Chapter 4 Developmental Psych Part II

Stranger Anxiety
• The fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age
Attachment
• An emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress in separation.
Body Contact
• It was first assumed that infants became attached to those who satisfied their need for nourishment.
Then these guys came along…
Harry Harlow and his
Discovered that monkeys preferred the soft body contact of a cloth mother, over the nourishment of a hard/wirily mother.
Discovering Love
Familiarity
• Attachments based on familiarity are formed during our critical periods .
Critical Periods : the optimal period shortly after birth when an organism ’ s exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produce proper development.
Imprinting
• The process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life.
• Lorenz discovered that some animals form attachment through imprinting.
Do human ’ s imprint?
Konrad Lorenz Imprinting Experiment
Konrad Lorenz Imprinting Experiment
Responsive Parenting
Do parents play a part in your attachment?
• Mary Ainsworth Stranger Paradigm :
Three types of attachment:
1) Secure attachments (66% of infants) confidently explore the novel environment while the parents are present; are distressed when they leave, and come to the parents when they return
2) Avoidant attachments (22% of infants) may resist being held by parents and will explore the novel environment; do not go to parents for comfort when they return from an absence
3) Anxious/ambivalent attachments (12% of infants) show stress when parents leave, but do not want comfort when parents return.
Mary Ainsworth Strange Situation
Secure Attachment Predicts
Social Competence
• Erik and Joan Erikson said that securely attached children approach life with a sense of basic trust .
• Basic trust – a sense that the world is predictable and reliable.
• Erikson attributed basic trust not to one ’ s positive environment or inborn temperament, but to early parenting
Deprivation of Attachment
• Often withdrawn, frightened and in extreme cases speechless.
•Harlow ’ s monkeys would either cower in fright or act extremely aggressive. Many could not mate and if they could, the mothers were unresponsive parents.
•Is there a connection between crime and lack of childhood attachment?
Dad ’ s Matter Too
• Dads are not just mobile sperm banks!!!!
•Paternal separation puts children at increased risk for various psychological and social pathologies.
Self - Concept
• A sense of one ’ s identity and self-worth
When does self-awareness start?
Child-Rearing Practices
• Parenting styles have been shown to have a positive correlational effect on a child ’ s self-concept
Three General Classifications of Parenting Styles:
Authoritarian Parents
• Impose rules and expect obedience
.
• “ Why, because I said so!!!!
”
Permissive Parents
• Parents submit to their children ’ s desires, make few demands and use little punishment.
Authoritative Parents
• Parents are both demanding and responsive.
• Exert control by setting rules, but explain reasoning behind the rules.
• Encourage open discussion.
Freud's Stages of
Psychosexual Development
• Freud believed that your personality developed in your childhood.
• Mostly from unresolved problems in the early childhood
• Freud believed that children pass through a series of psychosexual stages.
Fixation
• A lingering focus of pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier psychosexual stage
• Where conflicts were unresolved
* Orally fixated people may need to chain smoke or chew gum; or denying the dependence by acting tough or being very sarcastic
.
*Anally fixated people can either be anal expulsive or anal retentive.
Oral Stage
• 0-18 months
• Pleasure center is on the mouth
• Sucking, biting and chewing
• Babies put everything in their mouths.
• People fixated in this stage tend to overeat, smoke or have a childhood dependence on things.
Anal Stage
• 18-36 months
(developed during toilet training)
• Pleasure focuses on bladder and bowel control
• Controlling ones life and independence
• A person fixated may become overly controlling
(retentive) or out of control (expulsive)
Phallic Stage
• 3-6 years (children first recognize their gender)
• Pleasure zone is the genitals
• Coping with incestuous feelings -
Oedipus and Electra complexes
• Fixation can cause later problems in relationships
Fight for Kisses
Latency Stage
• 6- puberty
• Dormant sexual feeling (libido is hidden)
• Cooties stage
• Freud believed that fixation in this stage could lead to sexual issues.
Genital Stage
• Puberty to death
• Maturation of sexual interests
• Freud thought fixation in this stage is normal.
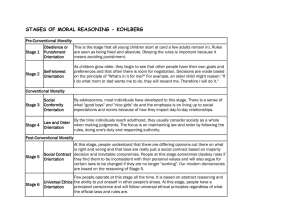
Lawrence Kohlberg and his stages of
Morality
•
Preconventional Morality
•
Conventional Morality
•
Postconventional Morality
Preconventional Morality
• Morality of self- interest
• Their actions are either to avoid punishment or to gain rewards.
Conventional Morality
Morality is based upon obeying laws to
1. Maintain social order
2. To gain social approval
Postconventional Morality
• Morality based on your own ethical principles.
Talk is Cheap!
How do we turn morality into action?
• Teach Empathy
• Self-discipline to delay gratification
• Model moral behavior