South, Southeast, and East Asia

South, Southeast, and East Asia
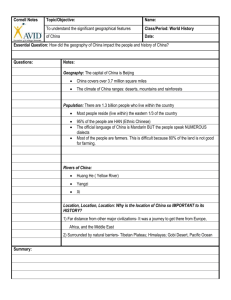
Physical Characteristics
Mountains influence the region
population settlement patterns
ability of people to move
climate
Mountains
Himalayas
Western and Eastern Ghats
Mount Fuji-Japan
Varied climate regions --ranging from tropical wet to humid continental
Many natural hazards -monsoons, typhoons, volcanoes, and earthquakes
Monsoon --a seasonal shift in the prevailing winds that influences large climate regions
Typhoon --a destructive tropical storm occurring in the western Pacific Ocean or the
China Sea, similar to a hurricane
Influence of water --(rivers, seas, and ocean currents) on agriculture, trade, and transportation
Important bodies of water --
Arabian Sea, Indian Ocean, Bay of Bengal, Ganges River, Indus
River, Brahmaputra River, Pacific
Ocean, Yangtze River (Chaing
Jiang), Mekong River, Yellow
River (Huang He)
Area have abundant arable land
areas of loess
Plateau of Tibet hard to live on
Gobi Desert--second largest in the world
Economic Characteristics
Varied economies in the region ranging from subsistence/commercial agriculture to high-tech industrial manufacturing
Active participation in global markets
Many newly industrialized countries--South Korea,
Taiwan, Singapore
Japan is the economic leader of the area
China is in a transition period-from a centrally planned economy to more of a tradition free market economy
Agricultural advancements and technology are enabling greater food production-“Green
Revolution”
Environmental degradation
deforestation
fishing is important
Many countries are members of the Association of
Southeast Asian Nations
(ASEAN) which was set up with the US
main crops are rice and tropical crops such as bananas
Cultural Characteristics
Areas of extremely dense and sparse population
severe contrast between rural and urban areas
serious religious conflicts-primarily between Hindus and
Muslims
deep respect for ancestors
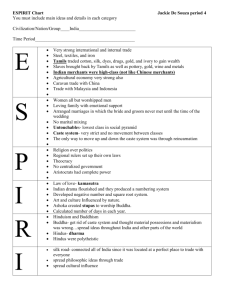
Religious diversity --
Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism,
Christianity, Taoism, Shinto,
Confucianism are the major religions
India has a strict caste system--(similar to a class structure) once born into a caste it is next to impossible to move out of that caste
Cultural heritage
Silks
Batik
wood and ivory carving
ideograms--unique alphabets
jewels
Important cities --Tokyo,
Japan; Beijing, China; New
Delhi,India
Cultural landscape --Taj
Mahal, Angkor Wat, Great
Wall of China, floating markets, mosques,minarets, pagodas, temples and shrines, terraced rice fields
Angkor Wat
Angkor Wat
Great Wall of China
Taj Mahal
Taj Mahal
Batik
Himalayas
Mount Fuji
Mount Fuji—outside of Tokyo
Mt. Fuji
Himalayas—Mt. Everest
Gobi Desert
Buddha
Buddha in New Delhi
Shinto Shrine
Temple
Pagoda
Pagoda
Temple