Term 3 Yr 11 Sci 21 Unit Plan
advertisement

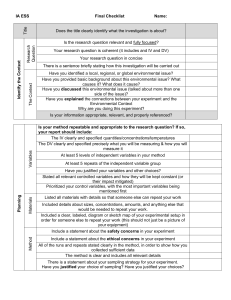
11 SCIENCE21 - Term 3 Unit 3: MICROBIOLOGY 1 UNIT 1: LEARNING GOALS: Students will investigate the following: Microbes culture techniques and associated research Health and economic issues relating to ‘germs’ in our environment. Students will design an investigation to test an antimicrobial agent, a nutrient medium or process or another process involving the culture of cells. ………………………………………………………………………………………. Resources Glossary: arrangement of atoms in molecules determines the properties, states of matter, water is fundamental to life, water as a solvent, solubility, biological reactions occur in water, photosynthesis, respiration, a reduction in biodiversity has consequences, interactions exist between living and non-living components of the environment, geological changes occur through physical and chemical processes, increased levels of nitrogen can damage aquatic ecosystems, global warming, tides, seasons, analogue and digital forms of information. Particle model, water cycle, abiotic and biotic features and relationships, water quality testing procedures – dissolved oxygen, bacteria, nitrates, phosphates, turbidity, total solids, pH, data collection and analysis, diversity Assessment Success Criteria: The student will be able to do the following: Accurate and successful completion of a logbook and EEI description and explanation of complex scientific information comparison and explanation of complex interrelationships between scientific ideas, concepts, theories, processes and phenomena interpretation and application of scientific knowledge and information to generate reasoned explanations of real-world phenomena. questions and/or hypotheses formulated by identifying problems and/or issues that inform justified and refined plans for investigation assessment and management of risk; safe selection and use of equipment and purposeful use of technology to gather and enhance the reliability of data and information systematic analysis and interpretation of data and information using appropriate quantitative and qualitative techniques to identify trends, relationships and anomalies identification and explanation of issues and evaluation of scientific impacts relevant to an inquiry synthesis of data to draw wellreasoned conclusions and express justified positions analysis of a range of factors influencing the development of scientific knowledge. Key Verbs DEFINE & EXPLAIN COMPARE INVESTIGATE (SCIENTIFIC) JUSTIFY SYNTHESISE ANALYSE