DESCRIPTIVE INORGANIC CHEMISTRY QUIZ III INSTRUCTIONS:
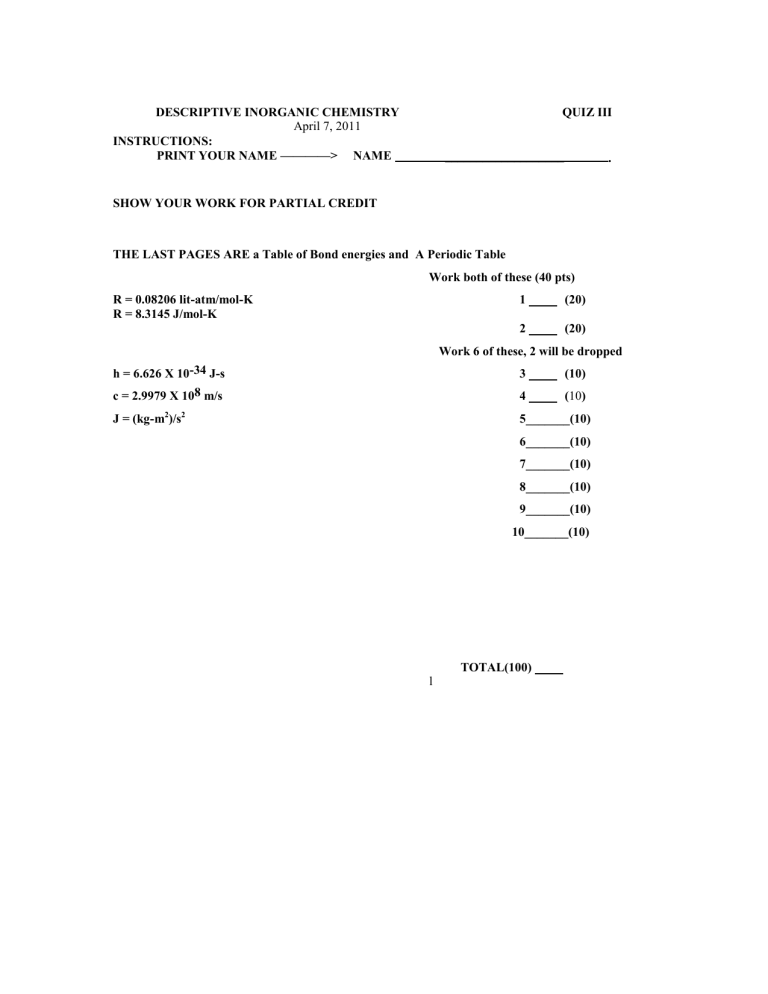
DESCRIPTIVE INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
INSTRUCTIONS:
April 7, 2011
QUIZ III
PRINT YOUR NAME ————> NAME ___________________ .
SHOW YOUR WORK FOR PARTIAL CREDIT
THE LAST PAGES ARE a Table of Bond energies and A Periodic Table
Work both of these (40 pts)
R = 0.08206 lit-atm/mol-K
R = 8.3145 J/mol-K
1 (20)
2 (20) h = 6.626 X 10-34 J-s c = 2.9979 X 108 m/s
J = (kg-m
2
)/s
2
Work 6 of these, 2 will be dropped
3 (10)
4 ( 10 )
5_______(10)
6_______(10)
7_______(10)
8_______(10)
9_______(10)
10_______(10)
TOTAL(100) l
1. Given the following data, construct the Born-Haber cycle to estimate the Enthalpy of formations for NaCl
2
. Explain why this compound is not stable. (Caution: I have included some irrelevant data in the table.)
Enthalpy Values
Na atomization
Estimated lattice energy NaCl
2 kJ/mol
+498
Cl-Cl bond energy +243
1
1
2 st st nd
electron affinity of Na -53
ionization of Na
ionization of Na
+498
+4560
1 st
Electron affinity of Cl -349
1st Ionization energy of Cl
2 nd
Ionization energy of Cl
+1255
+2295
-2500
2 . For each of the following pairs acids of (a)-(d), identify the stronger Brosted-Lowry acid in each pair and give a reason for your choice.
For each of the pairs of bases (e )-(g), identify the stronger Bronsted-Lowry base in each pair and give a reason for your choice.
Acids
(a) H-F H –Br ___________________________________________
(b) H
2
SO
4
H
2
SO
3
(c) K
+
(aq) Fe
3+
(aq)
___________________________________________
___________________________________________
(d) HPO
4
2-
H
3
PO
4
___________________________________________
Bases
(e) Cl
-
(aq) S
2-
(aq) ___________________________________________
(f) ClO
3
-
CO
3
2-
___________________________________________
(g) PO
4
3-
PO
3
3-
___________________________________________
3. (a) Using Bond Energy table at the end of the quiz, estimate the enthalpy of the following reaction.
4. Given that the enthalpy of atomization of Si is +450 kJ/mol, and the bond energies listed in the table at the end of the quiz, estimate the enthalpy of formation of SiF
4 using a diagram like a Born-Haber cycle. The actually value is -1615 kJ/mol. Explan why your value is not equal to the true value.
5. Diamond is unstable with respect to graphite. Explain why diamond rings do not crumble into graphite powder under normal conditions.
6.
Write an equation for the autoionization of the polar protic solvent HF.
7.
Dimethyl formamide is an aprotic polar solvent that good solvent for ionic salts. This is primarily due to stabilization of metal cations.
Dimethyl Formamide
Draw the structure of the interaction of dimethyl formamide with a Na cation. What type of acid base interaction is this?
8.
Write the equation using chemical structures demonstrating the acidic nature of a hydrated Ca
2+
ion ie [Ca(H
2
O)
6
]
2+
reacting with water. Explain the origin of the acidity.
9.
When NaF is dissolved in water, the solution is slightly basic. When CaF
2
is dissolved in water the solution is slightly acidic. Explain with acid base equations.
10 .
AgF is soluble in water and Ag(SCN) is not (Ksp = 1.0 x 10
-12
). On the other hand
Ca(SCN)
2 is soluble in water but CaF
2
(s) insoluble. (Ksp = 4.0 x 10
-11
). Explain why the two metals have opposite solubility behavior with these two anions.
‘
W3