Judaism Review Notes

JUDAISM
Beginning around the year 2000
BCE
DO NOW: ACROSTIC POEM
In your do now section on a piece of loose-leaf, but today’s date at the top of the page. Next, write the word “JUDAISM” vertically down your page. Come up with a word or phrase that starts with each letter of the word Judaism. Your information should be based on 2.3 and our activity on Friday. Be creative
I
A
S
M
J
U
D
STATION 1: OPEN-NOTE QUIZ
This was the standard quiz; 5 questions worth a total of
20 points
*That may vary a little time to time*
Partial credit is offered
For more difficult questions, I expect you to provide as much detail as you can
Use your best judgment, did you answer the question fully?
STATION 2: CENTRAL BELIEFS
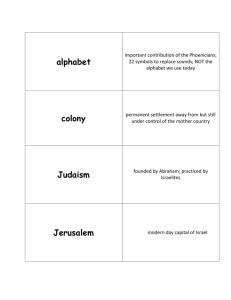
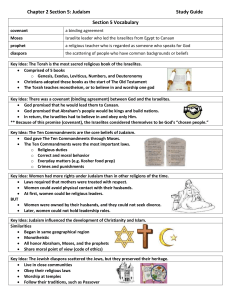
1) Belief in one God: this monotheistic belief was the most important characteristic of Judaism, standing out from the surrounding, polytheistic regions (1 st monotheism)
2) Justice and Righteousness: these moral codes would guide Jewish way of life and influence future religions to come. This also differed from some polytheistic religions that lacked a moral component
3) Obedience to the Law: Jewish law is extremely important. This adds to the idea that Judaism is a way of life and a very involved religion. The 10 Commandments are the most important laws with others dealing with food, such as eating only kosher food.
4) Jewish Sacred Texts: The most important of these are the Torah. The other parts of the Hebrew Bible are the Prophets and the Writings. The Talmud was written later and offers important interpretations. These texts provide unity.
Map
CHRONOLOGY
Check your notes and fix as we go!
If you would like to redo it as we go so that you have more room for notes, just start on a piece of loose-leaf
GOD MAKES A COVENANT WITH ABRAHAM
This was the solemn promise that God would deliver Abraham to a “Promised Land” and that his descendants would be many if he turned to monotheism
The idea of a covenant, or promise, is central to Judaism.
Represents how each side, God and the Jewish people, have rights and obligations to each other
Different from most religions of the time that are centered around unpredictable and temperamental gods with no promises
ABRAHAM LEAVES UR
God came to Abram and told him to make a journey
Abraham had to abandon his polytheistic beliefs and commit his life to the worship of 1 God
Believed that his father, was an idol merchant
Abraham and his wife, Sarah, have a son named Isaac and Isaac has a son named Jacob
ABRAHAM GOES TO CANAAN
Abraham accepts the covenant, adopts this monotheistic view, and heads to
Canaan
JACOB HAS 12 SONS
Jacob is the son of Isaac, who is the son of Abraham. They are known as patriarchs (or fathers)
Jacob is given the name Israel
*usually meaning “who prevails with
God”
Jacob’s 12 sons create the 12
Tribes of Israel
THE ISRAELITES GO TO EGYPT
A famine causes the
Israelites to search for more resources, many try Egypt
The pharaoh feels threatened by the presence of a large, new cultural group
MOSES LEADS THE ISRAELITES OUT OF EGYPT/
THE EXODUS
The Israelites were enslaved in Egypt and forced to work for the pharaoh
According to the Torah, Moses would lead the Israelites out of
Egypt. He was said to have been born an Israelite, but raised in pharaoh’s palace
The Torah says that God sent plagues to scare pharaoh into releasing the Israelites.
THE 10 COMMANDMENTS
After wandering for year,
Moses received the 10
Commandments from God on top of Mt. Sinai according to the Torah
These laws will come to structure not only Judaism, but future monotheistic religions
ISRAEL IS GOVERNED BY THE JUDGES
Instead of a centralized government, Israel organized underneath local judges
One of the most effective was Deborah
She is seen as a warrior and a strong female figure
ISRAEL NAMES SAUL KING
1st King of united Israel
Had some military successes, but overall was a jealous and weak ruler
David, his successor, was a beloved king of Israel
Solomon, David’s son, would continue the dynasty. The
Kingdom reached its peak under his leadership
BABYLONIAN CAPTIVITY
After the death of Solomon, the question of succession split Israel in half
The 10 tribes in the north formed Israel, the 2 tribes of the south formed Judah
The Assyrians attacked in 722 BCE and scattered the people of
Israel
The Chaldeans destroyed Judah in 586 BCE along with Solomon’s
Temple
They brought many Jews with them as slaves back to Babylon
DIASPORA
Babylonian Captivity was the start of Jewish diaspora, the scattering of the Jews outside of
Judah
This would spread the culture and influence of the Jews farther than ever before
People of Jewish descent would cling to their religion in order to preserve their unique identity while being removed from their “Promised Land”
STATION 5: MIMERY!
Put in order of followers from most to least
• Taoism
• Hinduism
• Christianity
• Buddhism
• Confucianism
• Islam
• Judaism
• Jainism
Followers
• Christianity-2.1 billion
• Islam-1.3-1.5 billion
• Hinduism-800-900 million
• Buddhism-376 million
• Judaism-13-14 million
• Confucianism-6.3 million
• Jainism-4.3 million
• Taoism-2.3 million
Put in chronological order of earliest to latest
• Hinduism
• Christianity
• Islam
• Judaism
• Buddhism
• http://www.newspadho.com/2015/07/animated-mapshows-how-religions-spread-around-the-world.html
• Hinduism-date difficult to determine, but oldest religion
• Judaism-2,000 BC
• Buddhism-500 BC
• Christianity-30 C.E.
• Islam-600’s C.E.