ME451: Control Systems Gain margin (GM)
advertisement

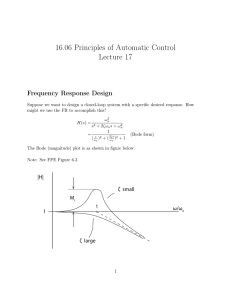
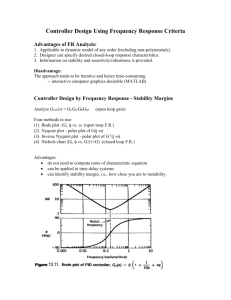
ME451: Control Systems Relative stability Dr. Jongeun Choi Department of Mechanical Engineering Michigan State University Gain margin (GM) Phase crossover frequency ωp: Gain margin (in dB) Indicates how much OL gain can be multiplied without violating CL stability. Nyquist plot of L(s) L(s) Examples of GM Im Im Re Re Reason why GM is inadequate Same gain margin, but different relative stability Gain margin is often inadequate to indicate relative stability Phase margin! Phase margin (PM) Gain crossover frequency ωg: Phase margin Nyquist plot of L(s) L(s) Indicates how much OL phase can be added without violating CL stability. Example 9.5 Relative stability on Bode plot ωg GM ωp PM Frequency shaping (Loop shaping) C(s) G(s) Controller Stable plant Reshape Bode plot of G(jω) into a “desired” shape of by a series connection of appropriate C(s). Typical shaping goal (review) SteadySteady-state accuracy Sensitivity Disturbance rejection Transient Response speed Noise reduction Relative stability Relative stability Noise reduction Transient Overshoot Notes on Bode plot Advantages Without computer, Bode plot can be sketched easily. GM, PM, crossover frequencies are easily determined on Bode plot. Controller design on Bode plot is simple. (Next week) Disadvantage If OL system is unstable, we cannot use Bode plot for stability analysis. Example 9.6 0 GM -50 -100 0 10 ωg 1 10 ωp 2 10 3 10 PM -180 -270 0 1 10 10 2 10 3 10 Relative stability with time delay 20 GM 0 -20 -1 10 0 10 -90 Time delay reduces relative stability! PM -180 -1 10 0 10 Delay time Bode plot of a time delay (review) 1 0.5 0 -0 . 5 -1 -2 10 10 -1 10 0 10 1 10 2 Huge phase lag! 0 -2 0 0 0 -4 0 0 0 -6 0 0 0 -2 10 10 -1 10 0 10 1 10 2 The phase lag causes instability of the closed-loop system, and thus, the difficulty in control.