Classification
advertisement

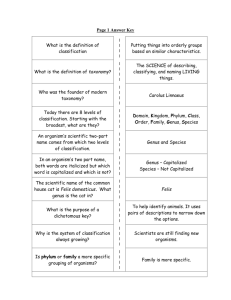
Biology Class Notes Lesson 30: Classification Systems Objective: 3.5.1, 3.5.2 Classification Grouping of 2 million+ organisms based on shared characteristics. Taxonomy: The science of identifying, classifying and naming living things. The Beginning of Classification • Aristotle (382-322 B.C.): Greek philosopher who created the first classification system. Ex: Plant vs. animal, and whether they flew, walked or swam. • Carolus Linnaeus (1701-1778): A Swedish botanist who developed a new classification system based on hierarchy (i.e. levels). *This is the system used today Linnaean Taxonomy • Divided into hierarchical levels: Domain (largest/most general: eukaryotes, prokaryotes, archaea) Kingdom Phylum (plural=phyla) Class Order Family Genus (plural=genera) Species (smallest and most specific group) Mnemonic: Do Kings Play Chess On Fine Green Silk Classification of Common Animals Ex: Domestic Dog Canis lupus familiaris • Domain: Eukarya • Kingdom: Animalia • Phylum: Chordata • Class: Mammalia • Order: Carnivora • Family: Canidae • Genus: Canis • Species: Canis lupus • Subspecies: Canis lupus familiaris Binomial Nomenclature: A two part naming system developed by Carolus Linnaeus with the first word being the genus and the second word being a unique identifier called a specific epithet. Three ways to write it are: italics, underlined or in (parentheses) with only the genus capitalized. Ex: Homo sapiens, Homo sapiens, or (Homo sapiens). Kingdoms of the Domain Eukarya (4) Protista Protists: Eukaryotic organisms that cannot be classified as fungi, plants or animals. • They can be unicellular and multicellular, as well as heterotrophic and autotrophic. Fungi (singular = fungus) • Obtain nutrition by feeding on dead or decaying organic matter. • Their cell walls contain chitin. • Mushrooms = Multicellular fungi and yeast = Unicellular fungi. Plantae Plants: Multicellular organisms that are photosynthetic autotrophs. • Their cell walls contain cellulose. Animalia Animals: Multicellular and heterotrophic organisms that obtain nutrition by eating plants or other animals. • Their cells lack cell walls and chloroplasts. Classification Chart for Domain Eukarya (*Copy and memorize this chart.) Domain Eukarya Summary Kingdom Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia Cell Type Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Eukaryote Cell Structur e Mixed Cell Wall, chitin Cell Wall, cellulose No cell wall Body Form Uni and Multicellular Uni and Multicellular Multicellula r Multicellular Nutrition Auto and Heterotrophi c Heterotrophi c Autotrophic Heterotrophi c Phylogeny The evolutionary history of a group of organisms. Phylogenetic Tree: A diagrams that depict relatedness or common ancestors of a group of organisms. Dichotomous Key: A tool that can be used to determine the identity of something by matching characteristics to a series of pair statements or questions. Classify Candies Lab Key Words: Taxonomy Species Domain Kingdom Prokaryote Eukaryote Autotroph Heterotroph Binomial nomenclature Genus Phylogeny Phylogenetic Tree Dichotomous key