Chapter 1
advertisement

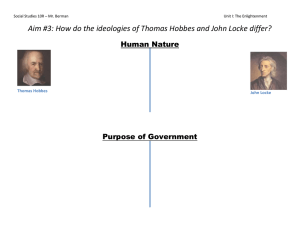
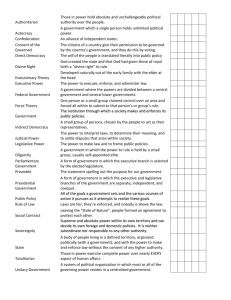
Chapter 1 The Political Landscape Where can this passage be found? When was it written? • We the people of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America. Some terminology.. • Government: a collective of individuals and institutions, the formal vehicles through which policies are made and affairs of state are conducted. • Citizens: by law, are members of the political community who by nature are entitled to all of the freedoms guaranteed by the government. • Politics: how policy decisions are made. What is the Government? • In exchange for our freedoms and guidance, the government expects us to obey the government, its laws and the constitution. • Citizens can support their government by joining the military, paying taxes, and voting. • Social Contract Functions of Government. • The Framers outlined key ideas over 200 years later! • People should be able to solve their own problems and make decisions once a simple mechanism, or vehicle was established. • The greatest debate our nation faces is over power. How much do the people have to give up to be guaranteed a comfortable level of security? – Freedom v. Order Establishing Justice! • One thing expected from governments is a system of laws for individuals to follow. Thus giving us: the Bill of Rights. • The Bill of Rights entitles people to a trial by jury, to know the charges against them, and to be tried in a courtroom presided over by an impartial judge. • Constitution Ensuring Domestic Tranquility. • The protect the people local governments have police forces and States have national guards. • After the September 11, 2001 attacks all governments took extraordinary measures to contain the threat of terrorism. • Department of Homeland Security: was created to coordinate U.S security. The most recent Department created (15/15) Providing for the Common Defense! • The framers did many things to help protect the United States from outside dangers – making the President of the United States the Commander in Chief of the armed forces. – Congress was also given the ability to raise an army in of times of need. Promoting the General Welfare • When the Framers added it to their list, it was more of an ideal than a mandate for government • Our views on what government should do have expanded over time. • Any government program providing aid (health care, Social Security income) Securing the Blessings of Liberty • In a free society people are free to criticize their government and even petition it when they disagree with it’s actions. Types of Governments… • Monarchy: government in which power is vested in hereditary kings and queens who govern in the interests of all. • Totalitarian: an economic system in which the government has total control over the economy. • Oligarchy: the right to participate is conditioned on the possession of wealth, social status, military position, or achievement. • Democracy: a system of government that gives power to the people, whether directly or through elected representatives. Ideology and the Scope of Government Social Contracts: • Social Contract: an agreement between the people and their government signifying their consent to be ruled. • What was the first Social Contract in America? – Mayflower Compact • Social Contract Theory: The belief that people are free and equal by God-given right and that this in turn requires that all people give their consent to be governed. (Locke and Hobbes) Thomas Hobbes (1588-1679) John Locke (1632-1704) Leviathan (1651) Second Treatise on Civil Government (1689) Both argue that all individual rights are free and equal by natural right. Also that all men and woman give their consent to be governed. • Argued that mans natural state is war. He theorized that a monarchy is necessary to restrain man’s bestial tendencies. • Warned life without government would be “solitary, poor, nasty, brutish, and short.” • Argues strongly that a single leader is needed to protect the rights of the people. Also that a mans fundamental right is property. • Said that people form governments to preserve life, liberty property and to ensure justice. Any of this sound familiar yet….? Hobbes and Locke Thomas Hobbes John Locke Hobbes, Locke, and Social Contract Theory • Hobbes argued for a single ruler • John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau saw the need for less centralized power • Colonists rejected a strong ruler upon declaring independence • Fled religious persecution, escaped a tyrant. Virginia House of Burgesses • Created in 1619, was the first representative assemble in North America. • The New England Town meetings today survive as an example of Direct Democracy: a system of government in which members of the polity meet to discuss all policy decisions and then agree to abide by majority rule. • Indirect Democracy: is a system of government that gives citizens the opportunity to vote for representatives who will work on their behalf. Republic! • A government rooted in the consent of the governed; a representative or indirect democracy. American Political Culture and the Characteristics of American Democracy • Political Culture: commonly shared attitudes, beliefs, and core values about how government should operate. • American political culture emphasizes the values of: personal liberty, equality, popular consent and majority rule, popular sovereignty, civil society and individualism. Personal Liberty.. • One of the most important characteristics of American democracy, personal liberty is defined as: Initially meaning freedom from governmental interference, today it includes demands for freedom to engage in practices free from governmental discrimination. (Political) Equality! • A second key characteristic of our democracy. • While some individuals clearly have more political pull than others, the adage “one person, one vote” implies a sense of political equality for all. • Equal protection under laws (14th Amendment) Popular Consent and Majority Rule • Popular Consent: the idea that government must draw their powers from the consent of the governed. • Majority rule: the central premise of direct democracy in which only policies that collectively garner the support of a majority of voters will be made into law. • It should also be mentioned that the Bill of Rights is an example of the importance to protect minority rights. Popular Sovereignty.. • Popular Sovereignty: The right of the majority to govern themselves. – Although not widely used until pre-civil war times, popular sovereignty is an idea found widely in our constitution. It is considered a natural law. • Natural Law: a doctrine that society should be governed by certain ethical principles that are part of nature and as such, can be understood by reason. The Changing Characteristics of the American People • Differences in Americans are what make up the political conflicts among the electorate. • A changing population size is America’s biggest changing characteristic. As of 2005 there were more than 293 million Americans! • As a result of this growth, many Americans feel far removed from their government. Cont’d. • Just as the diversity America is changing, the average age of American’s is increasing. • “Graying of America”- The U.S. population is getting older • How does average age affect policies implemented? –well, consider Florida. Most of Florida’s population is 65+, making policies • like social security a much larger issue to them than, let’s say, public • schools. Ideology of the American People • Political Ideology: the coherent set of values and beliefs about the purpose and scope of government held by groups and individuals. • In general, conservatives tend to identify with the Republican Party while liberals usually identify with the Democratic Party. The Concepts of Freedom, Order, and Equality • Freedom is used in two major senses: – Freedom of: the absence of constraints on behavior - freedom to do something (liberty) – Freedom from: immunity from fear and want; the fight against exploitation and oppression. Conservatives: • Conservative: one thought to believe that government is best that governs least and that big government can only infringe on individual, personal, and economic rights. • Less centralized government. • Oppose abortion • Oppose gun control laws • Oppose environmental regulations • Oppose social welfare programs Liberals: • Liberal: one considered to favor extensive governmental involvement in the economy and the provision of social services and to take an activist role in protecting the rights of women, the elderly, minorities, and the environment. • Favor more governmental involvement in general • Favor abortion rights • Favor environmental regulation • Favor gun control laws • Favor social welfare programs Libertarians: • Libertarian: one who favors a free market economy and no governmental interference in personal liberties – Favor abortion rights – Oppose environmental regulation – Oppose gun control laws – Oppose social welfare programs Problems With Political Labels • Labels can be misleading • More people consider themselves moderate, tend to vote for the best candidate or issues • Party Polarization: the tendency of the Democratic and Republican parties to be divisively separated by issues and ideas. – issues tend to separate (polarize) the parties further from the moderate stance Current attitudes towards Government • High Expectations – Expectations have changed as a result of major crises • Great Depression: people began to look to government for relief • Politicians promises • Has led to a decreasing faith in government Current attitudes towards Government • Voter Apathy: Voters do not care, have little interest or concern regarding government – Can influence political efficacy, the belief that one can make a difference in politics through acting politically. • Lack of perceived qualified candidates, lack real choices