Introduction to Life Science
advertisement

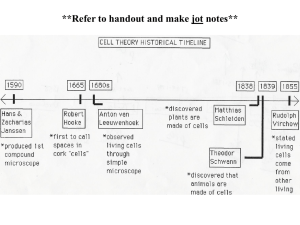
Introduction to Life Science What is Life? What Characteristics do all Living Things Share? 1.All living things have a cellular organization. A cell is the basic unit of life. Unicellular- one celled Multicellular- more than one cell 2. Cells are composed of chemicals. Water- the most abundant Carbohydrates- for energy Proteins and lipids- building materials Nucleic Acids- contain genetic material 3. Living things react to stimuli. A stimulus is something in the environment that causes a reaction, or a response. A response is an action or change in behavior. 4. Living things grow and develop. Growth- an increase in the size of an organism. Development- a progressive change in an organism over time. All living things have the ability to reproduce. 5. All living things arise from other living things. The theory of Spontaneous Generation, which proposed that life can appear spontaneously from non-living things, was disproved by experiments performed by Redi and Pasteur. Life Comes from Life • Living things come from living things. • 400 years ago people though that living things came from non-living things (Spontaneous Generation). • Francisco Redi, Louis Pasteur did experiments to disprove this theory. Redi’s Experiment Do Now! Answer questions #1-3 on pages 18-19 in your workbooks. 6. All living things use energy. Energy is used to nourish, repair and create new cells. We obtain energy from converting the foods that we eat into energy that can be used by the cells. 7. All living things can move. This process is called Locomotion. Plants move their branches and leaves toward the Sun! 8.All living things will die. One of the realities of life is that all life eventually comes to an end. This process is called Expiration. Do Now! Answer question #4 on page 20 in your workbook. What do All Living Things Need to Survive? 1. Water**** 2. Food 3. Living space 4. Stable internal conditions (Homeostasis) How do Organisms Obtain Food for Energy? • Autotrophs- make their own food (Plants). • Heterotrophs- obtain food from other sources. Herbivore- eat plants. Carnivore- eat animals (meat). Omnivore- eat plants and animals. Do Now! Answer questions #5,6 on page 21 in your workbook. Let’s go to the Video! QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture.