W s
advertisement

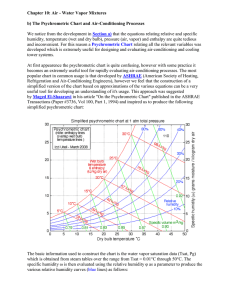
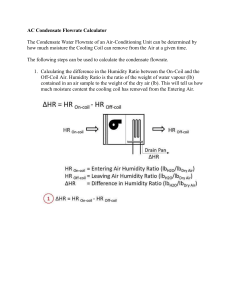
Objectives Learn about Psychometrics • Psychometric chart • Equations Humidity Ratio, W • W = mw/ma • Degree of saturation, µ = W/Ws • Humidity ratio is hard to measure, but very useful in calculations • What are units? • Is W a function of temperature? What about Ws? Ws = humidity ratio at saturation ma = mass of dry air mw = mass of water vapor Relative Humidity • Φ = xw/xw,s = Pw/Pws • Function of T 0.622 Ws 0.622 W Easy to measure and useful in some contexts, but often need to know temperature as well x = mole fraction P = pressure μ = degree of saturation W = humidity ratio Dew-point temperature, td • Temperature at which condensation will form • Under appropriate surface conditions • Vapor is saturated • Φ=? • Ws(P, td) = W Wet-bulb temperature, VBT (t*) • Temperature of wet surface or • Temperature at which water, by evaporating into the air, will bring air to saturation adiabatically • * superscript is designation that variable is evaluated at the wet-bulb temperature • Note, distinct from that measured by a sling psychrometer • Section 9.5 Tables for Moist Air (P = 1 atm) • Tables A.4 in your text • Ability to get Ws for calculations • Subscripts: • a = dry air, s = saturated air v = va+µvas h = ha+µhas s = sa+µsas Psychrometric Chart • Need two quantities for a state point • Can get all other quantities from a state point • Can do all calculations without a chart • Often require iteration • Many “digital” psychrometric charts available • Can make your own • Best source is ASHRAE fundamentals (Chapter 6) • Also in your text (back cover fold-out) Ref: Tao and Janis (2001) Ref: Tao and Janis (2001) Ref: Tao and Janis (2001) Ref: Tao and Janis (2001) Examples • What is enthalpy of air in the classroom right now? • Condensation on windows when taking a shower • How cold does it have to be outside for condensation to form on windows? – Assumption is that windows are the same temperature as outside air – 80 °F, RH = 80% Alternate calculation for W • PV = mRT (IGL) mw W ma PwV RwT Pw Ra PaV Pa Rw Ra T • What do we know about R ratio? R = gas constant • P = Pw + Pa P = pressure Pw W 0.622 P Pw V = volume T = absolute temperature W = humidity ratio Subscripts: w is water vapor, a is dry air Calculation of psychometric quantities • For an ideal gas, • hda = ∫cpadT, hw = ∫cpwdT • So, hda = cp,dat which assumes a reference state of 0 °F or 0 °C – Tables A4 • Note different reference • hw = cpwt + hg0 • h = cp,dat + W(cpwt + hg0) Or you can use: • h = cpt + W∙hg0, cp = cp,da + Wcpw cp = specific heat h = enthalpy T = absolute temperature t = temperature W = humidity ratio Subscripts: w is water vapor, a is dry air, g is saturated water vapor Adiabatic mixing m h m h Q • Governing equation in External heat out Sensible heating Q m c p t Dehumidification by Cooling Real Dehumidification Process Transport of saturated air tsurface < tdp Condensation Mold in a duct Humidification hw Specific enthalpy of water added to system hg Specific enthalpy of saturated water vapor Summary • Describe psychrometric quantities • Given any two psychrometric quantities, calculate any other quantity • Use Tables A4 or psychrometric charts to look up psychrometric quantities • Calculate psychrometric quantities at nonstandard conditions