BAP review nov2012
advertisement

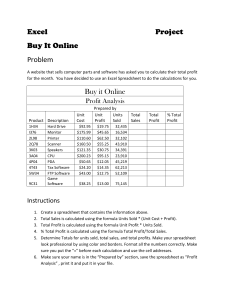
BAP module 8th, 9th and 10th November 2012 Day 1 Introduction to the module and the assignment. Example assignment, good points and weak points, detailed marking scheme. World news review – economic, business, political – the macro influences Students’ preliminary qualitative proposals for BAP projects. Accounting ratios – revision. See Summary of Operating and Financial Ratios We will be selective with key ratios, do NOT do all the ratios, they will not all be significant. Profit and its relation to stock market measures, see Summary of Operating and Financial Ratios Example of Tesco plc results and statements, see http://www.tescoplc.com/index.asp?pageid=164 Tesco has six explicit strategies. Reading between the lines; vocabulary of strategy, note the word “challenging”, understanding the sub-text. Key financial and performance figures – some specialist KPIs of supermarkets; CEO’s video interview and slide show presentation to (institutional) investors. Lecture: Globalisation and its influences, see Globalisation (Yip) 2011 Extending Yip’s 4Cs to 14Cs. The cost factors in globalization are very significant for the BAP module as are the collaboration and common platform aspects of competition. Lecture: The Real forces of competition, see Competition analysis (Porter) 2011 Important here to modify the five forces by including macro externalities (PESTEL pressures wrap around the micro 5 forces) and note the Downes and Mui additional 3 forces. The most important force is that of competitive rivalry (centre circle of diagram), should contain figures and data, quantitative. Case study video: “Sparks at Marks” – the story of M&S fall from grace in 1998, the inside story featuring CEO and Chairman Sir Richard Greenbury who was not given quantitative data collected internally. Spreadsheet example, see Sensitivity analysis Marks and Spencer 2010 This has example of Marks & Spencer P&L and Balance Sheet; P&L – key points emerge from the figures; Balance sheet - key points emerge from the figures; Livening up the spreadsheet by inserting cell formulae, checking arithmetic side by side with the original. Horizontal analysis - % differences between the years dramatically highlight trends that are not so apparent in the £ numbers; Generic strategies revision (Porter), updated by Bowman with his Strategy Clock. See Bowman Strategy Clock – mapping price and value Day 2 Lecture – Balanced Scorecard, see Balanced Scorecard 2011 Very widely used across industry, quantitative application, KPIs relevant to the specific industry sector. What are the industry-specific metrics in your chosen sector? Lecture – Where in the world to locate business, see Where in the world to locate 2011 Application of the Porter Diamond, sources of info, World Bank “Doing Business”, WEF “Global Competitiveness Report”, OECD and Forbes reports on relative taxation rates Online research for individual projects. Updates on preliminary presentations, discussion. Lecture – Strategy options and diversification, see Strategy options (Ansoff) 2011 Application of the Ansoff matrix, forms of diversification, risk. Process can go in to reverse in hard times with retrenchment and refocusing on core business. Poor record for full scale diversification. Investment appraisal techniques – spreadsheet based applications of loan repayment formula, NPV formula, IRR formula. See Loan repayment PMT NPV IRR calculator M&S spreadsheet revisited - Making a modelling spreadsheet by adding additional columns to represent future years. 1% changes to sales or to costs often produce 10 – 15% changes in the profit lines; Sales forecasts in your recommendations must not be too optimistic, they should be in line with published market forecasts; Note that the bottom line profit line “retained profit” goes into the balance sheet as both and asset (cash) and a liability (cumulative profit); See Sensitivity analysis Marks and Spencer 2010 Decision tree analysis, see Decision tree nov2012 Application with a spreadsheet example. Case study video “Mercedes goes to Motown” – the Daimler Chrysler merger. Complex story, see Case study – Daimler Chrysler merger Day 3 Lecture - Reasons for diversification, see Reasons to Diversify (Miller) 2011. See also Chapter extract from Miller Applications of Miller’s model for the 6 reasons for diversification. Great model to integrate resource-based strategy, market-based strategy, accounting-based strategy, internal investment-based strategy, growth strategy, and reducing risk (!) strategy. Examples, reference back to the Daimler-Chrysler case. Which boxes did this strategy tick? Competences (beware though “core” competence) as “bundles” of skills, assets, resources, IP etc. Discussion of due diligence, valuation methods, and post-merger integration (Daimler Chrysler had two PMI teams ! ) Online preparation of final slideshows. Final slideshows outlining BAP projects. Round up. Strategy revison – value price mapping using the Bowman strategy clock (updating Porter’s generic strategies). Students’ 5 minute Powerpoint overviews of their chosen focus companies and benchmark companies, key issues identified, some firms are in really tight positions. Discussion of the way forward for each project. Strategy revision – Strategy revision –Modelling using the example of the Marks & Spencer spreadsheet, inputting simple assumptions to the “sales” and “costs of sales” areas, examining outcomes on the profit lines. Round up