Translocation in the Phloem Plant Physiology Taiz & Zeiger Chapter 10 Tien-Shin Yu
advertisement

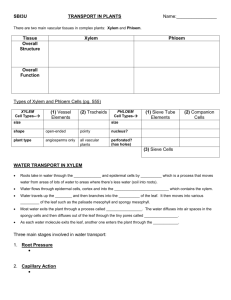
Tien-Shin Yu Institute of Plant & Microbial Biology Plant Physiology March 31, 2008 Translocation in the Phloem Plant Physiology Taiz & Zeiger Chapter 10 Phloem: •Nature of conduit •Substance being transported •Mechanism of phloem translocation •Direction: source to sink •An information superhighway Plant Vasculature: Xylem and Phloem Arrangement of Plant Vascular Tissue Phloem Xylem Shoot Root The Compositions of Phloem Phloem Parenchyma cell Companion cell Seive element Seive plate Architecture of Sieve Element-Companion Cell (SE-CC) Complex Protection: 1.P-protein 2.Callose Angiosperms CC-SE Complex Sieve pore SE Sieve pore CC SE Gymnosperms CC-SE Complex No P-proteins Pores appear blocked P-proteins PP1: phloem protein that forms filaments PP2: phloem lectin associated with filaments Types of Companion Cells: Apoplastic Loading Types of Companion Cells: Symplastic Loading Types of Companion Cells: Symplastic Loading Connection of CC-SE by Specialized Plasmodesmata Network of the phloem Stain with Aniline blue (callose) SE SE Phloem: •Nature of conduit •Substance being transported •Mechanism of phloem translocation •Direction: source to sink •An information superhighway Molecules in the Phloem Cucurbit phloem exudate Rate: 10 mL/hr Aphid stylet Rate: 100 nL/hr • Sugar, Ions, Hormone • Proteins, Peptides • RNA Xylem: water, minerals, and hormones (cytokinin) Phloem: photosynthate (sugars),ions, hormones (IAA, GA), amino acids, peptides, proteins, and RNA. Sugars in Phloem Sap Most abundant in the phloem Nitrogenous Compounds in Phloem Sap Protein Composition in Phloem Sap mRNA and small RNA in Phloem Sap At least 2,500 mRNA have been identified from phloem sap Phloem: •Nature of conduit •Substance being transported •Mechanism of phloem translocation •Direction: source to sink •An information superhighway Bulk Flow Hypothesis Flow rate: 1 m/hr Ernst Münch 1930 Loading into SE: Apoplastic and Symplastic Pathways Sucrose transporter Apoplasmic Step Model Symplasmic – Polymer-trap Model BS-IM PD size exclusion limit of 0.8 kDa IC-SE PD size exclusion limit of 25 kDa Phloem Unloading Apex Phloem Phloem Unloading from SE More common Type I Type II In Developing Seed Phloem: •Nature of conduit •Substance being transported •Mechanism of phloem translocation •Direction: source to sink •An information superhighway Direction & rate of phloem translocation is controlled by local Sink Strength Phloem translocation is a Non-Circulatory vascular system Phloem Translocation Regulates by Proximity Leaf Blade Sink-Source Transition from Tip to Base Major Vein: Unloading; Minor Vein: Loading Allocation and Partition Allocation: The regulation of Sugar distributes into various metabolic pathway Partitioning: Differential distribution of sugar within the plant Phloem: •Nature of conduit •Substance being transported •Mechanism of phloem translocation •Direction: source to sink •An information superhighway Signal Molecules in the Phloem •Hormones: Auxin, GA •Chemical: JA in pathogen defense •Sugars •Protein •mRNA •etc Protein Composition in Phloem Sap GFP Protein Unloading in the sink leaf Source Leaf Sink Leaf mRNA and small RNA in Phloem Sap At least 2,000 different RNA identified from phloem sap Florigen is a Phloem Mobile Macromolecule!! Non induction Floral induction Graft union Non-induced plant PCO-GUS PFT-GUS Thank you