File - Mrs. Johnson's Social Studies Page
advertisement

EQ
How do Hinduism and Buddhism compare and
contrast? 7.1.spi.3 Compare and contrast the
tenets of the five major world religions.
Activator
Because students just covered standards about the world’s five major faiths in sixth grade, have students create
a T-Chart on scrap paper of what they remember about Hinduism and Buddhism. Give 1 minute. After 1 minute,
allow students to give one, get one for 1 min. Share as a class and make a master list.
Teaching
Strategies
G/O- complete graphic organizer from previous lesson.
Read text p 626-628
View United Streaming video, Hinduism (28:00)
Have students add to their World Religion Graphic Organizer.
AP#1 Question and Answer: Each student should use their notes to quiz their partner over the knowledge
covered about Hinduism.
Read text p. 628-629, 641-642, 665
View United Streaming video, Making of a Monk (14:00)
Have students add to their World Religion Graphic Organizer
AP#2 Think/pair/share: How are Hinduism and Buddhism similar? How are they different?
• Have the students work in small groups to read India: Land of Many Faiths, Jr. Scholastic Article, December
2004. (Orren has this)
•Students will answer questions 1 – 10 at the end of the article (each must turn in their own paper.)
AP#3 Think & record: Using various slides with characteristics of Buddhism and Hinduism, have the students
hold up their right hand for Hinduism and hold up their left hand for Buddhism.
Summary
Students will individually complete a Venn Diagram and hand out as their ticket out the door.
Homework
Options
World Religions Poster and 8 Fold Path Personal Response
Social Studies Warm-Up
1. Get out your homework from Friday
5 Pillars of Islam
2. Answer the following questions.
- You may use your notes to do this!
Determine if you think it belongs with Christianity (C), Islam (I), or
Judaism (J)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
Their Holy Book is called the Qur’an.
Jesus is considered the Son of God.
This religion accepts both the Old and New Testaments as Holy Books.
Followers participate in a pilgrimage to Mecca.
This religion is the oldest of the three.
Abraham is regarded as the father of their people.
This religion believes in one Supreme Being.
This religion accepts the Old Testament as its only Holy Book.
Abraham and Moses are considered prophets.
Jerusalem is considered a holy city.
Followers of this religion call themselves Muslims.
The Ten Commandments are accepted as guidelines for ethical behavior.
Jesus is recognized as an important prophet.
This religion has a number of denominations or sects.
This religion believes in the divine creation of the universe.
This religion is the second oldest of the three.
Their Holy Book includes the story of the birth of Jesus at Bethlehem.
Their place of worship is a church.
Their place of worship is a mosque.
Their place of worship is a synagogue.
Homework
Shahada
Tradition in
Islam
Similar
Tradition in
Christianity
Similar
Tradition in
Judaism
Salat
Zakzt
Sawm
Haji
How are Hinduism and
Buddhism compare and
contrast?
7.1.spi.3
Tell me what you know
about Buddhism and
Hinduism
-
You will have one minute to tell what you know about
both Buddhism and Hinduism.
You must have at least 3 facts for each.
Hinduism
Text: Upanishads, Vedas, Bhagvadgita
Population and location: 800 million, India
When originated: 3000 BC, Indus Valley (Oldest)
Beliefs:
• Monotheistic (Truth is one) by Hindu standards, regarded by
most as polytheistic
• Karma (actions and reactions)
• Rebirth… life is a cycle
• No founder
Practices:
• Meditation and concentration
• Compassion towards living beings (many are vegetarian)
• Bathing in the Ganges river to be made anew.
Place of worship: Temple
Branches: Vaishnavites, Shaivites, neo-Hindus and reform Hindus
Your turn…
- Come up with four questions about
Hinduism (you must know the answer.)
- You will then trade papers with your
neighbor and they will answer your
questions.
- Trade back and grade their mini-quiz!!!
- How did you do?
Let’s Read
• Turn to page 628 in your SS Book
Let’s Watch
• Making of a Monk
• Add 10 new facts to your notes!!!
Buddhism
Text: Upanishads, Vedas, Bhagvadgita,
Tripitika
Population and location: 800 million, India
When found: 500 BC, 2500 years ago
Beliefs:
• Atheistic or no belief in a supreme being
but do believe in souls (polytheistic.)
