Free Body Diagrams
advertisement

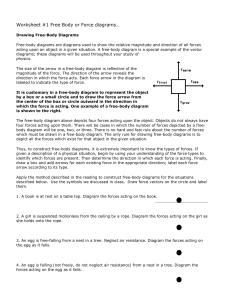
Free Body Diagrams Free Body Diagrams • Free-body diagrams are used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting on an object. How to draw free body diagrams Step One: Draw a box to represent the object. Label the mass of the object. 100 kg How to draw free body diagrams Step Two: Draw arrows to represent the forces. • The size of the arrow represents the magnitude of the force. Normal Friction 100 kg Gravity • Arrows must move out from the center of the object. Applied • Label the value of the force or label the type of force. Common Forces • Fn = Normal Force- how much force an object has to counteract gravity. • Fw = Weight Force- How much force the weight of an object puts on the earth. • Ff = Friction Force- How much force friction causes on an object. • F1 or F2 = Any push or pull force Forces • There can be any number of forces acting on an object, it doesn’t always have to be 4. Example 1 • A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 1 kg Example 1 • A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 1 kg Normal 1 kg Gravity There is a Normal Force (pushing up) & a Gravitational Force (pulling down) Example 2 An egg is free-falling from a nest in a tree. Neglect air resistance. Draw a free-body diagram showing the forces involved. There is only a Gravitational Force (pulling down) Gravity Example 3 A flying squirrel is gliding (no wing flaps) from a tree to the ground at constant velocity. Consider air resistance. Draw a free-body diagram showing the forces involved. Example 3 A flying squirrel is gliding (no wing flaps) from a tree to the ground at constant velocity. Consider air resistance. Draw a free-body diagram showing the forces involved. Air Resistance Gravity Example 4 A rightward force is applied to a book in order to move it across a desk. Consider frictional forces. Neglect air resistance. Construct a freebody diagram. 100 kg Example 4 A rightward force is applied to a book in order to move it across a desk. Consider frictional forces. Neglect air resistance. Construct a freebody diagram. Normal Friction 100 kg Gravity Applied Example 5 • A car runs out of gas and is coasting down a hill. Example 5 • A car runs out of gas and is coasting down a hill. Gravity Net Force We can use free body diagrams to help us solve force problems. 1) Draw the free body diagram with forces. 2) Label the forces with the appropriate value. 3) Add the forces like vectors. Net Force (Example 1) • What would be the resultant force? 1200 N 800 N Net Force (Example 2) • What would be the resultant force? 500 N 250 N 500 N