Table 3: Summary of information on each course/module
advertisement

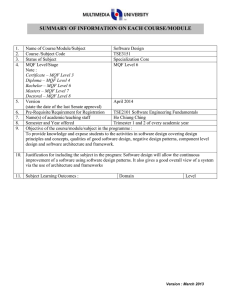
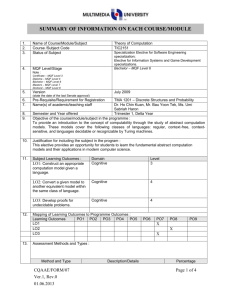
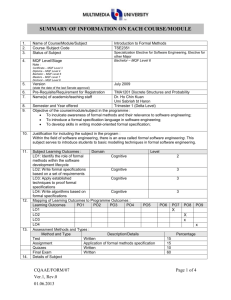
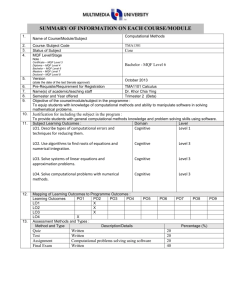
SUMMARY OF INFORMATION ON EACH COURSE/MODULE 1. 2. 3. 4. Name of Course/Module/Subject Course /Subject Code Status of Subject MQF Level/Stage Programming Fundamentals TCP1101 Core Bachelor – MQF Level 6 Note : Certificate – MQF Level 3 Diploma – MQF Level 4 Bachelor – MQF Level 6 Masters – MQF Level 7 Doctoral – MQF Level 8 5. Version July 2009 (state the date of the last Senate approval) 6. 7. Pre-Requisite/Requirement for Registration Name(s) of academic/teaching staff None Dr. Wong Ya Ping Dr. Ku Day Chyi Mr. Bau Yoon Teck Mr. Lee Kian Chin 8. 9. Semester and Year offered Trimester 1 (Beta Level) Objective of the course/module/subject in the programme: To give an introduction to basic programming concepts through the use of the C++ programming language. It covers the basic notions and techniques for algorithm development and the implementation of algorithms in a high-level programming language. 10. Justification for including the subject in the program: To provide students with an adequate first course in computer programming, equipping them to study the follow up programming courses. 11. 12. Subject Learning Outcomes : Domain LO1: Identify basic concepts of Cognitive a high level programming language correctly. LO2 Demonstrate the basic Cognitive notions and techniques for algorithm development. LO3 Develop programs for Cognitive problem solving Mapping of Learning Outcomes to Programme Outcomes: Learning Outcomes PO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 LO1 LO2 LO3 13. X X X X X X X Level 2 3 6 PO5 PO6 X X Assessment Methods and Types : Method and Type Description/Details Assignment Programming Test Written Test & Programming Lab Test CQAAE/FORM/07 Ver.1, Rev.0 01.06.2013 PO7 PO8 PO9 Percentage 10 20 Page 1 of 4 14. Quiz Final Exam Details of Subject Written Written Exam 30 40 Mode of Delivery Topics 1. Problem Solving and Software Development Problem solving; program design and programming methodology; structure chart; flowchart; pseudo code. 2. Element of Structured Programming Basic constructs of structured programming: sequence, repetition, selection; data types; identifiers; variables; reference; scope and lifetime of variables; statements; operators; operator precedence; type conversion; bitwise manipulation. 3. Functions Top-down design; standard library functions; procedural abstraction; local and global variables; function overloading; function return types; function parameters: call-by-value, callby-reference; command line arguments; testing and debugging functions; general debugging techniques. 4. Arrays Single and multi-dimensional arrays; arrays as function parameters; simple sorting and searching on arrays; Standard Template Library’s Vector class. 5. Classes and Abstraction Basic UML class diagrams; struct and class; object instantiation; public and private members; accessor and mutator functions; class constructors; copy constructor; destructors; passing object reference variable to function; assignment operator; encapsulation; abstract data type (ADT). 6. File Handling, Separate Compilation and Namespaces Concept of files; files and I/O streams; standard file handling functions; separate compilation; namespaces; name qualifiers. CQAAE/FORM/07 Ver.1, Rev.0 01.06.2013 Indicate allocation of SLT (lecture, tutorial, lab) for each subtopic (eg : Lecture, Tutorial, Workshop, Seminar, etc.) Lecture (Hrs) Lab (Hrs) 6 2 6 4 6 4 6 4 8 4 1 2 Tutorial (Hrs) Page 2 of 4 15. 16. 17. 7. Pointers Pointer variables; arrays and pointers; strings and pointers; pointers and functions. 8. Dynamic Memory Allocation Dynamic variables; dynamic array; pointer arithmetic; destructors and dynamic memory in classes. Total Total Student Learning Time (SLT) Lectures Tutorials (Incl. Quiz) Test Assignment Test Final Exam Sub Total Total SLT Credit Value Reading Materials : Textbook CQAAE/FORM/07 Ver.1, Rev.0 01.06.2013 6 4 3 2 42 26 Face to Face Independent Learning 42 26 1 0 1 2 42 26 4 10 4 16 72 102 4 (174/40 = 4.35) Reference Materials 1. Walter Savitch, Problem Solving with C++, Addison-Wesley, 2008. 2. Cay S. Horstmann, Timothy A. Budd, Big C++, Wiley, 2008. 3. Deitel & Deitel, C++ How to Program, Prentice Hall, 2007. 4. Ira Pohl, C++ by Dissection, AddisonWesley, 2003. 5. Stroustrup, The C++ Programming Language, Addison-Wesley, 2000. Page 3 of 4 18. Appendix (to be compiled when submitting the complete syllabus for the programme) : 1. Mission and Vision of the University and Faculty 2. Programme Objectives or Programme Educational Objectives 3. Programme Outcomes (POs) 4. Mapping of POs to the 8 MQF domain 5. Mapping of Los to the POs 6. Summary of the Bloom’s Taxonomy’s Domain Coverage in all the Los in the format below : Bloom’s Taxonomy Domain Learning Outcomes Subject (please state the Affective learning 0utcomes) Cognitive Psychomotor 7. Summary of LO to PO measurement 8. Measurement and Tabulation of result for LO achievement 9. Measurement Tabulation of result for PO achievement Mapping Learning Outcome to Assessment No. A1 Assessment % 20 LO1 LO2 X A2 Test 30 X X A3 Quizzes 10 X X A4 Final Exams 40 X X Assignment CQAAE/FORM/07 Ver.1, Rev.0 01.06.2013 LO3 X X Page 4 of 4