• Karma (actions and reactions)
• Rebirth… life is a cycle
• Desire equals suffering. Removal of
desire equals removal of suffering.
• Founded by Siddhartha Gautama (a
Hindu)
Practices:
• Some worship Buddha, some do not.
• Compassion towards living beings (many
are vegetarian)
• Meditation and concentration, chanting
Place of worship: Temple
Branches: Mahayana, Theravada, Lamaism,
(Vajrayana/Tibetan/Tantric)
Beliefs
Four Noble Truths:
1. All of life is marked by suffering.
2. Suffering is caused by desire and attachment.
3. Suffering can be eliminated.
4. Suffering is eliminated by following the Noble
Eightfold Path.
Noble Eightfold Path:
1. Right beliefs
2. Right aspirations
3. Right speech
4. Right conduct
5. Right livelihood
6. Right effort
7. Right mindfulness
8. Right meditational attainment.
• Think/pair/share: How are Hinduism
and Buddhism similar? How are they
different?
India: Land of Many Faiths
• Read with your table
• Each member of your table should
answer questions 1-10 at the end of the
article.
Let’s Review
• Tell me which religion the following
statements belong to by raising your
hand.
• Everyone must participate!!!!
• Right Hand = Hinduism
• Left Hand = Buddhism
• Some questions may have both as an
answer
Biblical tithing is followed;
followers also give of their
time to charity
Fasting during the month of
Ramadan
monks
No ritual pilgrimage required
although many religious sites
recognized
Some followers “give up”
items or practices during Lent
Making a pilgrimage to Mecca
at least once in a lifetime
Began when Siddhartha
Gautama witnessed the state
of the world around him
Fasting is observed during
Yom Kippur
Upanishads and
Bhagavad-Gita
Prayer on an individual basis;
no prescribed times
Belief that Christ is the
Messiah
Based on eliminating suffering
Three sets of prayers recited
each day;
sunrise, noon, and sundown
Wheel and lotus
Oldest of the faiths
Majority of followers are in
India
Worship in temples
There is only one God;
Muhammad is his prophet
Belief in reincarnation
Followers are urged to tithe
10% of their income
Majority of followers are in SE
Asia
Belief that Muhammad was
the final and greatest prophet
One spiritual ritual is to have
bad karma washed away by
the Ganges River
belief in one God
Om
Prayers are performed 5 times
daily
8 Fold Path
and 4 Noble Truths
Uses Torah / Old Testament
5 Pillars of faith suggest a Hajj
to Mecca once in a lifetime
Worship in a synagogue
Worship in cathedrals and
churches
Birthplace in the Middle East
Belief in one God;
Jesus Christ is the son of God;
the Trinity
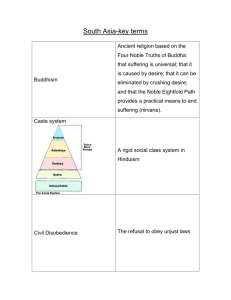
The following diagram compares and contrasts Hinduism and Buddhism. Read each item at
the bottom of the page and place the corresponding letter in the appropriate oval. If the item
is true for both religions, place the letter in the area where the ovals overlap.
Hinduism
Buddhism
Both
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
F.
Reincarnation
Began in India
Major religion of India today
Has no founder
Founded by Siddhartha Gautauma
Caste System
G.
H.
I.
J.
K.
8-Fold Path
Brahman—the eternal spirit
Karma
4 Noble Truths
Polytheistic
B Answer Key
What are the basics of Buddhism?
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
Record on the timeline.
Where did Buddhism originate?
What is the foundation of Buddhism?
What is Buddhism’s rank in the world by
population? What is that population?
Where are the concentrated areas of
Buddhism practice?
What is the holy text of the Buddhists?
There are two names for leaders of
Buddhisms. What are they?
What is the place of prayer and meditation
called?
Explain the theism of Buddhism.
What is the ultimate reality and why?
Do Buddhist believe humans have souls?
What is the goal of a Buddhist’s life?
What is nirvana?
What is the reoccurring theme found in
the Four Noble Truths?
In the Noble Eightfold Path the word
“Right” occurs over and over. What is the
definition of the word “right” in this case?
