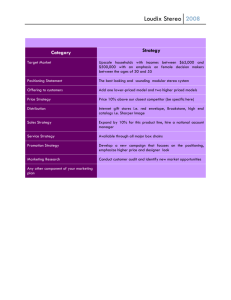
Kotler Keller 10
advertisement

Principles of marketing Positioning Session-21,22 What is Positioning? Positioning is the act of designing the company’s offering and image to occupy a distinctive place in the mind of the target market. Positioning Strategies 1. Determine consumers’ perceptions and evaluations of the product or service in relation to competitors’. 2. Identify competitors’ positions. 3. Determine consumer preferences. 4. Select the position. 5. Monitor the positioning strategy. Types of Positioning • Product Attributes position many technical products. The positioning of Ericssons EH237 mobile phone is its Low weight and number features • The Benefits they offer or the needs they fill position many products – Crest toothpaste reduces cavities. • Usage occasions position many products. Mentadcnt Night Action toothpaste, for instance, is for evening use • Competitors' Positioning: A product can be positioned directly against a competitor. For example, in ads for their personal computers, Compaq and Tandy have directly compared their products with IBM personal computers. • Product Class: Its a means of positioning. For example, Van Den Bergh's I Can't Believe It's Not Butter is clearly positioned against butter, while other yellow fats are promoted as cooking oils. • Quality Positioning: A product can be positioned on the basis of quality for example Sony • Price Positioning: The price of the product sets in the mind and they believe that the product is very well priced example Akai. Perceptual Maps © 2007 McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., McGraw-Hill/Irwin Types of Positioning Errors • Under Positioning – that is, failing to position the company at all another entry in the market like Vanilla Coke, Diet Pepsi. • Over Positioning – that is, giving buyers too narrow a picture of the company. Thus a consumer might think that the Steuben glass company makes only fine art glass costing 1,000 and up, when it also makes affordable fine glass starting at around 50. • Confused Positioning: Leaving buyers with a confused image of the company. Company making too many claims • Doubtful Positioning: Buyers find hard to believe the brand claims in view of product features, price, manufacturer like slimming