2 YEAR CHEMISTRY WEIGHTAGE
advertisement
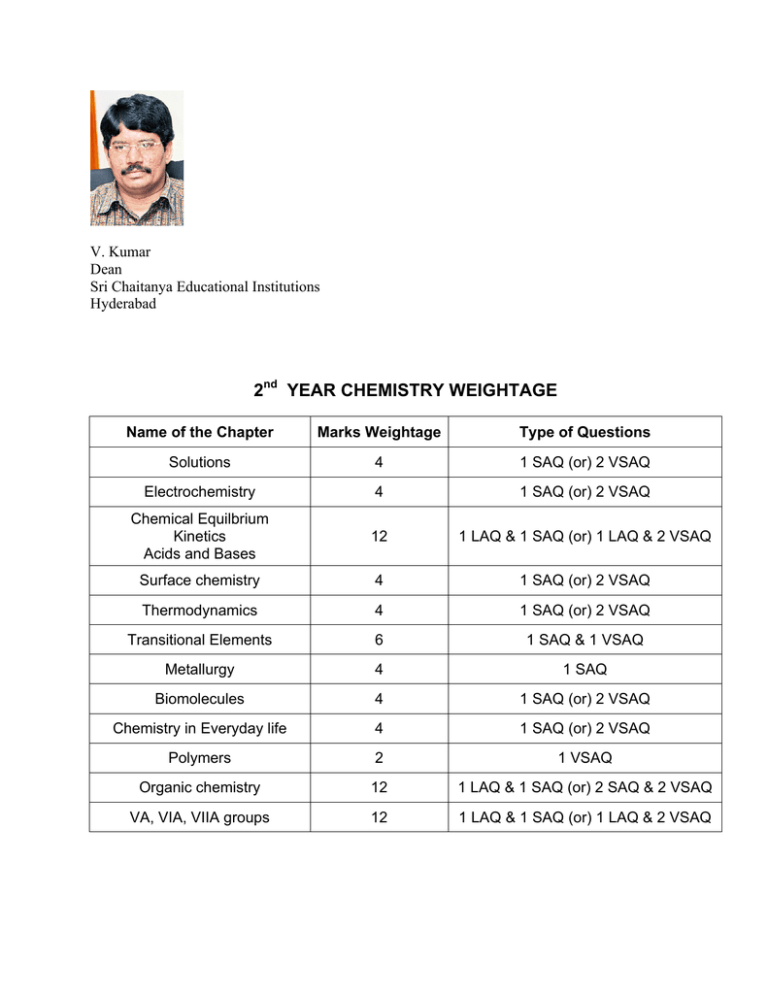
V. Kumar Dean Sri Chaitanya Educational Institutions Hyderabad 2nd YEAR CHEMISTRY WEIGHTAGE Name of the Chapter Marks Weightage Type of Questions Solutions 4 1 SAQ (or) 2 VSAQ Electrochemistry 4 1 SAQ (or) 2 VSAQ Chemical Equilbrium Kinetics Acids and Bases 12 1 LAQ & 1 SAQ (or) 1 LAQ & 2 VSAQ Surface chemistry 4 1 SAQ (or) 2 VSAQ Thermodynamics 4 1 SAQ (or) 2 VSAQ Transitional Elements 6 1 SAQ & 1 VSAQ Metallurgy 4 1 SAQ Biomolecules 4 1 SAQ (or) 2 VSAQ Chemistry in Everyday life 4 1 SAQ (or) 2 VSAQ Polymers 2 1 VSAQ Organic chemistry 12 1 LAQ & 1 SAQ (or) 2 SAQ & 2 VSAQ VA, VIA, VIIA groups 12 1 LAQ & 1 SAQ (or) 1 LAQ & 2 VSAQ Note : LAQ can be given as a combination from 2 chapters as 4M + 4M The above analysis is based on previous question papers 1). Long answer question (8 marks each): These questions may be given from the following chapters: 1. Organic chemistry 2. Chemical equilibrium, kinetics and Acids & Bases. 3. VA , VIA and VIIA Groups. 2). Short answer questions (4 marks each): These questions may come from all the chapters except Polymers. 3). VSAQ ( 2 marks each): These questions may come from all the chapters NOTE: 1).The chapter to which 4 marks weightage is given, from that chapter either one SAQ or two VSAQ may be given. 2). The chapter to which 6 marks weightage is given ,from that chapter one SAQ and one VSAQ may be given. 3). For scoring nearly 50 % of marks students need to rely on important questions but for the best score they need to be thorough with all the concepts and all the questions(including assert yourself type of questions) given in the telugu academy text book. IMPORTANT LAQ TYPE QUESTIONS 1. State Le Chatelier’s principle ? Apply it for Haber’s process and contact’s process. 2. 3. Define rate of chemical reaction and explain the factors that effect the rate of reaction. Discuss molecular collision theory of reaction rates. Support your explanation with a relevant diagram 4). State and explain Law of Mass action. Derive an expression for equilibrium constant for the reaction given below mA + nB ↔ pC + q D 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Explain the term “Hydrolysis of salts” with suitable examples. Give the relation between hydrolysis constant ( K h ) , ionization constant ( K a ) , and ionic product ( K w ) of water for sodium acetate solution How is ozone prepared in the laboratory ? Give any three oxidation/reduction reactions of O3 How do you prepare hypo in the laboratory? Give any four chemical properties of hypo with proper equations. (a) Describe Whytlaw- Gray method of for the preparation of fluorine ? (b) Write the chemical properties of F2 with relevant equations. What is the principle of preparing Cl2 in the laboratory ? Describe Nelson’s method for its manufactures. Give any four equations for chemical properties of chlorine. (a) How is bleaching powder prepared industrially ? (b) Give any four chemical properties of bleaching powder with proper equations. a).Explain the preparation of ethyl chloride from (i) Grove’s process (ii) Ethylene (iii) Ethane (b) What happens when ethyl chloride is treated with (i) Aqueous potassium hydroxide (ii) Aqueous ethanolic potassium cyanide (iii) Hot aqueous ethanolic silver nitrate (iv) Sodium ethoxide (v) Lithium aluminium hydride (vi) Ethanolic potassium hydroxide. a).How is chloroform obtained from i) Ethyl alcohol (ii) Acetone (iii) Chloral hydrate b) What happens when chloroform is treated with (iii) Hot aqueous KOH i) HNO3 vapours (ii) Metallic silver iv) Acetone in the presence of KOH (v) phenol in the presence of an alkali a) Write the preparation of ethyl alcohol from (i) Molasses (ii) Starch b) What happens when ethyl alcohol reacts with (i) Metallic Na (ii) Acetic acid (iii) Methyl magnesium bromide (iv) Conc. H 2 SO4 ,1700 C 14. How are the following converted to diethyl ether ? (i) C2 H 5OH a) (iii) C2 H 5ONa Write the equations for the action of (i) Cl2 , sunlight (ii) Conc. H 2 SO4 at low temp. and high temp (iii) PCl5 , 15. (ii) C2 H 5 Br On diethyl ether. Give two uses of ether. a)How is acetaldehyde prepared from. (i) CH 3CH 2OH (ii) Calcium salts of fatty acids (iii) C2 H 4 (iv) CH 3CHCl2 b).How does acetaldehyde react with (i) HCN (ii) NH 2 − NH 2 (iii) C2 H 5 MgBr; H 2O (iv) Dil. NaOH 16. a).How is acetic acid obtained from (i) CH 3CH 2OH (ii) CH 3CN (iii) CO2 & CH 3 MgBr (iv) CH 3CHO b) What happens when acetic acid is treated with (i) Na (ii) NaOH (iii) NH 3 17. 18. (iv) Cl2 red P (HVZ) a) How is benzene converted into nitrobenzene ? b ) Explain the reduction of nitrobenzene in different media with different reagents. a) How are (i) C6 H 5 NO2 (ii) C6 H 5OH (iii) C6 H 5Cl are converted to aniline? b) What happens when aniline is treated with (ii) Chloroform and alcoholic KOH (i) C6 H 5COCl (iii) Benzaldehyde (iv) CH 3 Br (v) HCl







