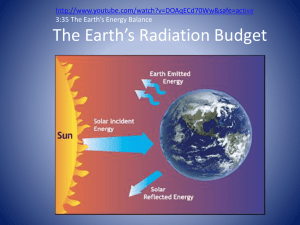
weather - Port Washington School
advertisement

Do Now: Focused Free Write Look at the bottle of clear solution on my desk, what do you think it is? Does it have ENERGY? Do Now: Take a lab from the Do Now Desk Get into your groups from last time! Get that data! Do Now: Copy HW & Lab Pass UP -Pass up Water Shoe box lab Monday: No HW Tuesday: Energy Homework Wednesday: Energy Transfer Practice Question in Packet on Page 7 Thursday: Specific Heat WS Friday: No Homework Extra Help: Thursday Morning Unit 1: ENERGY Stop Monkey-N-ing around and Go Green already! P.S. I’m Mookie the Monkey 4 What is ENERGY? Energy is the ability to do Work _______ 5 Work occurs when a force _____ causes an move in object to _____ the same direction as the force. 6 FORMS OF ENERGY Both basic states of energy, Kinetic and potential, can exist in many forms! THERMAL (HEAT) The totalKinetic ________ energy of the particles in matter. (molecular motion) 9 SOUND A type of mechanical energy. It is the energy produced when objects vibrate ________. Ex: tuning 10 MECHANICAL Energy with which moving ______ objects perform work. Ex: Wind, flowing water, using a hammer 11 ELECTRICITY A form of energy produced by themovement ________ ofelectrons ________ 12 CHEMICAL Energy STORED in chemicalbonds ____ that can be released. Ex: food, fossil fuels, battery 13 STORED MECHANICAL ENERGY: Stored energy due to a change in the shape of an object. Ex: A stretched rubber band _______________ 14 STORED MECHANICAL ENERGY: 15 LIGHT radiant A form of _______ energy that moves in a wave ______. Ex: lamp, stars 16 SOLAR ENERGY All forms of energy that SUN come from the ______. 17 NUCLEAR Energy STORED in nucleus the ________ (center) of an atom. Ex: nuclear bombs 18 GEOTHERMAL (HEAT) Heat energy STORED Earth Ex: within the _____. Volcanic eruptions, geysers 19 All forms of energy can be classified as Kinetic or potential. The two basic states of energy. So, what’s the difference? 20 POTENTIAL ENERGY 1) Potential energy is stored energy due to and object’s Position _____________ 24 POTENTIAL ENERGY 2) An object that is lifted from its position on Earth hasgravitational __________ potential Energy which depends on height and mass ______ 25 POTENTIAL ENERGY 3) Massive objects have more _____ potential energy than less massive objects 26 POTENTIAL ENERGY 4) An object at a higher elevation will have more _____ potential energy than an object at a lower elevation 27 Do Now Pass up procedure for your signed test Take out Homework Complete worksheet on Do Now desk KINETIC ENERGY 1) Kinetic is energy of ___________ Motion 29 KINETIC ENERGY 2) Kinetic depends MASS on the _____ and theSPEED _______ of an object. 30 KINETIC ENERGY 3) Faster objects have More ____ kinetic energy than slower objects. 31 REVIEW QUESTONS: WHICH SKIIER HAS THE GREATEST KINETIC ENERGY? A B D C WHICH SKIIER HAS THE GREATEST POTENTIAL ENERGY? A B D C ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS Do you remember the LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS AND ENERGY? 34 Law of Conservation of ENERGY: (same for mass) Can’t be made Mass/ NRG ____________ Mass/ NRG ______________ Can’t be destroyed Mass/ Energy can only __________ Change form!!! DURING ENERGY CHANGES, IF ONE BODYIS LOSING ENERGY, Gaining ENERGY: THE OTHER IS _______ THE WAVE LOSES ENERGY: THE SAND GAINS ENERGY DURING ENERGY CHANGES, IF ONE BODYIS LOSING ENERGY THE OTHER IS GAINING ENERGY: THE WAVE LOSES ENERGY: THE SAND GAINS ENERGY DURING ENERGY CHANGES THE TOTAL ENERGY REMAINS THE SAME ENERGY ALWAYS FLOWS FROM HIGH TO LOW (source to sink) THE ENERGY WILL FLOW FROM: THE FLAME TO THE FINGER ENERGY WILL FLOW FROM ICE THE FINGER TO THE ICE THE LIQUID LOSES ENERGY AS THE ICE GAINS ENERGY WHEN WILL THE EXCHANGE OF ENERGY STOP? WHEN EQUILIBRIUM IS REACHED THE LIQUID AND THE ICE REACH THE SAME TEMPERATURE UNUSABLE ENERGY: Very often during the energy transformation process, some heat ____ energy is produced due to friction. This is wasted energy and is lost to the environment. 