Why Electrical Engineering I?
advertisement

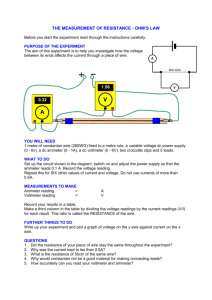
Resistance • Section 2.4 in your book Resistance • Property of a device that indicates how freely it will allow current to flow given a specific voltage applied. If low in value, current flows more freely. • Measured in ohms (Ω = V/A or KΩ = V/mA) R = Voltage or V = I∙R Current • Obeys the passive sign convention This is Ohm’s Law! I + V if I > 0 then V > 0 Resistors • Resistors are devices that are used in a variety of circuits to make the currents and voltages what you desire • They are color-coded and come in various tolerances, ± 1%, , ± 5% and , ± 10% are most common Resistor Color Code 56 * 10 kW = 560 kW 237 * 1 W = 237 W http://www.elexp.com/t_resist.htm Conductance (G) • • • • Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance Its unit is the siemen = amps/volts = 1/Ω G=I/V=1/R An equivalent measure of how freely a current is allowed to flow in a device Resistivity (ρ) • Property of a material that indicates how much it will oppose current flow • R= (ρ · length) / (cross sectional area) • Units are ohms · meters (Ω · m) • As the wire gets bigger, so does the cross section making the resistance smaller • As the length gets longer, the resistance goes up proportionately Conductors • Materials with electrons that are loosely bound to the nucleus and move easily (usually one electron in the outer shell) • Their low resistance goes up as the material is heated, due to the vibration of the atoms interfering with the movement of the electrons • The best conductors are superconductors at temperatures near 0o Kelvin Conductor Animation • http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/electromag/java /filamentresistance/ Semiconductors • Materials with electrons that are bound more tightly than conductors (usually 4 electrons in the outer shell) • Impurities are added in controlled amounts to adjust the resistivity down • Semiconductors become better conductors at higher temperatures because the added energy frees up more electrons (even though the electron flow is impeded by the increased atomic vibration) Insulators • Materials that have all 8 electrons in the outer shell tightly bound to the nucleus • It takes high temperatures or very high electric fields to break the atomic bonds to free up electrons to conduct a current • Very high resistivities and resistances Resistivity of Materials • • • • • • • Glass • Gold • Silver • Silicon • Aluminum • Copper Put a number 1 beside the material that is the best conductor, a 2 next to the material next most conductive, etc. Resistivity of Materials 1 Silver - A conductor - ρ=1.64 ·10-8 ohm-m 2 Copper - A conductor - ρ= 1.72·10-8 ohm-m 3 Gold – A conductor - ρ=2.45·10-8 ohm-m 4 Aluminum - A conductor - ρ= 2.8·10-8 ohm-m 5 Silicon - A semiconductor - ρ=6.4 ·102 ohm-m 6 Glass – An insulator – ρ=1012 ohm-m Example • • • • • • A round wire has a radius of 1 mm = 10-3m The wire is 10 meters long The wire is made of copper R= (1.72 · 10-8 Ω·m · 10 m) /( π ·(10-3m) 2 ) R = 0.0547 Ω This is negligible in most circuits where resistances are often thousands of ohms Power used by Resistors • • • • We saw that P = I ∙ V If by Ohm’s law, V = I ∙ R, then P = I2 ∙ R Or since I = V /R, then P = V2 / R Since resistance is always positive for passive devices, then power is always positive (meaning that power is always absorbed or used) Application • Calculate the power lost in a 100 foot AWG 14 copper wire handling 20 amps. – AWG 14 wire has a cross section of 2.08 mm2 and 2.52 ohms/1000 feet • What current is an AWG 12 copper wire handling if it had the same power loss as the AWG 14 cable? – AWG 12 wire has a cross section of 3.31 mm2 and 1.59 ohms/1000 feet Application • What is the voltage drop across the wire in each case? – For the AWG 14 wire ____________ – For the AWG 12 wire ____________ Conclusion • When you need to handle more current, use bigger or more conductive wire – – – – Avoids loss of power Lessens voltage drop Avoids dangerous heating of wiring But costs more Voltage & Current Sources Section 2.3 in your book Independent Voltage Sources • Most common in everyday life • Voltage is fixed and independent of the current required by the circuit • Ideally is capable of providing any current that the circuit requires + - Vs is fixed AC or DC Indpendent Current Sources • Current is fixed and independent of the voltage across the source • The voltage across the source adjusts to whatever the circuit requires to produce the fixed current – it does not usually have zero volts across it Is is fixed, AC or DC Dependent Sources • May be voltage or current sources – May be AC or DC • Are dependent on a current or voltage somewhere in the circuit K∙Vx or r∙Ix + - K∙Ix or g∙Vx Dependent Sources • Used in modeling more complex devices like transistors and operational amplifiers – The voltage applied to the gate of a MOSFET controls the conductivity of the channel so that more current flows from drain to source Gate Source Drain Example • A light sensor produces a 0 to 1 amp current proportional to the outside illumination, K amps • The sensor current supplies a 100Ω resistor to get the dependent voltage, VL • The source powering the room lights equals 120 - VL/5 volts • What is the voltage across the lights when K = 0, .4, .7 or 1 amp? Circuit Diagram Vs =120v -VL/5 + - Light Sensor Room Lights + 100Ω VL Is = K amps _ Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles IEEE – USA Position Statement Adopted June 15, 2007 • Use PHEVs to add resilence to our transportation fleet and increase energy independence – In the case of an oil shutdown or price spike, a PHEV would allow people to make necessary trips to work and shopping – Although current hybrids increase mileage between 16 and 47%, PHEVs could displace almost all imported oil Other Recommendations • Increase research to improve – Batteries, including weight, size, cost, life and safety considerations – Power electronics – Controls – Integration with the electric power grid Final Recommendations • Use incentives to encourage adoption of PHEVs • Encourage electric metering and pricing that will help PHEVs realize their potential – To encourage consumers to charge their vehicle during off-peak hours – To encourage consumers to make their vehicle battery storage available to meet peak loads Progressive X Prize • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NT2FI0 H8CWA&feature=user