Electricity & Magnetism
advertisement

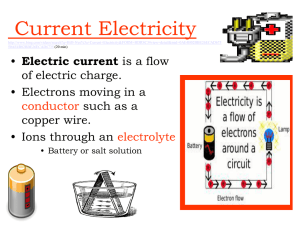
Electricity & Magnetism Static, Currents, Circuits Magnetic Fields & Electro Magnets Motors & Generators Atoms… Have neutrons, protons neutrons, protons,, and electrons.. electrons Protons are positively charged Electrons are negatively charged Electrons… Are located on the outer edges of atoms…they can be moved moved.. A concentration of electrons in an atom creates a net negative charge. If electrons are stripped away, the atom becomes positively charged. The world is filled with electrical charges:: charges + - + + + + + + + + + - What is this electrical potential called? Static - Electricity - - - + ++ ++ Static Electricity The build up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy.. It does not move. It is energy stored.. stored Static Discharge… Occurs when there is a loss of static electricity due to three possible things: Friction - rubbing Conduction – direct contact Induction – through an electrical field (not direct contact) Electricity that moves moves… … Current Current:: The flow of electrons from one place to another. Measured in amperes (amps) Kinetic energy How can we control currents? With circuits. circuits. Circuit Circuit:: is a path for the flow of electrons. We use wires wires.. There are 2 types of currents: Direct Current (DC) – Where electrons flow in the same direction in a wire. There are 2 types of currents: Alternating Current (AC) – electrons flow in different directions in a wire There are 2 types of circuits: Series Circuit:: the components Circuit are lined up along one path. If the circuit is broken, all components turn off. Series Circuit There are 2 types of circuits: Parallel Circuit – there are several branching paths to the components. If the circuit is broken at any one branch, only the components on that branch will turn off. off. Parallel Circuit Conductors vs. Insulators Conductors – material through which electric current flows easily easily.. Insulators – materials through which electric current cannot move.. move Examples Conductors Conductors:: Insulators Insulators:: Metal Styrofoam Water Rubber Plastic Paper What is Resistance? The opposition to the flow of an electric current, producing heat heat.. The greater the resistance, the less current gets through. Good conductors have low resistance. Measured in ohms. What Influences Resistance? Material of wire – aluminum and copper have low resistance Thickness – the thicker the wire the lower the resistance Length – shorter wire has lower resistance Temperature – lower temperature has lower resistance What is Voltage? The measure of energy given to the charge flowing in a circuit. The greater the voltage, the greater the force or “pressure” that drives the charge through the circuit. Difference b/t Volts and Amps Example Amps – you could say that… measure how much water comes out of a hose. Volts measure how hard the water comes out of a hose. Ohm’s Law Resistance Ohms = Voltage / Current = Volts / Amps Practice with Ohm’s Law Ohms 4 15 2 9 6 Volts 100 150 30 45 48 Amps 25 10 15 5 8 What is an electromagnet? Electromagnet – a magnet made from a current bearing coil of wire wrapped around an iron or steel core. What is a generator? Generator – a machine that changes mechanical energy to electrical energy Usually use moving magnets to create currents in coils of wire. What is a motor? Motor – a device that changes electrical energy to mechanical energy that can do work work.. That’s It !!!!