Rigid Body Equilibrium 1.
advertisement

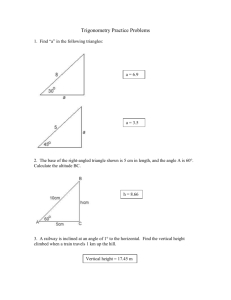
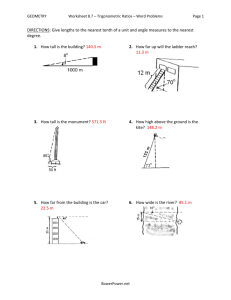
Rigid Body Equilibrium Data Sheet for Statics Lab Lab day and time Sketch _____ Analysis ______ Answers ______ Neatness _______ Total _______ Group members (Each member must print name) 1. Determine the masses and weights. . Mass (kg) Weight (N) Ladder _________________ _________________ 'Climber' _________________ _________________ Horizontal load _________________ _________________ Vertical load _________________ _________________ 2. Measure the ladder and climber lengths. Length of ladder cm Length of 'climber' cm (Measure between ladder bearing centers.) 3. Using a horizontal load of 4.5 newtons, adjust the slope angle of the ladder until it reaches equilibrium. Equilibrium angle 4. Add a vertical load of 2 newtons to the top of the ladder and determine the angle for equilibrium. Equilibrium angle 5. Add the 'block' that represents a climber so that the bottom of the 'block' is 10 cm from the center of the bottom bearing. Measure the angle for equilibrium. Equilibrium angle 6. Assignment: Show all work including basic equations and sketches where appropriate. Submit the following results as a group: a. Sketch the apparatus. b. Draw a single generic but COMPLETE free body diagram of the ladder (include the 'climber block'). c. For each configuration calculate the theoretical angle for the ladder and compare it to the measured angle. 0610 - 302 Rochester Institute of Technology Report Cover Sheet Page 1 of 2 Revised pjb/mg 10/18/04 0610-302 Rigid Body in Equilibrium (Ladder) #5 Bx Ladder W of Ladder θ AX = 4.5 N AY C:\WEBSHARE\WWWROOT\megite\302 lab rigid body equilibrium.rtf Rochester Institute of Technology USE THIS DIAGRAM AS A GUIDE ONLY – PLEASE CONSTRUCT YOUR OWN FBD’s Revised pjb 4