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
Date founded: c. 520 BCE
Place founded: Northeastern India
Founder: Siddharta Gautama ("the Buddha"), an Indian prince
Adherents: 360 million {1} Size rank: Fourth largest world religion
{2}
Main locations: China, Japan, Korea, Southeast Asia
Sacred texts: Tripitaka
Spiritual leader: Monk (lama in Tibetan Buddhism)
Place of ritual: Temple, meditation hall.
Some branches are atheistic; While other branches are polytheistic.
Ultimate reality: None. Nothing is permanent.
Human nature: There is no self or soul. Human existence is nothing
more than a combination of five impermanent components
(khandas).
Purpose of life: Theravada - Become an arhat, escape the cycle of
rebirth, and attain nirvana. Mahayana - Become a boddhisatva then
help others attain enlightenment.
Afterlife: Rebirth or nirvana. Nirvana is seen simply as the cessation
of suffering by some and as a heavenly paradise by others.
Four Noble Truths:
1. All of life is marked by suffering.
2. Suffering is caused by desire and attachment.
3. Suffering can be eliminated.
4. Suffering is eliminated by following the Noble Eightfold Path.
Noble Eightfold Path: 1. Right beliefs
2. Right aspirations
3. Right speech
4. Right conduct
5. Right livelihood
6. Right effort
7. Right mindfulness
8. Right meditational attainment
Because the lotus flower begins in the muck of mud, grows through
the water towards light then blossoms at the surface it is the symbol
for Buddhism. It is seen as a direct symbolic reference of life. Life
is the muck. Following the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold
Path is the journey towards the light and if you have lived that
selfless life you will achieve true enlightenment.
•
B
What are the basics of Buddhism?
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Date founded: c. 520 BCE
Place founded: Northeastern India
Founder: Siddharta Gautama ("the Buddha"),
an Indian prince
Adherents: 360 million {1} Size rank: Fourth
largest world religion {2}
Main locations: China, Japan, Korea, Southeast
Asia
Sacred texts: Tripitaka
Spiritual leader: Monk (lama in Tibetan
Buddhism)
Place of ritual: Temple, meditation hall.
Some branches are atheistic; While other
branches are polytheistic.
Ultimate reality: None. Nothing is permanent.
Human nature: There is no self or soul. Human
existence is nothing more than a combination
of five impermanent components (khandas).
Purpose of life: Theravada - Become an arhat,
escape the cycle of rebirth, and attain nirvana.
Mahayana - Become a boddhisatva then help
others attain enlightenment.
•
•
•
Afterlife: Rebirth or nirvana. Nirvana is
seen simply as the cessation of suffering
by some and as a heavenly paradise by
others.
Four Noble Truths:
1. All of life is marked by suffering.
2. Suffering is caused by desire and
attachment.
3. Suffering can be eliminated.
4. Suffering is eliminated by following the
Noble Eightfold Path.
Noble Eightfold Path:
1. Right beliefs
2. Right aspirations
3. Right speech
4. Right conduct
5. Right livelihood
6. Right effort
7. Right mindfulness
8. Right meditational attainment
Because the lotus flower begins in the
muck of mud, grows through the water
towards light then blossoms at the surface
it is the symbol for Buddhism. It is seen
as a direct symbolic reference of life. Life
is the muck. Following the Four Noble
Truths and the Eightfold Path is the
journey towards the light and if you have
lived that selfless life you will achieve
true enlightenment.
H
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
3rd largest c. 1,000,000,000 followers
Oldest c. 5,000 BC
Location: Most of the Hindus live in India, Nepal, and Sri Lanka with considerable presence in all
other parts of the world also. About 85% of Hindus live in India. That is why India is also called as
“Hindustan.”
Known as: People who follow Hinduism are called as “Hindus.”
Founder: Hinduism has no single founder. It has been evolving over the thousands of years and will
continue to.
Origin: Hinduism originated in India. Hinduism is largely based on the teachings from Vedas
Karma: Karma means your deeds. Hindus believe that our fate depends upon our Karma i.e. as you
sow so shall you reap. If you do bad Karma, you have to compensate for it in this as well as your next
life. Your next life depends upon your Karma.
