Current Electricity
advertisement

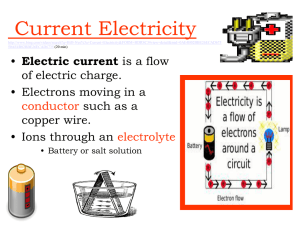
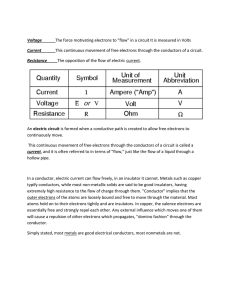
Current Electricity Current Electricity Electric current is a flow of electric charge. Electrons moving in a conductor such as a copper wire. Ions through an electrolyte Battery or salt solution CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS Conductors allow electrons to flow through them easily. Copper atom has one valence electron. Valence electrons of conductors can gain enough energy to break away and become free electrons. Free electrons can move from one atom to another. http://www.ndt- ed.org/EducationResources/HighSchool/Electricity/v alenceshell.htm Cu CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS Insulators do not allow electrons to flow through them easily. They are materials that do not have any free electrons. They do not make good conductors of electrical currents. Ex wood, plastic, rubber, noble gases Insulators can protect us from electric shock Electric Circuit: If the (+ve) & (-ve) sides of the battery are connected by a conductor, electrical current will flow as the electrons move from the (-ve) side to the (+ve )side. (+) (-) Components of a Simple Circuit: 1. Source of electrical energy: • 2. Electrical load: • 3. Anything that converts electrical energy to another form of energy (ie: toaster converts electrical energy to heat) Circuit control device: • 4. (ie: a battery) (ie: a switch, a timer) Connectors: • wires that connect the components of a circuit together Schematic Diagram of a simple circuit: CURRENT ELECTRICITY: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5laTkjINH rg (10 min) (intro current, coulomb) Introducing Current Electricity: Read page 507-509 Answer # 2-6 page 510 Electric Current: Read page 556-557 Answer # 1-3 page 557 Potential Difference: Read page 560-561 Answer # 2-4 page 561 Review of Static Electricity for Quiz Page 498 # 1, 4, 7, 16 Page 499 # 23 Page 500 -501 Self Quiz # 1-12, 14, 15a, 18