Media & Politics - Media Literacy Clearinghouse
advertisement

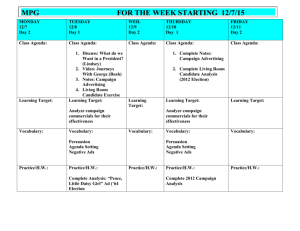
Understanding Political Campaign Advertising Frank Baker: Media Educator August 19, 2008 www.pbs.org/vote2008 www.ciconline.com Understanding Political Campaign Advertising Some givens: Candidates need the media Candidates try to control their image McCain, Aurora CO July 30, 2008 Candidates depend on media consultants Candidates depend on media consultants Source: Robert Arial Understanding Political Campaign Advertising Some givens: Fundraising $$= purchasing TV time for ads Political ads resemble traditional ads New media (YouTube; Facebook; etc.) effective at reaching young voters and raising money Understanding Political Campaign Advertising Some givens: In today’s media saturated world, the life of any 30 second TV spot lives on, online AND as newscasts and pundits review them continuously Understanding Political Campaign Advertising “When we study commercials ….we talk about the issues and the quality of the message…it’s not just about political ideology, it’s also about the art of creating a persuasive message.” Source: Illinois High School teacher Source: Gallup USA Today Understanding Political Campaign Advertising IMPORTANT FACT Political ads are considered “free speech” and thus are not subject to any requirements that they “tell the truth” so, in effect, these ads contain many unsubstantiated claims Understanding Political Campaign Advertising “ The thing to remember about these ads is that they cost a fortune…and it raises the cost of campaigns, and the money (raised) comes overwhelmingly from the wealthiest handful of Americans.” Source: Media Critic Robert McChensey Primary Ad Spending IOWA Romney $7.9 M McCain 0 Clinton Obama SC FLORIDA OHIO $0.9M $0.45M $1.9M $2.3M $8.3 M $4.4M Source: Meet The Press, 8/3/08 Battleground States Colorado Nevada Iowa Ohio Michigan Pennsylvania Missouri Virginia North Dakota West Virginia New Hampshire Wisconsin New Mexico North Carolina Georgia SC TV Markets (ranked by size) # 26 Charlotte NC # 36 Greenville, Spartanburg, Asheville NC, Anderson 1,045,240 826,290 # 83 Columbia 377,940 # 97 Savannah GA 298,130 #100 Charleston 290,110 #105 Florence/Myrtle Beach 272,340 #114 Augusta GA 247,450 #136 Wilmington NC 174,170 Questioning the Message And The Messenger Media Literacy’s 5 Core Concepts All messages are constructed Messages are constructed using languages with their own set of rules Messages: values and points-of-view Different people see the same message differently Media: power and/or profit Questioning the Message And The Messenger Critical thinking/viewing questions Who created the message? (author) Why was it made? (purpose) For whose eyeballs? (audience) Using what methods/techniques? Who, what is omitted/why? Understanding Political Campaign Advertising the use of complementary colors (red, white and blue, for example) to promote a sense of patriotism props, such as desks, planes, podiums and people to connote action, power, authority and warmth symbols, such as children and flags to imply patriotism and caring Source: The People’s Choice: Digital Imagery and the Art of Persuasion Understanding Political Campaign Advertising certain types of clothing to connote strength or authority music and sound to provide a certain type of ambience or mood superimposed words to emphasize the speaker’s words code words to provoke reflexive, almost visceral, viewer reactions Source: The People’s Choice: Digital Imagery and the Art of Persuasion Understanding Political Campaign Advertising COLORS PROPS PEOPLE SYMBOLS CLOTHING MUSIC SUPERIMPOSED WORDS CODE WORDS Types of Political Ads Negative - One candidate portrays the other in an unfavorable light. Warm and Fuzzy - Candidates make the viewer feel good about the country or his/her campaign. Humorous - Candidates elicit a laugh or smile from the viewer. Types of Political Ads Scary - Candidates evoke images of fear (usually combined with a negative ad). Advocacy- advocates for/against an issue/person The Role of Media In Politics Ads Appeal to Emotions Not Intellect Techniques of Persuasion Testimonial Ad Techniques of Persuasion Transfer Techniques of Persuasion Appeals to Fear Types of Political Ads “Morning In America” Candidate: Ronald Reagan (R) Year: 1984 Types of Political Ads “Daisy” Candidate: Lyndon Johnson (D) Year: 1964 Types of Political Ads “Revolving Door” Candidate: George HW Bush (R) Year: 1988 Types of Political Ads “Bear In The Woods” Candidate: Ronald Reagan (R) Year: 1984 Types of Political Ads “3 AM” Candidate: Hillary Clinton (D) Year: 2008 Types of Political Ads “Country I Love” Candidate: Barack Obama (D) 2008 Techniques in Ads Music Clip courtesy Comedy Central With Jon Stewart Ad Watch/Fact-Reality Checks Source: New York Times/ June 20, 2008 Ad Watch/Fact-Reality Checks Ad Watch/Fact-Reality Checks Country I Love Wisconsin TV Station Reality Check News Segment Questions/Evaluations