Chapter 19 Section 1 Review Page 474
advertisement

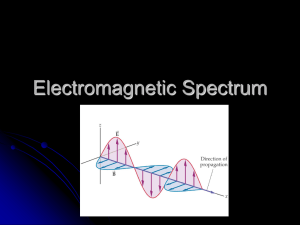
Chapter 22 Section 2 Review Page 560 Earth’s Atmosphere 1. Explain how radiant energy reaches Earth. • Radiation from the sun travels through space in the form of electromagnetic waves. 2. List and describe the types of electromagnetic waves. • Long wavelength: TV/radio waves, microwave, infrared, and visible light • Short wavelength: UV rays, X rays, Gamma Rays Electromagnetic Spectrum 3. Describe how gases and particles in the atmosphere interact with light rays. • Nitrogen, oxygen, and ozone in the upper atmosphere absorbs most short wavelength radiation • CO2 and water vapor absorb infrared radiation in the lower atmosphere. • About 50% of visible light reaches Earth’s surface. Clouds, particulates and gases scatter and reflect much of the light. Formation of OZONE 4. Describe how visible light and infrared energy warm Earth. • Infrared and visible light that reach Earth’s surface are absorbed. Heated surfaces radiate heat back into the air where greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat. Infrared radiation Infrared Images 5. Explain how variations in intensity of sunlight can cause temperature differences on Earth’s surface. • Concentrated sunlight at the equator makes the surface hotter and at higher latitudes where sunlight is spread over a larger area the surface is cooler. 6. You decide not to be outside during the hottest hours of a summer day. When will the hottest hours probably be? How do you know? • The hottest hours will probably be in the late afternoon when Earth’s surface has had time to absorb and reradiate energy. This is also when convection reaches its peak. • The End??? “You should have seen the one that got away”