43 ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS Example: A television changes electrical NRG into light and sound NRG 44 ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS 45 Do Now Turn to page 7 in your note packet Take out “Energy HW” Method’s of NRG transfer Convection 1. __________________: Heated air rises through earth’s atmosphere. Conduction 2. __________________: An ice cube melts when dropped into a glass of warm water. Radiation 3. __________________: Light leaves the sun and 8 minutes later strikes earth. Conduction 4. __________________: You burn you tongue eating hot pizza. Convection 5. __________________: Hot magma rises inside earth’s mantle, cool, and sinks. Radiation 6. __________________: A microwave oven heats soup. Convection 7. __________________: A fireplace warming a room. 28 A 26 26 26 24 23 26 24 23 24 B 22 25 Methods of Energy Transfer Energy moves from regions of high _________ concentration to ________ low concentrations of energy. 52 Source _______ To sink _______ There are 3 methods of Energy Transfer Radiation ConDuction ConVection ConDuction Explanation of Transfer Direct contact (touch) Molecule To Molecule -Conduction is a form of heat transfer by contact of direct _______ molecules 57 Best Medium for energy transfer -Conduction occurs solids fastest in _______ 58 metals -_______ are the best conductors of he heat energy. 59 Examples Touching a hot surface Electricity Do Now Take a Conduction lab & read: Con ection Explanation of Transfer Energy transfer Due to Density differences -Convection is a form of heat transfer that occurs by up and down motions of a fluid _______ due to differences in ______ density 64 Best Medium for energy transfer fluids -occurs ONLY in _____ which are liquids and gases! 65 Examples Hot air or water rising Volcanoes Lava lamp convection Radiatio Explanation of Transfer Electromagnetic (EM) waves that move Through a vacuum (empty space) -radiation is the transfer waves of heat in _____. 70 -Electromagnetic radiation travels at the speed of ______. light 71 Best Medium for energy transfer No medium needed Examples Gamma X-rays UV Visible Infrared Microwave radio Do Now: Name that type of heat transfer! Convection! Conduction! Radiation! 74 Do Now: Focused Free Write (No HW tonight) What is different about how each of the three popcorns? How were they made? Explain! Do Now: In which direction does the air move? 28 A 26 26 26 24 23 26 24 23 24 B 22 25 Do Now: In which direction does the energy move? 28 A 26 26 26 24 23 26 24 23 24 B 22 25 Do Now: What will heat up faster 1. Or 2. Or 3. Or HEAT NOTES 1. HEAT: the energy of particles moving __________ 81 HEAT NOTES 2. HOT OBJECTS more contain __________ heat than cold ones 82 HEAT NOTES 3. All objects above Absolute zero contain __________ heat 83 HEAT NOTES 4. Heat always flows hotter objects from ______ to ______ cooler objects until the objects same reach _____ temperature. 84 HEAT NOTES 5. The greater the difference in temperature between the two objects, the faster heat is _________ transferred. 85 HOW IS HEAT TRANSFERRED BETWEEN OBJECTS? 86 Heat Transfer at Work Name that type of heat transfer! Conduction! Radiation! Convection! 88 Do Now Read the article about Latent Heat while I set up the Demo I will collect both labs tomorrow! Tomorrow report to large computer room in the Library Heat Transfer across the globe http://www.classzone.com/b ooks/earth_science/terc/con tent/visualizations/es1705/e s1705page01.cfm Do Now: HW on Desk Take a Lab from Do Now desk Reflect on these two questions: 1) Would it take more energy to raise 5 g of water 5ºC or 20ºC? 2) Would it take more energy to raise 5 grams of water 10ºC or 100 grams of water 10ºC Specific Heat Quantity of heat needed to raise One gram of any Substance by 1 degree Celsius Specific Heat The higher the Specific heat… The more energy is needed to raise the temperature Measuring Specific Heat Energy can be measures in many different ways. Typical units include: Joules ____________________, Watts _________________, & calories ___________________ The term “Joule” is named after English Scientist James Prescott Joule who lived from 1818 to 1889. He discovered that Heat is a type of Energy! 