Language Awareness for English Language Teachers XXD511
advertisement

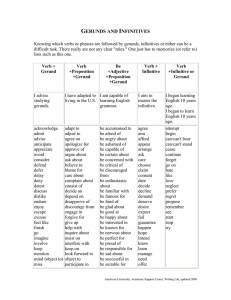
ESP COURSE (English for Specific Purposes) for Class Teachers (17-18) Vera Savic, MA Lecturer in English 2010/2011 Faculty of Education in Jagodina University of Kragujevac vera.savic@pefja.kg.ac.rs Coherence: Transitions Transition words and phrases – used to connect sentences or paragraphs together or relate ideas to one another, also called connectives. Coherence – arranging ideas in a clear and logical way; necessary to understand the meaning of the text as a whole. Additional information - and - also - in addition - in fact - furthermore - moreover - Another ... Is ... Examples - for example - for instance - in general - generally - especially - in particular - e.g. Transitions (cont.) Contrast - however - on the other hand - but - yet - in spite of - in contrast - although / though - Instead Cause and effect - therefore - so - thus - as a result - since - because Concluding ideas - in conclusion - in summary - finally - therefore - to conclude - to summarise TASK: Use the right connective to connect the following sentences: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. His lectures are very theoretical and illustrative. _________, he gives very good handouts. I shall ________ __ by saying that this is an interesting text that should be extremely useful to ESP students in academic writing. The library is closed on Saturdays and Sundays. _______ you cannot borrow that book over the weekend. He passed his final exam. _________, he received BA in education. I didn’t tell her to study psychology. ___________, I tried to persuade her to study languages. The seminar papers were brief. ___________, they were better than I expected. _________ English is not the language with the largest number of native speakers, it has become a lingua franca. Grammar Errors: • • • • • Word order Verb tense Word form Relative clauses Subject-verb agreement • Articles, prepositions, spelling Common errors: • Reduced adverb clauses: e.g. when moving equipment e.g. done with style, ... • Reduced adjective clauses: e.g. the team developing a new system e.g. categories depending on the day and the aims of a lesson e.g. decisions made in her classroom • Uncountable nouns: e.g. equipment, information, knowledge, research • Irregular plural forms of nouns: e.g. criterion – criteria, phenomenon, medium, analysis, basis, hypothesis • Quantifiers e.g. few/a few, little/a little • Subject noun phrase e.g. some/many books + pl. verb e.g. some/much information + sg. verb Three Kinds of Teacher questions (cont.) 1. Her job is to create conditions that enable students to learn for themselves. 2. They move between categories depending on the day and the class and the aims of a lesson. 3. This teacher takes her lead from the students, seeing herself as someone whose job is to create conditions for learning. 4. They have limited knowledge of teaching methodology. infinitive, gerund or participle: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Many teachers know their subject matter very well, but have __________ (limit) knowledge of teaching methodology. This kind of teacher relies mainly on ‘explaining’ or ‘lecturing’ as a way of ____________ (convey) information to the students. ____________ (do) with style or enthusiasm or wit or imagination this teacher’s lessons can be very entertaining, ____________ (interest) and informative. The learners often get practice by _____________(do) individual exercises after one phase of the lecture has finished. This teacher also knows the subject matter that is being __________ (deal) with. infinitive, gerund or participle: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Essentially ______________ (teach) is about working with other human beings. Decisions made in her classroom may often be ____________ (share) or negotiated. In many cases she takes her lead from the students, seeing herself as someone whose job is to create the conditions that enable the students _________ (learn) for themselves. Sometimes this will ____________ (involve) her in less traditional ‘teaching’. Activities in the classroom can include how __________ (guess) the meaning of unknown words. There are many factors ______________ (influence) the teaching event. Tasks 1. How many phonemes are there in each of these words: reflection, memorize, techniques, appropriate 2. How many syllables are there in each of these words? average, evidence, deskwork, curriculum 3. Which of the following words is stressed on the first syllable? research, psychology, attitude, motivation 3. Underline a minimal pair: yet – jet, by – buy, here – hear