The Work of Rivers File
advertisement

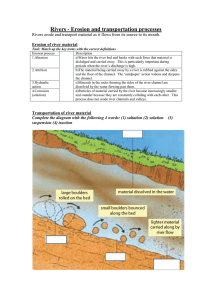
Rivers Chapter 7 Start on high, Flow down low, Creating features As they flow! Youth Stage = Upper Course Mature Stage = Middle Course Old age Stage = Lower Course The Work of Rivers Stage Slope Main processes Valley shape Main features Upper Course Middle Course Lower Course Stage Slope Main processes Valley shape Main features Upper Course Middle Course Lower Course The Work of Rivers Processes of erosion: 1. Hydraulic Action The force of the moving water causes erosion of the river bed and the banks of the river. The greater the speed and amount of water the greater the force. The Work of Rivers Processes of erosion: 2. Abrasion The rivers load is bounced and dragged along the river bed causing it to scrape and deepen the course of the river. The Work of Rivers Processes of erosion: 3. Attrition The rivers load is constantly colliding in the moving river water causing the load to break down into smaller pieces. The Work of Rivers Processes of erosion: 4. Cavitation As a river flows over the uneven river bed air bubbles travel up to the top of the river, pop and send ripples out towards the river banks. These ripples gently erode the rivers banks. The Work of Rivers Processes of erosion: 5. Solution Chemicals in the rivers water and rocks along the river course change the river chemically which reacts with and erodes various rocks along the way. F.E.E.D F: Feature (Name, erosion or deposition, stage it is found) E: Explain with at least one or two processes explained E: Three examples, one Irish D: Clear 1/2/3 diagram/s to show how the feature is formed. Youth Stage = Waterfalls Mature Stage = Meanders and Oxbow Lakes Old age Stage = Deltas • V – Shaped Valleys • Interlocking Spurs • Waterfalls A typical upper course V-Shaped valley with interlocking spurs, steep valley sides and active slope processes. The diagram below shows the formation of interlocking spurs. 1 2 3 4 Waterfall Youth Stage Hydraulic Action Abrasion Waterfalls are features of erosion usually found in the upper course (youth stage) of a river. They are found in areas where a river is flowing over bands of hard and soft rock. The hard rock is slower to break down but the river can erode the soft rock much quicker. A band of hard rock lies on an area of soft rock. The river erodes the soft rock by the processes of hydraulic action (the force of the moving water) and abrasion (the scraping of the rivers load against the banks and bed). This causes a small notch to be formed into the soft rock which is eroded further into a drop over which the water falls. As the water falls over the drop there is a greater rate of hydraulic action and the rivers load also scrapes and deepens a hole in the bottom of the waterfall. This hole is called a Plunge Pool. The hard rock is slowly eroded and hangs over the edge called a Overhang. This is eventually worn down by the river and is carried away as the rivers load. Examples of waterfalls include: 1 2 3 Diagram of a waterfall being formed foe/sor (e) px2 weu Aoh/sr srw ucipp neisr pp@bow rfovd Weu= Waterfall erodes upstream foe/sor= Feature of erosion….stage of river Aoh/sr srw= Areas of hard/soft rock, soft rock weaker Ucipp= Undercut collapses into plunge pool pp@bow= Plunge pool at base of waterfall (e) px2= Erosion, Process are hydrualic action and abrasion Rfovd= River falls over vertical drop Neisr= Notch eroded in soft rock Can you put the labels below into the correct place on he diagram? Meanders and Ox Bow Lakes Mature and Old Age Stage Erosion and Depositon Ox Bow lake on Mississippi F.E.E.D F: Feature (Name, erosion or deposition, stage it is found) E: Explain with at least one or two processes explained E: Three examples, one Irish D: Clear 1/2/3 diagram/s to show how the feature is formed. F.E.E.D F: Feature (Name, erosion or deposition, stage it is found) E: Explain with at least one or two processes explained E: Three examples, one Irish D: Clear 1/2/3 diagram/s to show how the feature is formed. Examples of deltas include: The River Nile, Egypt The Mississippi River in Louisiana, USA The River Shannon in Limerick, Ireland 1. Name the river and the city of this case study? 2. The city is between two physical areas…what are they? 3. How is the city protected from flooding? 4. What did the President do to the amount of money available for protection of the land? 5. When did the disaster strike? 6. What was the name of the hurricane? 7. How many poor people could not leave the area? 8. How many people drowned in this disaster?