Parts of Speech
advertisement

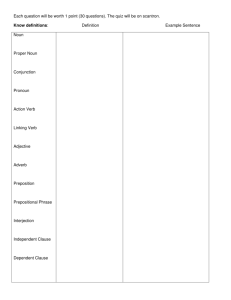
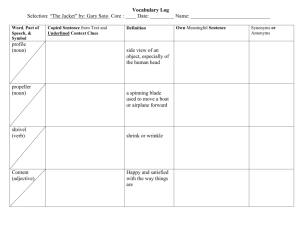
The Eight Parts of Speech Mrs. Crystal Hurd John S. Battle High School 1. Noun A noun is a person, place, thing, or idea. Ask yourself, “Does the word name a person, place, or thing? The theater is playing several movies tonight. (sing.) (Plur.) Noun = Subject The noun is the subject of a sentence. The subject is what the rest of the sentence modifies. Everything else in the sentence is considered the predicate. The predicate includes the verb and everything after it. The sun is very hot today. subj predicate My aunt travels from Florida to New York every summer. Direct/Indirect Object A direct object is a noun that receives the action of the verb. In the sentence below, ask yourself, made a what? She made a phone call Vb do I visited the Air and Space Museum. Indirect Objects (which may or may not appear in a sentence) appears with the direct object and names the person or thing that something is given to or done for. (For whom or for what?) We made the couch a slipcover. vb IO DO 2. Pronoun A pronoun replaces a noun. This prevents repetition in a sentence or paragraph. Ask yourself, “Does the word stand for a noun? Erica mixed the ingredients in the bowl, then she poured it into a cake pan. She modifies Erica. Cody and Veronica love to watch T.V. on Wednesday nights. They love reality television. Cody and Veronica = They 3. Verb Verbs describe an action or state of being and links the subject to the direct object. Ask yourself, “Does the word tell what someone or something did?” “Does the word link one word wit another word that identifies or describes it?” “Does the word merely show that something exists?” The little girl rides her bike down the street. Mike walks down the street every morning on his way to the school bus. Linking Verbs Linking verbs link the subject to a word generally found near the end of the sentence and identifies, renames, or describes the subject. Augustus was emperor. I am thirsty Was links Augustus to emperor (renames) Am links I to thirsty (describes) Verb Forms SINGULAR (add an –s to the verb) Tim sings. She shops as soon as she gets paid! PLURAL (drop the –s) We sing carols every Christmas. They shop every Friday. Verb forms • I walk We walk • You walk You walk • He/she/it walks They walk 4. Adjective Adjectives modify or describe a noun. Ask yourself, “Does the word tell what kind, which one, how many, or how much?” The misty rain made it difficult to see the road. Misty describes road. The noun being modified usually proceeds (comes after) the adjective. Silver hammer Adj noun 5. Adverb An adverb modifies a verb. Ask yourself, “Does the word tell Where, when, in what way, or to what extent?” *Hint: many adverbs end in -ly She quickly hid the cookie jar from the curious child. 6. Conjunction Conjunctions join two words, phrases, or sentences together. Ask yourself, “Does the work connect other words in the sentence?” My elbow hurt so I went to see my physician. We ate at IHOP because all of the other restaurants were closed. *Conjunctions connect two phrases/sentences (they are 7. Preposition Preposition comes before a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase and connects it to another part of the sentence. Prepositions are usually in a phrase (prepositional phrase). Ask yourself, “Is the word part of a phrase that includes a noun or pronoun?” The dog sleeps under the porch during the summer. Through the window, I saw snow falling. I passed by her in K-Mart. 8. Interjection Interjections stand alone and express surprise and emotion (usually followed by an exclamation point). Ask yourself, “Does the word express emotion and function independently of the sentence?” Oh! The new SAW movie is out. Ouch! I just touched a hot stove. Ha! That comedian is really funny. Practice! Identify the nouns and verbs in each sentence: My mother makes the best chocolate cake. Kevin likes to read comic books. Alisha cleans up after her brothers and sisters. Answers! My mother makes the best chocolate cake. noun/subj vb noun/do Kevin likes to read comic books. noun/subj vb noun/do Alisha cleans up after her brothers and sisters. noun/subj vb prepositional phrase More Practice Identify the Adjective or adverb in each sentence. The child slowly walked away. The bare trees were evidence that it was winter. The paper airplane soared lightly through the air and landed on the teacher’s desk. More Answers! The child slowly walked away. adv (describes how the child walked) The bare trees were evidence that it was winter. adj (describes trees) The paper airplane soared lightly through the air adj (describes airplane) adv (describes soared) and landed on the teacher’s desk. adj (describes desk) This is a compound sentence. More?? Determine whether the underlined word is a conjunction, a preposition, or an interjection. Wow! That car is really fast! There are flowers growing under the bridge. The sign had fallen so I picked it up. After the movie, we went to a pizza place. I called but you were busy. Gees! Time goes by so quickly. More Answers Wow! That car is really fast! Interjection There are flowers growing under the bridge. Prepositional phrase The sign had fallen so I picked it up. Conjunction After the movie, we went to a pizza place. Prepositional Phrase I called but you were busy. Conjunction Gees! Time goes by so quickly. Interjection