physics 2 - IDS-Curriculum
advertisement
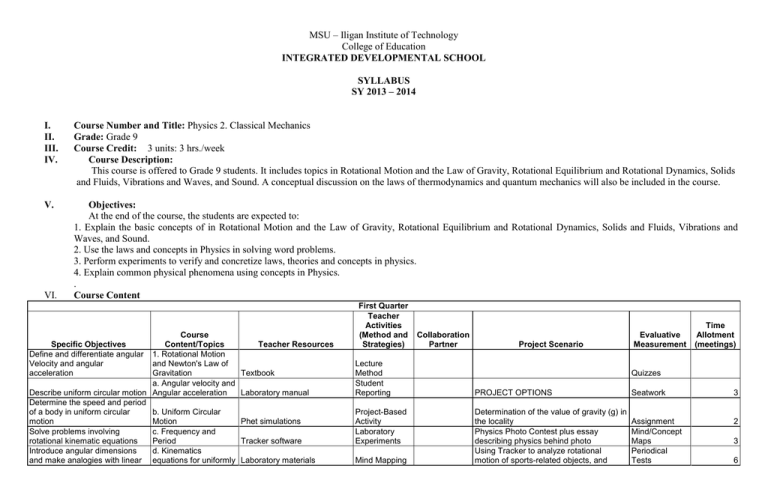
MSU – Iligan Institute of Technology College of Education INTEGRATED DEVELOPMENTAL SCHOOL SYLLABUS SY 2013 – 2014 I. II. III. IV. Course Number and Title: Physics 2. Classical Mechanics Grade: Grade 9 Course Credit: 3 units: 3 hrs./week Course Description: This course is offered to Grade 9 students. It includes topics in Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity, Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics, Solids and Fluids, Vibrations and Waves, and Sound. A conceptual discussion on the laws of thermodynamics and quantum mechanics will also be included in the course. V. Objectives: At the end of the course, the students are expected to: 1. Explain the basic concepts of in Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity, Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics, Solids and Fluids, Vibrations and Waves, and Sound. 2. Use the laws and concepts in Physics in solving word problems. 3. Perform experiments to verify and concretize laws, theories and concepts in physics. 4. Explain common physical phenomena using concepts in Physics. . Course Content VI. Course Specific Objectives Content/Topics Teacher Resources Define and differentiate angular 1. Rotational Motion Velocity and angular and Newton's Law of acceleration Gravitation Textbook a. Angular velocity and Describe uniform circular motion Angular acceleration Laboratory manual Determine the speed and period of a body in uniform circular b. Uniform Circular motion Motion Phet simulations Solve problems involving c. Frequency and rotational kinematic equations Period Tracker software Introduce angular dimensions d. Kinematics and make analogies with linear equations for uniformly Laboratory materials First Quarter Teacher Activities (Method and Strategies) Lecture Method Student Reporting Project-Based Activity Laboratory Experiments Mind Mapping Collaboration Partner Project Scenario Evaluative Measurement Time Allotment (meetings) Quizzes PROJECT OPTIONS Seatwork 3 Determination of the value of gravity (g) in the locality Physics Photo Contest plus essay describing physics behind photo Using Tracker to analyze rotational motion of sports-related objects, and Assignment Mind/Concept Maps Periodical Tests 2 3 6 variables Apply the concept of circular motion to satellites and the motion of the planets. State and explain Kepler's laws of planetary motion State and explain Newton's law of universal gravitation. Solve problems on law of gravitation Explain the concepts of weightlessness Specific Objectives Explain the concepts of Torque, Rotational Inertia, rotational kinetic energy, angular momentum and conservation of angular momentum Solve problems on rotational dynamics and rotational equilibrium Locate the center of gravity of an object. Describe the different types of equilibrium Relate the idea of torque to center of gravity Relate the idea of torque and angular acceleration accelerated rotational motion e. Relationship between angular and linear quantities of motion f. Centripetal acceleration g. Kepler's Laws on Planetary Motion h. Newton's Law of Gravitation output is presented in a blog Audio-video presentations Word Problem Solving Assignments and Seatworks Word problems Boardwork Demonstration materials 2 2 3 Internet Course Content/Topics Teacher Resources 2. Rotational Dynamics Textbook and Rotational Equilibrium 3 Second Quarter Teacher Activities (Method and Collaboration Strategies) Partner Lecture Method a.Torque Laboratory manual Student Reporting b. Rotational Inertia Phet simulations c. The Two Conditions for equilibrium d. The Center of Gravity e. Examples of Objects in Equilibrium f. Relationship between Torque and Angular Acceleration g. Rotational Kinetic Energy h. Angular Momentum Tracker software Project-Based Activity Laboratory Experiments Mind Mapping Laboratory materials Demonstration materials Audio-video presentations Word problems Internet Project Scenario Students are expected to apply the concepts of rotational dynamics and equilibrium by creating a short video production describing various concepts and real life examples of rotating objects Evaluative Measurement Quizzes Time Allotment Seatwork 3 Assignment 3 Mind/ concept maps Periodical Tests 3 3 Word Problem Solving Assignments and Seatworks 3 Boardwork 3 3 3 i. Conservation of Angular Momentum 3 Specific Objectives Course Content/Topics Teacher Resources Differentiate periodic from nonperiodic motion. Identify the relationships of frequency, amplitude, wavelength and speed. Solve problems on simple harmonic motion. 