DDEEOOXXYYRRIIBBOONNUUCCLLEEIICC AACCIIDD ((DDNNAA)) Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) The structure of DNA
advertisement
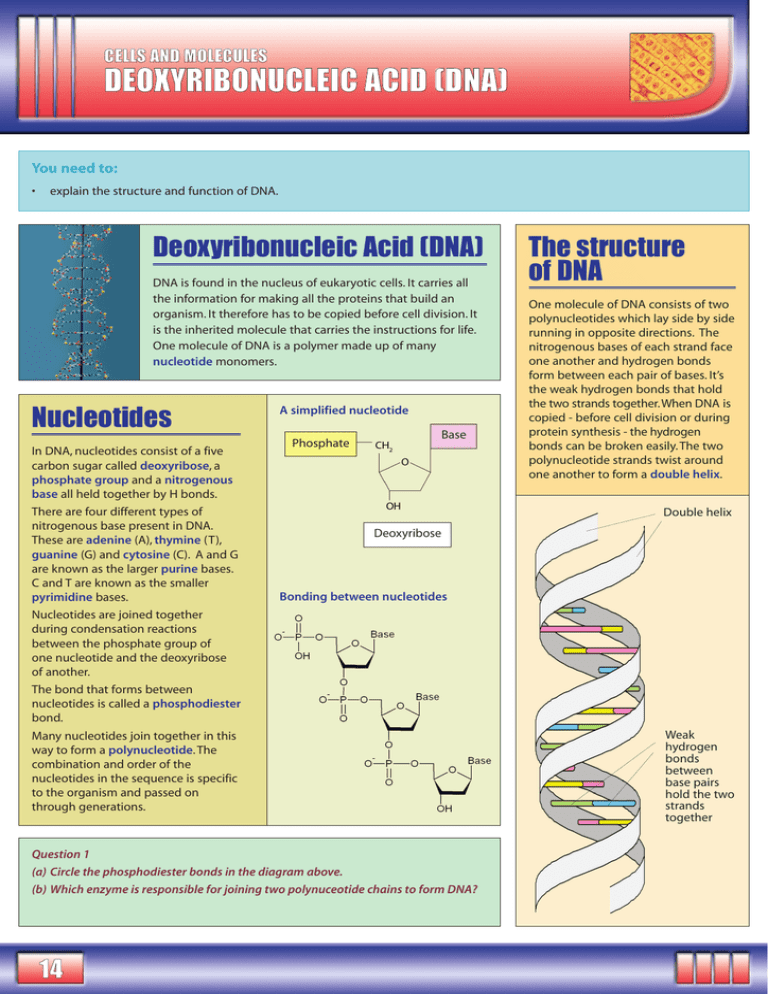
CELLS AND MOLECULES DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID (DNA ) You need to: • explain the structure and function of DNA. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA is found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It carries all the information for making all the proteins that build an organism. It therefore has to be copied before cell division. It is the inherited molecule that carries the instructions for life. One molecule of DNA is a polymer made up of many nucleotide monomers. Nucleotides In DNA, nucleotides consist of a five carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base all held together by H bonds. There are four different types of nitrogenous base present in DNA. These are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). A and G are known as the larger purine bases. C and T are known as the smaller pyrimidine bases. Nucleotides are joined together during condensation reactions between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the deoxyribose of another. The bond that forms between nucleotides is called a phosphodiester bond. Many nucleotides join together in this way to form a polynucleotide. The combination and order of the nucleotides in the sequence is specific to the organism and passed on through generations. A simplified nucleotide Base Phosphate One molecule of DNA consists of two polynucleotides which lay side by side running in opposite directions. The nitrogenous bases of each strand face one another and hydrogen bonds form between each pair of bases. It’s the weak hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together.When DNA is copied - before cell division or during protein synthesis - the hydrogen bonds can be broken easily. The two polynucleotide strands twist around one another to form a double helix. Double helix Deoxyribose Bonding between nucleotides Question 1 (a) Circle the phosphodiester bonds in the diagram above. (b) Which enzyme is responsible for joining two polynuceotide chains to form DNA? 14 The structure of DNA Weak hydrogen bonds between base pairs hold the two strands together Complementary base pairing The DNA bases adenine guanine thymine cytosine The space between the two DNA strands allows the pairing of a purine base with a pyrimidine base. Because of the structures of the different bases, adenine will only ever pair with thymine, and guanine will only ever pair with cytosine. This is known as complementary base pairing. Question 2 (a) If 30% of a DNA molecule is guanine, what percentage of the molecule is adenine? (b) The bases of a section of one DNA strand are shown below. Copy out the sequence and write the sequence of the other strand underneath it. AAGTTTCGCACAAG Base pairing label the DNA bases ... (a) ________________ (c) ________________ (b) ________________ (d) ________________ This base pairing is held together by three hydrogen bonds. This base pairing is held together by two hydrogen bonds. your notes and answers ... REVISION GUIDE / OCR AS UNIT 4 THE ADVANCED RESOURCE: APPLIED SCIENCE © 4SCIENCE 2006 15







