Imperfect Competition Market Structure Characteristics: Implications for Competition
advertisement

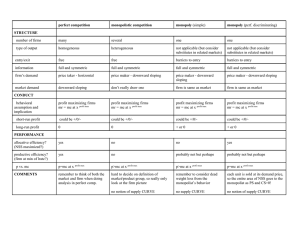
Market Structure Characteristics: Implications for Competition Imperfect Competition Farmers vs Agribusinesses Market Structure Characteristics Ø 1. Market concentration Ø 1. Market concentration Ø 2. Degree of product differentiation Ø 3. Extent of barriers to entry and exit Ø 4. Market environment Market Structure Characteristics Ø 3. • Due to absolute cost advantages, economies of scale, capital startstart-up costs, patents, licensing, preferential government policies • The greater the barriers, the less the competition and the greater the market and price control • Number and size distribution of sellers and buyers • The greater the market concentration, the less likely that price will be determined by the natural forces of supply and demand Ø 2. Degree of product differentiation • The more perceived differentiation, the greater the market and price control Extent of barriers to entry and exit Ø 4. l Market environment Unique market conditions: • Level of output in the industry (thin markets, more price control) • Elasticity of supply and demand • Proportion of consumers food dollar 1 Perfect Competition Ø Most farmers and ranchers Ø Faces l l Imperfect Competition Ø Most l horizontal demand curve MR = price = demand No price control / influence Ø Three l l Ø Since price and profits are low, try to make it up with increased output l Monopolistic Competition • Many small firms with few barriers to entry • Differentiated Product – Ice cream, bread, hamburgers – Feed supplements, hand tools • Downward sloping demand curve – Attempt to make as inelastic as possible • Over the long run – Market price is higher than perfect competition Output is lower Only normal profits main types Monopolistic Competition Oligopoly / Oilgopsony Monopoly / Monopsony Ø All – – – of the food and fiber industry Input suppliers and commodity buyers to market retailers face downward sloping demand curves Oligopoly / Oligopsony • Few (~3(~3-7) buyers / sellers, each with significant influence on price and volume • Differentiated product – Farm machinery, cigarette manufacturers, meat processors • Downward sloping demand curve – Demand is even more inelastic than monopolistic competition • Interdependent marketing strategies and pricing behavior – Price leadership – Rely on nonnon-price competition and price stability – Economic profits can be earned 2 Monopoly / Monopsony • One buyer / seller in the market • No competition – Barriers may be economic or legal • Higher price and lower volume provided • Economic profits can exist (but not guaranteed!) • Examples include: Where does all this leave the farmer? – RoundRound-up Ready corn and soybeans – Marketing orders for milk – French coco-ops and certified lowlow-THC hemp seed 3