1. Periodic Motion Textbook Expres the relationship/similarities of periodic motion and uniform circular motion. Cite phenomena that provide proofs of the existence of the properties of sound waves. Explain how musical instruments produce and different sounds. Solve simple word problems on waves. Exhibit appreciation of applications of the lesson on periodic motion and sound waves. Host a symposium for grade school students to share what they have learned on sound waves and periodic motion. a. Definition of Periodic Laboratory Manual Motion Third Quarter Teacher Activities (Method and Strategies) Lecture Method Student Reporting Collaboration Project Scenario Partner Evaluative Measurement Music Teacher Students will prepare a mini-symposium for Kinder or Grade School Students on Pre-Selected Topics relevant to the English understanding and applications of Teacher sounds. For the Symposium to be Grade School successful, the students must 1) prepare the program; 2) assign speakers, hosts, Teacher facilitators and working committee; 3) invite students to attend the symposium; Field Experts 4) prepare audio-visual/demonstration materials; 5) conduct research on their topic through literature review and interview with experts. Journal Entries Time Allotment (Meetings) Presentation and Product Rubrics Quizzes 1 Seatwork 1 b. Characteristics of Phet Simulations Periodic Motion: (frequency, amplitude, wavelength, speed) c. Hooke's Law and Laboratory Materials Simple Harmonic Motion ProjectBasedActivity i. Force, Period and Potential Energy of a Spring ii. Force, Period and Potential Energy of a Pendulum 2. Comparing Simple Harmonic Motion and Uniform Circular Motion: position, velocity and acceleration as a function of time 3. Waves Musical Instruments Mind Mapping Assignment 1 Demonstration Materials Word Problem Solving Mind/Concept Maps 1 Audio-Video Presentations Assignments and Seatworks Periodical Tests 2 Peer and Selfevaluation 1 a. Definition of Waves Word Problems b. Wave Classifications i. Mechanical and EM Waves Internet Laboratory Experiments Experts: Music Boardwork Teacher/Physician/Engineers ii. Longitudinal and Transverse Waves 4. Sound Waves a. Properties of Sound Waves i. Reflection (Echoes and Reverberation) ii. Refraction iii. Diffraction iv. Resonance iv. Interference (Standing Waves, Harmonics and Beats) 5. Application a. Doppler Effect b. Musical Instruments i. Stringed Instruments ii. Wind Instruments iii. Percussion Instruments iv. Building Accoustics 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 Fourth Quarter Teacher Activities (Method and Strategies) Lecture Method Student Reporting Specific Objectives Course Content/Topics Teacher Resources Differentiate solids from fluids by comparing their characteristics Cite applications of the concept of elasticity, stress, strain and moduli. Enumerate the properties of fluids. 1. Solids and Fluids Textbook a.States of Matter Laboratory Manual b. Deformation of Solids: Elasticity and Forms of Moduli i. Elasticity Phet Simulations ProjectBasedActivity Grade School Teacher Laboratory Materials Laboratory Experiments Field Experts Cite instances/phenomena that could be explained by the concepts of fluid dynamics Express understanding and appreciation of the practical applications of the lessons. Perform experiments/demostrations that illustrate the concepts of solids, fluids and theirproperties. Solve simple word problems on Collaboration Project Scenario Partner Evaluative Measurement Trigonometry Teacher Music/Art Teacher Journal Entries Students are expected to apply the concepts of fluid dynamics in designing and flying a kite. The students are then expected to adopt and teach a Grade School/Kinder Student how to create and fly a kite. A kite flying event will be held as a culminating activity. Product Rubrics Time Allotment 1 Quizzes Seatwork ii. Young's Modulus, Sample Kite Shear Modulus and Bulk Modulus c. Definition and Demonstration Materials Characteristics of Fluids (Ideal and Real) Mind Mapping Assignment 2 Word Problem Solving Mind/Concept Maps 1 d. Properties of Fluids: Audio-Video Presentations Assignments Periodical elasticity, moduli, fluid dynamics Density, Viscosity, and fluid motion. Surface Tension Teach Kinder or Grade School 2. Fluid Dynamics students how to create and fly kites as an application of their lessons on fluid motion. a. Fluid Pressure b. Archimedes Principle and Buoyant Force 3. Fluid Motion: Laminar and Turbulent Flow a. On Laminar Flow: Volume Flow Rate b. On Laminar Flow: Continuity Equation c. On Laminar Flow: Bernoulli's Equation 4. Application of Fluid Mechanics a. Airplane's Lift b. Pascal's Principle: Hydraulic Jack, Hydraulic Brakes c. Venturi Meter d. Torricelli's Theorem VII. Experts: Parents/Physics Teachers/Engineers and Seatworks Tests Boardwork Peer and Selfevaluation Word Problems Internet 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 Grading System: Averaging Periodical Test - 30% Class Standing – 70% Components of Class Standing: Quizzes, Seatwork and Assignments, Laboratory Activity, Project-based activity, Quarterly Examination, Attendance/Behavior VII. References 1. Cutnell, John D. and Kenneth W. Johnson. Physics 6th ed. 2004. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New Jersey USA. 2. Ferrer, Rhodora Angela F. and Ungson, Olivia B. 2011. Physics Teachers Guide. Sibs Publishing House Inc. Quezon City 3. Serway, Raymond and Chris Vuille. Physics Fundamentals 1. 2012. Cengage Learning Asia Pte. Ltd. First Philippine reprint 2011. Pasig City, Philippines. Prepared by: Prof.Charity I. Mulig Chair, SMD-IDS Mr. Neal Alfie Y. Lasta Instructor Noted by: ________________ Chair, SMD/RSD Approved By: Prof. Esmar N. Sedurifa Dean, CED Prof. Leila V. Bernaldez Principal, IDS