Biomes
advertisement

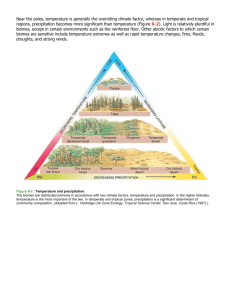
Biomes Chapter 6 Biomes Biome – a large region that is determined by 2 things 1. similar climate – average weather in an area. 2. similar plants and animals – (soil type) Climate – average weather of an area Precipitation Type (snow, rain, etc.) Amount See Figure 3, Page 154 Temperature and Precipitation Biomes also vary with altitude and latitude Altitude – height of an object above sea level as altitude increases, temperature decreases. Latitude – distance north or south of the equator – the closer to the equator the hotter it is. See Figure 4, Page 155 Latitude and Altitude Plants and Animals The soil type determines the types of plants that will grow. The types of plants determines the types of animals Plants have adaptations that allow them to live in certain biomes. 3 Major types of plant adaptations Size Color Shape See Figure 1, Page 153 – Biome map The World’s Major Terrestrial Biomes 3 Major Types of Biomes Forests Grasslands Deserts Tropical Rain Forests Forests All forests contain an abundance of small and large trees 4 types of Forests 1. Tropical Rain Forest 2. Temperate Rain Forest 3. Temperate Deciduous Forest 4. Taiga Tropical Rain Forest The Most biodiverse (has large variety of living things) Very high temperatures Very humid A lot of rain 200-450 cm/year Located near the equator (latitude) Most near sea level (altitude) Tropical Rainforest continued… Soil contains very few nutrients because things are decomposed quickly and the nutrients are immediately absorbed by plants Main type of plants is trees See Figure 7, Page 158 Layers of the Rain Forest Layers of Tropical Rainforest Understory (Bottom layer)– receives very little light Canopy (Middle layer) – divided between upper & lower canopy This is the main level of rainforest, absorbs 95% of sunlight. Emergent Layer (Top layer) – tallest trees Tropical Rainforest is one of the most threatened biomes Main threat is habitat destruction – caused by the cutting down of trees We cut down trees for paper/wood – but mostly for grazing livestock and growing cash crops. Temperate Rain Forest Has seasonal variations Moderate (medium) temperatures High humidity Large amounts of rain Found in North America (Pacific Northwest, Australia, and New Zealand Temperate Deciduous Forests Temperate Deciduous Forest Deciduous trees are trees that lose their leaves seasonally Moderate temperatures 4 seasons Temperatures vary greatly from season to season; sometimes day to day We live in this Biome Made up mostly of trees that lose their leaves seasonally The soil contains a lot of nutrients because decomposition is slow Plants in this biome grow in layers This biome contains a large variety of plants and animals. Taiga Taiga (Northern Coniferous Forest) Very cold temperatures Moderate amount of snow & rain Long winters, short summers Majority of trees are conifers which reproduce using cones and keep their needle-like leaves year around. Contains many lakes and swamps Most of the northern portion of the United States Grasslands Contain mostly grasses and weeds, very few trees and the land is usually relatively flat. 4 Different types Savanna Temperate Grasslands Chaparral Tundra Savannas Savanna Type of grassland that contains grasses, shrubs and small trees Very warm temperatures Most of the rain falls during the rainy or wet season Some animals found here include elephants, antelope, lions, giraffes and cheetah Found in parts of Africa, Western India, Northern Australia and parts of South America Temperate Grasslands Temperate Grasslands North America – prairie Asia – steppe South America – pampas 4 distinct seasons Moderate temperatures Moderate rainfall Usually found in the interior of continents Periodic droughts Plant life consists of grasses, wildflowers and a few small bushes Very fertile soil Many have been converted to farmland America’s most endangered biome Used for Grazing livestock animals (cattle, sheep, horses) Grassland Plants Chaparral Chaparral Temperate – 4 seasons Moderate temperatures Dominated by shrubs (small bushes) Usually found by coasts Dry climate Plants must be adapted to survive droughts by conserving water Transitional biome – often found in between grassland and desert biomes Tundra Tundra Coldest climate of any biome Dry – little precipitation Precipitation in the form of snow and ice Contains permafrost (a layer of soil that is frozen year round – it never thaws) 2 types of Tundra Artic – high latitudes far from equator – North & South Poles Alpine – high altitudes (mountaintops) Plants only grow during summer, they are small and low to the ground Animals – penguins, moose, polar bear, caribou Tundra very fragile and endangered (global warming) Deserts Deserts Have very little precipitation Less than 5 inches or 10 cm per year Widely scattered vegetation In most deserts, there is a large temperature range throughout the day, hot days & cold nights Many desert plants will drop their leaves if it gets too dry – and regrow new ones when it rains 3 Types of Deserts Tropical Temperate Polar 1. Tropical Desert Hot year round Rain one or two months per year Example: Sahara (Africa) 2. Temperate desert Medium temperatures More precipitation and plants (cacti, snakes – reptiles, insects & arachnids) Example: Mojave (US) 3. Polar Desert Winters cold, summers warm Little precipitation Example: Gobi (China)