Elements of Poetry
advertisement

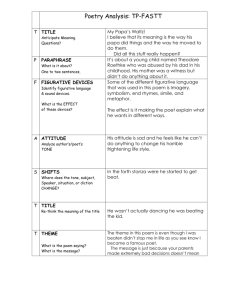
ELEMENTS OF POETRY What is poetry? KWL • Fill out the KNOW section of the KWL chart with a partner. • What do you 100% know? • Flip through the handouts and the textbook. • What do you still need to know? • Which terms have you heard of but are not sure about? • What seems brand new that you definitely want me to go over? What makes poetry different? Poetry • Lines – a single word, phrase, part of a sentence • Stanzas – a poem paragraph or a grouping of lines • Sounds different - may rhyme or have rhythm, figurative language, sensory language • A poems has a speaker – not necessarily the poet Prose • Sentences • Paragraphs • Traditional – what you expect to read RHYME SCHEME – a rhyming pattern at the end of each line of the poem. You label each word with a letter of the alphabet, rhymes are assigned the same letter. The rhyme scheme starts over with each stanza. Example. Line 1 – lettuce – A Line 2 – romaine – B Line 3 – cranium – C Line 4 – brain – B PUN – word play or a verbal joke Example. “Lettuce alone” in the last line sounds like “let us alone” which is funny because the lettuce says he is “shy.” Can you think of another pun? “A Fine Head of Lettuce” What is different about the poem v. the image I chose on the right? What is different about this poem compared to “A Fine Head of Lettuce”? How do you summarize a stanza, especially for the STAAR test? STEP 1. What had happened was? STEP 2. What was the result of that? Complete sentences amongst incomplete sentences, italicized words, capital letters, dialogue, etc… that break the normal pattern of the poem are done for a reason. The STAAR test loves to ask about this stuff. What are some reasons? 1. Emphasis 2. Why do they want to emphasize it? 3. It is usually connected to a feeling. “Losing Face” Elements of Poetry • Sound devices – rhyme, meter, rhythm, alliteration, refrain • Figurative Language –simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole • Imagery – Sight, sound, touch, taste, smell • Poems are packed with these elements. Poems often hold more meaning with less words because these elements hold so much hidden information and the words are so precisely chosen. Sound Devices • Rhyme – repetition of accented vowel sounds at the end of a line. • Toe, bow, grow • Cry, sky, try • Can you think of a rhyme? • Meter – a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables. It gives the poem/song a beat. • Rhythm – a musical quality created by alternating accented and unaccented syllables. • Meter and rhythm go hand in hand. Think about the song “Tick Tock” by Ke$ha… More Sound Devices • Alliteration – repetition of consonant sounds close together at the beginning or end of a word. • Sometimes alliteration mimics natural sounds like an onomatopoeia. • Tick tock on the clock • What does the alliteration above imply? Another Sound Device • Refrain – a word or line repeated in a poem to create a certain effect. Baby, baby, baby, oh! Baby, baby, baby, no! I’m like baby, baby, baby no! I thought you’d always be mine, mine! • What effect does Justin Beiber create in his refrain? Do you remember how to label the rhyme scheme? Can you read it with rhyme and rhythm? What is the big question that this speaker is wondering? “Pete at the Zoo” “Fireworks” What kinds of sounds do you associate with fireworks? What sound devices help you “hear” the fireworks in this poem? What is an onomatopoeia? Figurative Language • Use of imaginative comparisons to help see something common in a new way. • It is NOT literal. • Did you know that people use the word “literally” wrong all the time? What they actually means in figuratively. Figurative Language • SIMILE – a comparison between 2 unlike things using like or as. • What two things are being compared in the example poem? Use the picture to help you. • Can you think of a simile? Figurative Language • Metaphor – a comparison between two unlike things without like or as. • Sometimes it just calls one item by another name • Muffins, take out your homework! • Sometimes it uses a “be” verb to call something another thing • Love is a rose. • What is the comparison in the sample poem? Figurative Language • Personification – description of an object, animal, or idea with human qualities • What is being compared using personification in the poem? • Can you think of your own example? Figurative Language • Hyperbole – uses exaggeration to create a certain effect • What is being exaggerated in the example? Imagery • To use sensory language and sometimes figurative language to appeal to your senses of sight, smell, taste, touch, and smell. • Most imagery is visual. • Most often uses adjectives. C-BAGS? • What did you see or hear in each of the previous examples? “Like Bookends” • What poetic devices do you immediately notice? • What is a bookend? • Why is the poem titled “Like Bookends”? Is it about real bookends? • Complete the rest of the questions independently. KWL • Complete the “Learned” section. • For each word in the “what I need to know” section, you must write at least one statement in the “Learned” section. • You may add extra things that you learned in this lesson to the “Learned” section.