Reincarnation: A soul dwells in every living thing. Body is mortal but the soul is immortal. When we
die, our soul enters a new body and the cycle continues until we get salvation. It will be easier to
understand the basic concept of Hinduism if you know Law of Conservation of Energy. For those who
have a science background or have some interest in science know the Law of Conservation of Energy
very well. It is like this:
“Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Only one form of energy can be transformed into
other. The sum of all the energies in the universe remains the same.”
According to Hinduism, human body is perishable but the soul is immortal and is subjected to the
continuous cycle of birth and rebirth. The soul changes bodies as a living person changes his/her
clothes. So, the thing which we call death is actually just a transformation of soul from one body to
another as the energy changes from one form to the other. This cycle continues births after births and
the soul is subjected to sufferings endlessly.
So, the ultimate goal of a Hindu’s life is to attend salvation (also called as Moksha or Nirvana) i.e.
freedom from the cycle of birth and rebirth. One can attend salvation when the soul of a person fully
becomes one with the supreme spirit called “Brahman” (or God) who is eternal, genderless,
omnipotent, and omniscient.
H
•
•
•
•
•
Meaning of the word: The word “Hinduism” actually has no real meaning because
Hinduism was not founded as a religion. The name “Hindu” is given by the people
outside of the India, especially Greeks and Arabs, to those living in the vicinity of
“Sindhu” river. So, the way of life those people were following is called “Hinduism.”
What do they worship: Hindus believe in one God named as “Brahman” but view
other Gods and Goddesses as manifestations of Him. Therefore, in practice, they
worship more than one God. Most Hindus worship God in the form of an
idol. Rivers, mountains, trees, animals, and natural things which are useful for a
human being are revered in Hinduism. Cow is the most revered animal for Hindus.
Main Deities: Lord Brahma, Lord Vishnu, and Lord Shiva are the creator, protector,
and destroyer respectively. These are the three main deities in Hinduism. Besides
them, Lord Ganesha, Lord Krishna, Lord Hanuman, Lord Rama, and Goddess
Parvati are the most popular deities in Hinduism.
Aims of life: Dharma (righteousness), Artha (wealth), Kama (desire), and Moksha
(salvation) are the four objectives of a Hindu’s life. Salvation is the ultimate goal of a
Hindu’s life.
Contributions:
– Yoga, vegetarianism, and meditation are the best gifts of Hinduism to the world. Palmistry,
acupuncture, martial art, and many other ancient wonders originated in India and are parts of
Hinduism Religion.
– Hinduism is the source of inspiration for three other major religions of the world viz. Buddhism,
Sikhism, and Jainism.
– Zero and decimal system were invented in India. On the basis of which the modern science
exists.
H
Symbols: According to Vedas, Om is the sound which was present at the time of creation of universe and it is the only
symbol, which represents the God (Brahman).
Sacred Books or Scriptures: Four Vedas, Upanishadas, and Bhagvadgita are a few of the main books relied upon for
guidance.
Language: Most of the Hindu scriptures are written in Sanskrit. Sanskrit is considered to be the mother of all the
languages. Sanskrit is considered to be the language of demi-Gods.
Eating Habits: Most of the Hindus do not eat beef and/or pork. They also do not eat non-vegetarian food on auspicious
days. Hinduism strongly advocates vegetarianism. Food is highly revered and wasting the food is considered as a
very bad habit.
Important Hindu Festivals:
1. Diwali – The festival of lights
2. Gudhipadawa – Hindu New Year
3. Mahashivratri – The day on which the universe was created.
Vedic restraints for Hindus are:
1. Ahimsa (not to harm others)
2. Satya (truthfullness)
3. Asteya (Nonstealing)
4. Brahmacharya (Avoiding promiscuity in thoughts, word, and deed)
5. Kshama (Forgiveness)
6. Dhriti (Steadfastness)
7. Daya (Compassion)
8. Arjaya (Honesty)
Other random facts:
•
Parents, teachers, and food are considered next to God.
•
Wasting food is considered as a very bad habit in Hinduism.
•
Hindus do not wear footwear inside the temples or homes.
•
Because of the usefulness of rivers, they are highly revered in Hinduism. People call them as mother. Ganges is the
highest revered river for Hindus.
•
Hindus believe that we get the human body when our soul passes through 8,400,000 species (Yonis).