfe. A fairly low gain transistor might have a current gain of 20 to 50, while a high gain type may have a gain of 300 to 800 or more. The spread of values of for any given transistor is quite large, even in transistors of the same type and batch. Characteristic curves (graphs) can be drawn to show other parameters of a transistor and are used both to detail the performance of a particular device and as an aid to the design of amplifiers. Voltage Gain: Ib Vi Zb Vo I o R C βI b R C V β i R C Zb V βR C AV o Vi Zb substituting Z b β(re R E ) gives AV Vo RC Vi re R E and for the approximation Z b βR E AV Vo R C Vi RE Current Gain: The magnitude of R B is often too close to Z b to permit the approximation I b I i . Applyingthe current - divider rule to the input circuit will result in : Ib R B Ii R B Zb Ib RB Ii R B Zb I o I b Io Ib Ai Io Io Ib RB Ii I b Ii R B Zb A i A v Zi RC Common-Base Input Resistance Apply test current, with load resistor Present at output. : Question: What is D.C load line? How will draw a D.C load line on the output characteristics curve of a transistor & importance. IC(sat) = VCC/(RC+RE) DC Load Line IC (mA) VCE(off) = VCC VCE • • The straight line is known as the DC load line Its significance is that regardless of the behavior of the transistor, the collector current I and the collector-emitter voltage V must always lie on the load C line, depends ONLY on the V , R and R • CC C CE E (i.e. The dc load line is a graph that represents all the possible combinations of I and V for a given amplifier. For every possible value of I , and C CE amplifier will have a corresponding value of V .) • CE C It must be true at the same time as the transistor characteristic. Solve two condition using simultaneous equation graphically Q-point !! Importance Of D.C load line: Load line is important tools in electronics because it contains every possible operating point for the transistor circuit. Stated another way when the base resistance varies from zero to infinite, it causes to vary that makes & to vary over entire ranges. If we plot the & a values for every possible value. We’ll get the load line. Therefore the load line is a visual summery of all the possible transistor operating points. Question: What is operating point? How it is determined? What is saturation point & Cut-off point? Explain briefly. The "Q point" for a transistor amplifier circuit is the point along its operating region in a "quiescent ", where no input signal gets amplified. The currents and voltages in an electronic circuit when the input signal is replaced by its average value, so that all currents and voltages can be approximated by series expansions around this point. Also known as Q point. When the signal of applied variation of collector current and collector emitter voltage take place about this point that is : why it is called silent point. Saturation Point: The point at which the load line intersects the characteristic curve near the collector current axis is referred to as the saturation point. At this point of time, the current through the transistor is maximum and the voltage across collector is minimum for a given value of load. Therefore saturation current for the fixed bias circuit, Ic (sat) =Vcc/Rc Cutoff Point: The point where the load line intersects the cutoff region of the collector curves is referred as the cutoff point (i.e. end of load line). At this point, collector current is approximately zero and emitter is grounded for fixed bias circuit. Therefore, Vce (cut) = Vc = Vcc