1,000 joules =1 kilojoule = 1 Btu Do Now! Read the did you know and complete practice questions 1-10! 1. What substance has the highest specific heat?Use your Reference Tables Liquid water 4.18 Joules/gramºC 2. Why do metals have low specific heats? They are solid 3. Why are pans made of metals with low specific ? heats Because metals are good Conductors And have low specific heats. Therefore they will heat up quickly and cook your food faster. 4. Which would Take more energy to raise its Temperature, water Or land? water 5. Which would Heat up and cool off Faster, land or water? land Water (liquid) = 4.18 Iron (Fe) = 0.45 Copper (Cu) = 0.38 6. Which of these three substances will heat up fastest? Copper because it has the lowest specific heat Do Now: 1) Describe the energy exchange occurs when liquid water at 0°C turns to ice at 0°C? a. The water loses energy b. The air around the water loses energy c. The ice gains energy. d. The air and the water both gain energy. 2) As heat energy is added to an open container of boiling water, the temperature of the boiling water will.. a. decrease b. increase c. remain the same 7. Which material would require the greatest amount of heat energy to raise its temperature from 50C to 100 C? A. B. C. D. 10 10 10 10 grams grams grams grams of of of of granite ice lead iron 8. Which pan would you use if you wanted to cook your food quickly? copper Cp = 0.38 iron Cp = 0.45 9. Which material would require the greatest amount of heat energy to raise its temperature from 50C to 100 C? A. B. C. D. granite ice lead iron 10. Calculate how many joules would be required to raise 3 grams of water from 50 C to 65 C. 3g x15 ˚C x 4.18 J =188.1j g˚C Do Now: Copy HW & Green house ditto on desk -Pass up Phase change lab Monday: Study for exam Tuesday: Review book read pages 105 to 109 Answer Questions 11-31 on page 110 Wednesday: Review Book read pages 116 to 118 Questions 39 to 48 on 119 Thursday: Insolation Worksheet Friday: No HW Do Now: Take out review sheet Do Now: Copy HW & Lab Pass UP -Pass up signed progress report Monday: Specific Heat HW Tuesday: Electromagnetic Spectrum HW Wednesday: Electromagnetic Spectrum WS #1 Thursday: Wave WS & Study Friday: Quiz Today Extra Help: Tuesday Morning Do Now: Focused Free Write What is different about how each of the three popcorns? How were they made? Explain! Do Now: -Take a lab from the do now desk -Take out last night’s HW -Complete the FOCUSED FREE WRITE on the front page of the lab: Which spoon would heat up faster when placed in a bowl of very hot soup, a wooden spoon or a metal spoon? Explain your answer in terms of specific heat, which spoon has the lower specific heat and why? Take out your concept map and reading from last nights homework Heat Transfer through radiation Lab Find the symbol on the Top right corner of your Lab. Time to get in Lab Groups, Listen for directions.. Directions: -You will work in groups of four to complete this Lab. -If your paper has an “A” in the top right corner, you and your partner will be monitoring the SAND AND WATER cups. -If your paper has a “B” in the top right corner, you and your partner will be monitoring the BLACK AND SILVER cans. -Both groups are responsible for both sets of data so it is important to communicate to each other. Make a Prediction In the space provided on your lab, predict what which cup will heat up fastest, the cup of sand or the cup of