Water Cycle and Weather
advertisement

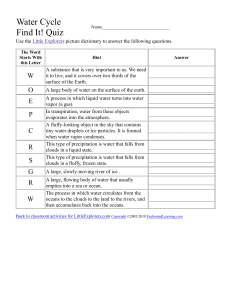
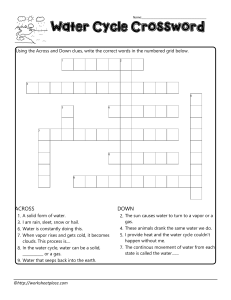
Water Cycle and Weather Unit Review Water Cycle Evaporation When the sun heats up the (liquid) water and turns it into a gas (water vapor). The gas rises up in the atmosphere and collects in the clouds. Condensation When the water vapor (warm moist air) meets the cooler air in the upper atmosphere, it condenses (or changes) back to a liquid or solid form. It collects in the clouds. Precipitation When the clouds become saturated ( or full) of condensed water vapor, the water falls back to the Earth’s surface as rain, sleet, snow or hail. Forms of Precipitation Rain: liquid water because air temperature is warm Sleet: frozen rain because the air temperature is freezing Snow: ice crystals Hail: balls of ice because the water in the clouds is frozen and does not have time to melt on the way down. (Usually happens during storms) States of Matter Solid: Example: ice Liquid: Example: water Gas: Example: air, water vapor *Freezing temperature: 0 C/ 32 F *Boiling Temperature: 100 C/212 F Weather vs. Climate Weather: What is happening outside right now. Climate: weather in one area over a long period of time. Weather map Climate Map/Zones Layers of the Atmosphere Troposphere: weather happens here Stratosphere: above weather/clouds, where planes fly, ozone layer Mesosphere: where meteors burn up before hitting earth Thermosphere: radio waves are reflected back to earth