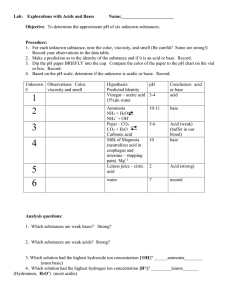
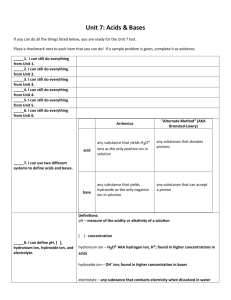
Acidic, Basic and Neutral Solutions
advertisement

Acidic, Basic and Neutral Solutions Chapter 9, Lesson 2 Acids • An acid is a substance that releases a positively charged hydrogen ion, H+, in water. – Acids taste sour and turn blue litmus paper red. – The hydrogen ion from an acid combines with a water molecule in solution to form a hydronium ion, which has the formula H3O+ – Because acid solutions contain ions, they conduct electricity. Hydronium ion • When an acid dissolves, it releases a hydrogen ion. • The H+ ion combines with water to form H3O+, the positively charged hydronium ion. Hydrogen ion Water molecule Hydronium ion What is a hydronium ion? Uses of Acids • Acids are important in several body processes, including breaking down food in the stomach. • Acids are also used in making many products, such as fertilizers, detergent, and cleaners. Bases • A base is a substance that produces hydroxide ions when dissolved in water. – The formula for the hydroxide ion is OH– Bases feel slippery on your skin, taste bitter, and turn red litmus paper blue. – Most bases are ionic compounds. Hydroxide ion • In water, bases separate into a positive ion and the hydroxide ion (OH–). • All the properties of bases are a result of the presence of hydroxide ions that form when the base is dissolved in water. Uses of Bases • Common bases include baking soda and cleaning agents. • Bases are also used to produce new products, such as soap, paper, and plaster. Acids and Bases What is pH? • pH is a numerical scale used to indicate how acidic or basic a solution is. • The pH scale runs from 0 to 14. – Acids are below 7; strong acids are near 0. – Bases are above 7; strong bases near 14. – Neutral solutions have a pH of 7. pH and Hydronium ion Concentration • The higher the concentration of hydronium ions, the more acidic a solution is. • All acid and base solutions contain both hydronium ions and hydroxide ions. • In a neutral solution (pH=7) the hydronium and hydroxide ion concentrations are equal. • A change in one pH unit represents a tenfold change in the acidity or alkalinity (how basic) of a solution. Neutralization • When an acid and a base are mixed, a neutralization reaction occurs. • A neutralization reaction produces water and a salt. • Stomach acid reacts with magnesium hydroxide in the following equation: 2HCl + Mg(OH)2 → MgCl2 + 2H2O • Neither of the products is acidic or basic. How is pH measured? • An indicator is a compound that changes form one color to another within a particular pH range. – Indicators can be used to determine approximate pH, simply whether something is acidic or basic. How is pH measured? pH strips • Litmus is one of the simplest indicator test papers but also the least accurate. • pH testing strips are a quick way of determining the approximate pH of a solution. pH Meters • pH meters are electronic instruments with an electrode that is sensitive to hydronium ions present in a solution. – Accurately measures pH – Requires an electric source to operate pH Meters (cont’d) Lesson Review 9-2 1. An acid with a pH of 3 is contains how many times as many hydronium ions as an acid with a pH of 6? A 1000 B3 C 30 D 100 Lesson Review 9-2 2. When an acid and base are mixed, the products are ____ and ____. A water; a base B water; ammonia C water; salt D ammonia; salt Lesson Review 9-2 3. Red litmus paper is dipped in a solution. The paper turns blue. The solution must have been ____. A acidic B homogeneous C basic D polar Lesson Review 9-2 4. Blue litmus paper turns ____ in acid solutions. A red B orange C green D blue Lesson Review 9-2 5. Which of the following is a hydroxide ion? A H3O+ B H+ C OH– D NH4+ Lesson Review 9-2 6. Which is a property of a base? A sour taste B produces OH– in water C produces H+ in water D reacts with metal to produce hydrogen gas Lesson Review 9-2 7. What ions are present in the greatest amount in a solution with a pH of 2.5? A hydroxide B hydrogen C hydronium D oxygen Lesson Review 9-2 8. What is the symbol for the hydrogen ion? A H3O+ B H2O C H+ D OH–