water? Explain your choice! Make a Prediction In the space provided on your lab, predict what which cup will heat up fastest, the black cup or the silver cup? Explain your choice! Prepare to Begin - One partner is responsible for turning on the heat lamp - The other partner should take a temperature reading for each cup for time 0 in Degrees Celsius Quick! Record Time 0 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 1. Examine the lamp, what type of electromagnetic energy is the lamp producing? Two Minute Timer Quick! Record Time 2 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 2. Define the word: specific heat Two Minute Timer Quick! Record Time 4 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 3. What is the method of energy transfer responsible for the heat transfer between the lamp and the cans? Two Minute Timer Quick! Record Time 6 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 4. Look at the data for sand and water which cup is heating up faster? Two Minute Timer Quick! Record Time 8 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 5. Note which can is getting hotter faster, the black can or the silver can. Explain the data in your own words. Two Minute Timer Without disturbing the positions of the cans, TURN OFF THE LAMP and MOVE IT AWAY FROM THE CANS/CUPS Half Way Done!!! Quick! Record Time 10 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 6. Note which cup is hotter: The sand or the water. Based on this compare the density of the air over the sand to the density of the air over the water. Two Minute Timer Quick! Record Time 12 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 7. Explain why the black can appears black based on last nights reading. Two Minute Timer Quick! Record Time 14 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 8. Look at the data for sand and water which cup is cooling down up faster? Two Minute Timer Quick! Record Time 16 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 9. Relate this experiment to real life. What type of surface on earth could be represented the silver can? The black can? Two Minute Timer Quick! Record Time 18 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 10. Compare your answers to questions 6 and 8, complete this sentence: “Good Absorbers are also good… _______________” Two Minute Timer Quick! Record Time 20 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 11. Texture also plays a key role in the absorption of heat energy. Compare a rough surface and a smooth surface, which one will absorb more energy and why? Two Minute Timer Quick! Record Time 22 for your set up - Trade data Answer this question: 12. By 3:00 P.M. on a summer day would the air be cooler over ocean or land? Two Minute Timer Graph your data before you answer the questions!!!! Conclusion: Write a short paragraph summarizing your understanding of the interaction between radiation and earth’s different surfaces. Use at least five of vocabulary words of these vocabulary words: Electromagnetic spectrum, visible light, prism, ozone, absorption, reflection, temperature, specific heat, reradiation, and infrared radiation. Do Now: HW on Desk -Pass up procedure for 3D topo lab - Reflect on these two questions: 1) Would it take more energy to raise 5 g of water 5ºC or 20ºC? 2) Would it take more energy to raise 5 grams of water 10ºC or 100 grams of water 10ºC Do Now: Calculate the amount of energy in joules required to raise the temperature of 5 grams of granite from 82º C degrees to 100º C PHASES OF Matter: Matter is anything made of atoms and molecules. A) SOLID B) LIQUID C) GAS Solid Liquid Gas Motion (Kinetic energy) Little K.E. Molecules vibrate More K.E. Molecules move freely Most K.E. Molecules move fast How is it bonded? Does it have Volume? A definite shape? Strong yes yes Not bonded rigidly no yes Not bonded no no What are the changes of phase called? MELTING solid liquid FREEZING VAPORIZATION liquid gas CONDENSATION 2. ENERGY IS RELEASED (lost) DURING: FREEZING SOLID LIQUID CONDENSATION LIQUID GAS from higher K.E. to lower K.E. 3. ENERGY IS ABSORBED (gained) DURING: SOLID MELTING LIQUID VAPORIZATION LIQUID GAS from lower K.ETo higher K.E. Do Now -Take out lab, pass up procedure Energy stored during a phase change is called Latent heat __________________ No change in temperature 149 TAKE OUT YOUR EARTH SCIENCE REFERENCE TABLES 150 (Earth Science Reference Tables : front page) Properties of Water Heating Curve of Water VAPORIZATION 100 STEAM temp 0C 0 CONDENSATION MELT FREEZE WATER ICE HEAT ENERGY ADDED (Joules) Do Now: -Take out sheet from do now desk and complete, this replaces yesterdays there was a typo -Take out Homework Problem 1 : Does temperature change during a phase change? ___________ NO!!!! Explain: The energy gained by boiling water or melting ice is stored as latent heat. Likewise this latent heat is released to the environment during condensation and freezing. This absorbed or released heat is used to change the phase not the temperature. Problem 2: How many Joules of heat energy must be added to 20 grams of ice at 0oC to melt it completely to liquid water at 0oC? Show All work.: P∆= LH x Mass P∆= 334J/g x 20g P∆= 6680 J 3. The most energy is released during which phase change condensation 4: The most energy is absorbed during which phase change: Vaporization 5. Which phase has the most K.E.? GAS (STEAM) Problem 6: How many joules of heat (Q) energy must be added to 35 grams of liquid water to change the temperature from 10oC to 100oC water vapor? Is this a phase change problem or specific heat? Specific Heat (C) Q= C x Mass x T∆ Q= 4.18J/g°C x 35g x 90°C Q= 13167 J Problem 7 : How many joules of heat energy must be added to 35 grams to change liquid water at 100oC to water vapor at 100oC? Is this a phase change problem or specific heat? Phase Change (LH) P∆= LH x Mass P∆= 2260 J/g x 35g P∆= 79100 J Problem 8: How many Joules of heat energy must be added to 35 grams of water vapor to change its temperature from 100oC to 145oC? Show all work. Is this a phase change problem or specific heat? Specific Heat (C) Q= C x Mass x T∆ Q= 2.00 J/g°C x 35g x 45°C Q= 3150 J Problem 9: How many Joules of heat energy must be added to 35 grams of ice to change the temperature from 10oC to 145oC water vapor? How many steps are in this problem? Show All work. MELTING / FREEZING E EARTH SCIENCE REFERENCE TABLE: Energy is absorbed + 334 J/gram 00 C - 334 J/gram Energy is released 00 C VAPORIZATION/ CONDENSATION Energy is absorbed +2260 J/g 1000 C -2260 J/g Energy is released 1000 C -Quiz is still Friday… will cover everything up to the greenhouse effect. More details tomorrow. -No lunch club today, sorry! -Single period exam on Tuesday on Entire Energy Packet Do Now Test is moved to Tuesday Do Now Worksheet on Desk Extra-help on Monday after school Pass-up Procedure for phase change lab Take out Mookie the Monkey Note-packet The Earth is always trying to achieve Equilibrium Energy is constantly being re-distributed flowing from source to sink The Earth Receives Energy from two sources: SUN Radioactive Energy CORE All matter radiates some Electromagnetic _____________ Energy _____________ The sun emits energy ALL wavelengths in _____ of the electromagnetic spectrum. Read about the Electromagnetic Spectrum. ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM: REFERENCE TABLE PAGE 14 10-10 gamma 10-8 10-6 10-4 X ray 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 Microwaves Ultra violet Infrared Radio waves Increasingwavelength ecreasingwavelength visible Violet Blue Green Yellow Orange Red 4 Each type of energy differs wavelength __________ in its 10-10 gamma 10-8 10-6 10-4 X ray 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 Microwaves Ultra violet Infrared Radio waves Increasingwavelength ecreasingwavelength visible Violet Blue Green Yellow Orange Red 4 Read about Waves! A wavelength is the distance between two crests of the wave. Frequency is defined as a number of cycles per unit time. 1. Explain the diagram above in no more than 3 sentences: ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ 2. Which types of electromagnetic energy have the greatest and least amount of energy? (Highest temperatures vs. lowest temperatures) ___________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 3. How are the different types of electromagnetic energy distinguished from one another? ___________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 4. What types of electromagnetic energy are between Microwaves and X-Rays? ___________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Explain how Gamma Rays and X-Rays are different and similar? ___________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 6. Why do you think you wear a lead shield when you have an X-Ray? ___________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 7. Based on the electromagnetic spectrum why do you think UV rays are dangerous to human health? ___________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ The Sun gives off light VISIBLE and heat in the form of _________________ and UV __________________ electromagnetic energy. However, the short wavelengths (dangerous UV radiation) are mostly GAMMA absorbed by the ozone so they don’t reach OZONE earth’s surface The Ozone layer is found in thestratosphere _________________ layer of the atmosphere. 10-10 gamma 10-8 10-6 10-4 X ray 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 Microwaves Ultra violet Infrared Radio waves Increasingwavelength ecreasingwavelength visible Violet Blue Green Yellow Orange Red 4 SHORT WAVE LENGTHS ARE MOSTLY ABSORBED by THE OZONE IN THE STRATOSPHERE gamma, x-rays, UV OZONE This energy is absorbed by Earth’s surface, which in turn reradiates the energy in the form of heat called infrared ________________ radiation OZONE VISIBLE LIGHT : PASSES THROUGH THE ATMOSPHERE WITH THE GREATEST INTENSITY Sun emits all Infrared: Heat energy that Earth re-radiates wavelengths 10-10 gamma 10-8 10-6 10-4 X ray 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 Microwaves Ultra violet Infrared Radio waves Increasingwavelength ecreasingwavelength visible Violet Blue Green Yellow Orange Red 4 How does too Much CO2 contribute to Global warming? H20 CO2 VAPOR INFRARED METHANE GAS CO2 absorbs infrared Do Now: Take a sheet from the do now desk. -This is the answer key to the review packet handed out the first day of energy -Focused Free Write: Is temperature a measure of heat energy? Interactions between Electromagnetic Energy & The Environment: 1. ABSORBTION - UV ABSORBED by OZONE IN STRATOSPHERE 2&H2O vapor INFRARED ABSORBED BY CO methane, nitrous oxide 2. REFLECTION - BY CLOUDS, ICE, SNOW & WATER 3. SCATTERING - BY AEROSOLS, WATER DROPLETS, ICE CRYSTALS, AIR POLLUTANTS, DUST, POLLEN 4. LIGHT IS BENT AS IT REFRACTION MOVES THROUGH VARIED DENSITIES 5. TRANSMISSION WHEN ENERGY PASSES THROUGH A MEDIUM Do Now: Turn to page 15 in your note packet, start filling in the blanks 1. ABSORPTION 2. REFLECTION 3.SCATTERING 4. REFRACTION 5. TRANSMISSION Less than half of the ______ incoming solar radiation is received by the Earth’s surface Do Now Ditto On Do Now Desk Sit Quietly in your Assigned seats Take out HW Worksheet Smile its Friday! Surface properties of the Earth and Absorption of Energy: Reflection vs. Absorption & Radiation Color: Light (white) reflects dark (black) absorbs Texture: Rough surface absorbs smooth surface reflects Absorption Good absorbers are also good re-radiators. What type of surface is the best absorber? –Dark –Rough Pavement warms before grassy lawns. What type of surface is the best reflector of radiation? –Light –Shiny –Flat Snow and Ice reflect insolation and remain cold. ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM: LAB 10-10 gamma 10-8 10-6 10-4 X ray 10-2 10 0 10 2 10 Microwaves Ultra violet Infrared Radio waves Increasingwavelength ecreasingwavelength visible Violet Blue Green Yellow Orange Red 4 Spectroscope Lab Do Now on Desk Aim: Greenhouse Effect Phase change lab due tomorrow Review Packet due tomorrow Energy Exam next Tuesday Extra Help Today After School Greenhouse Effect Short wavelength visible light enters the greenhouse, is absorbed, then re-radiated as longer wavelength infrared (heat). The glass traps the infrared. What is Global Warming? increase in An ___________ the Earth’s Average surface air temperature THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT 204 THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT HEAT IS TRAPPED BY THE GLASS OF THE GREENHOUSE Incoming is Short wave Ex: Visible light outgoing is Longer wave Infrared Energy absorbed 205 Short wave radiation like ___________ Visible light passes through the glass of a greenhouse and is absorbed by _______________ the objects inside the greenhouse. 206 These objects reradiate __________________ the energy as ____________________ infrared Long Wave Radiation , which get reflected back into the greenhouse and warms the air. 207 In Earth’s atmosphere, there are many gases that act like the glass of a greenhouse and trap ________ long-wave radiation, keeping it in the Earth’s Atmosphere. These are known as… 208 Greenhouse Gases! 209 Greenhouse Effect CO2and H2O absorb infrared that is re-radiated from the surface of the Earth. Therefore, holding that heat in the atmosphere and raising the global temperature. What are the Greenhouse gases? H20 METHANE GAS VAPOR CO2 INFRARED Ozone CFCs Without some greenhouse gases, the Earth would cold be too _____________ for us to survive. But an overload of greenhouse gases creates a problem as well! How does too Much CO2 contribute to Global warming? H20 CO2 VAPOR INFRARED METHANE GAS CO2 absorbs infrared Greenhouse Effect What human activities contribute to CO2 production and an increase in the greenhouse effect? –Burning of fossil fuels –Global deforestation If present trends continue possible effects may include Rising sea levels due to melting polar ice caps; Increasing frequency and severity of storms and hurricanes; More frequent heat waves and droughts; and Relocation of major crop growing areas. Which of the following best represents the type of energy received by the Earth and the re-emitted by the Earth? A B c Which of the following best represents the type of energy received by the Earth and the re-emitted by the Earth? A B c WHICH TYPE OF ENERGY IS REPRESENTED BY THE RADIATION AT B? A) INSOLATION C) VISIBLE LIGHT B) ULTRAVIOLET D) INFRARED ENERGY B A WHICH TYPE OF ENERGY IS REPRESENTED BY THE RADIATION AT B? A) INSOLATION C) VISIBLE LIGHT B) ULTRAVIOLET D) INFRARED ENERGY B A What is a NON-RENEWABLE RESOURCE? An energy resource that is Being used faster __________________ than Earth Produces __________________ it . ___ 220 What is a NON-RENEWABLE RESOURCE? Examples: Fossil Fuels, minerals __________________ 221 What is a NON-RENEWABLE RESOURCE? To make our nonrenewable resources last longer we can Reduce __________________ Reuse __________________ Recycle . _________ 222 What is a RENEWABLE RESOURCE? An energy resource that is Earth supplies faster __________________ than we use it __________________ “unlimited” ___. 223 What is a RENEWABLE RESOURCE? Examples: Solar, wind, biomass __________________ (trees etc..) _____________ 224 What is a RENEWABLE RESOURCE? A renewable resource produces less _________ pollution (substance that can harm living things and/or the environment 225 Look at the pie graph!!! Only 7% of our energy consumption is from renewable resources!!! Try to make little changes in your life to reduce your dependence on NonRenewable Resources! What do you plan to do?