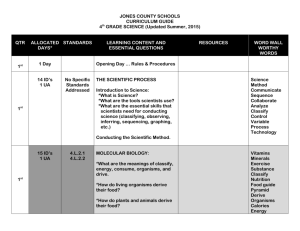
Third Grade Science—Timeline for 2011-2012
advertisement
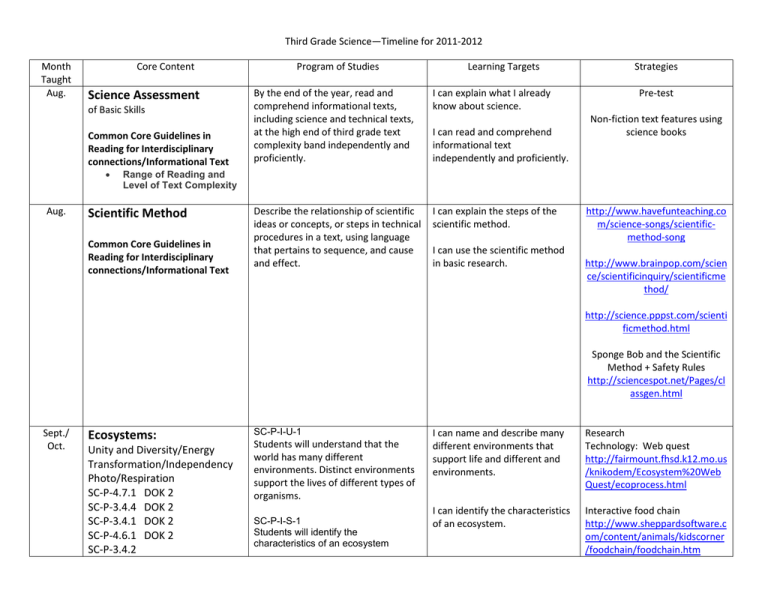
Third Grade Science—Timeline for 2011-2012 Month Taught Aug. Core Content Science Assessment of Basic Skills Common Core Guidelines in Reading for Interdisciplinary connections/Informational Text Aug. Program of Studies Learning Targets By the end of the year, read and comprehend informational texts, including science and technical texts, at the high end of third grade text complexity band independently and proficiently. I can explain what I already know about science. Describe the relationship of scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to sequence, and cause and effect. I can explain the steps of the scientific method. I can read and comprehend informational text independently and proficiently. Strategies Pre-test Non-fiction text features using science books Range of Reading and Level of Text Complexity Scientific Method Common Core Guidelines in Reading for Interdisciplinary connections/Informational Text I can use the scientific method in basic research. http://www.havefunteaching.co m/science-songs/scientificmethod-song http://www.brainpop.com/scien ce/scientificinquiry/scientificme thod/ http://science.pppst.com/scienti ficmethod.html Sponge Bob and the Scientific Method + Safety Rules http://sciencespot.net/Pages/cl assgen.html Sept./ Oct. Ecosystems: Unity and Diversity/Energy Transformation/Independency Photo/Respiration SC-P-4.7.1 DOK 2 SC-P-3.4.4 DOK 2 SC-P-3.4.1 DOK 2 SC-P-4.6.1 DOK 2 SC-P-3.4.2 SC-P-I-U-1 Students will understand that the world has many different environments. Distinct environments support the lives of different types of organisms. SC-P-I-S-1 Students will identify the characteristics of an ecosystem I can name and describe many different environments that support life and different and environments. Research Technology: Web quest http://fairmount.fhsd.k12.mo.us /knikodem/Ecosystem%20Web Quest/ecoprocess.html I can identify the characteristics of an ecosystem. Interactive food chain http://www.sheppardsoftware.c om/content/animals/kidscorner /foodchain/foodchain.htm SC-P-3.4.3 DOK 2 SC-P-I-S-2 Students will observe, document and explain how organisms depend on their environments SC-P-I-S-3 Students will describe and explain how the environment can be affected by the organisms living there SC-P-I-S-5 Students will ask questions that can be explored using a variety of appropriate print and non-print resources (e.g., why certain plants cannot survive in a particular area; why some animals are endangered or extinct; why some areas are ‘protected’) SC-P-UD-U-3 Students will understand that some animals are alike in the way they look and in the things they do, and others are very different from one another. SC-P-UD-U-4 Students will understand that the offspring all living things are very much like their parents, but not exactly alike. SC-P-UD-S-5 Students will use scientific tools (e.g., hand lens/magnifier, metric ruler, balance) to observe and make comparisons of organisms; and to classify organisms using one or more of their external characteristics (e.g., body coverings, body structures) SC-P-UD-S-6 Students will analyze and compare a variety of plant and animal life cycles I can observe and then explain how organisms depend on their environment. I can describe and explain interdependency within an environment, using both plants and animals. I can explain why certain species have a better chance of survival within the same ecosystem. http://www.authorstream.com/ Presentation/tutray-329470Ecosystem-WebQuest-sciencehabitats-ecosystems-webquEducation-ppt-powerpoint/ Food chains using chains http://classroom.jcschools.net/sci-units/livingthings.htm#3 Food webs Using spider webs and 3/5 cards create a food chain in students ecosystem I can explain why some animals look the same, while other animals are different. I can explain how offspring are similar to their parents, but not exactly alike. I can use scientific tools to observe and compare organisms. I can classify organisms using one or more of their characteristics. I can analyze and compare a variety of plant life cycles. I can analyze and compare a variety of animal life cycles. Buckle Down Science Study Island Project: Do a report on an ecosystem and create a diorama of their habitat in order to uncover patterns of growth, development, reproduction and death of an organism SC-P-UD-S-7 Students will ask questions that can be investigated, plan and conduct ‘fair tests,’ and communicate (e.g., write, draw, speak, multi-media) findings to others I can ask questions that can be researched and shared with others. I can explain how the basic needs of living organisms. SC-P-UD-U-1 Students will understand that most living things need water, food and air, while nonliving things can continue to exist without any requirements. SC-P-ET-U-2 Students will understand that almost all kinds of food that animals eat can be traced back to plants. Food chains/webs are useful models of these relationships. SC-P-ET-S-3 Students will observe, illustrate and explain basic relationships of plants and animals in an ecosystem (e.g., use simple food chains and webs to explain how plants and animals get food/energy to live and grow) I can explain how all energy begins with producers. I can create and explain a model of a food chain within an ecosystem using both producers and consumers. I can create and explain a model of a food web within an ecosystem using both producers and consumers. I can infer from models of food chains and food webs whether they complete or not. SC-P-ET-S-7 Students will explore a variety of models (e.g., food chains, webs, circuit diagrams) to infer whether the representation is complete or only part of the actual event/object I can explain how plants and animals features help them to survive in different environments. SC-P-UD-U-2 I can describe how the basic needs of organisms are met in different environments. Students will understand that plants and animals have features that help them live in different environments. SC-P-UD-S-1 Students will describe the basic needs of organisms and explain how these survival needs can be met only in certain environments Students will identify the characteristics that define a habitat. SC-P-UD-S-2 Students will identify the characteristics that define a habitat Nov. Matter SC-P-1.1.1 DOK 3 SC-P-1.1.2 SC-P-STM-S-1 Students will use senses to observe and describe properties of material objects (color, size, shape, texture, flexibility, magnetism) SC-P-STM-S-2 Students will use appropriate tools (e.g., balance, metric ruler, thermometer, graduated cylinder) to measure and record length, width, volume, temperature and mass of material objects and to answer questions about objects and materials SC-P-STM-S-5 Students will observe and predict the properties of material objects Dec. Nutrition PL-1.2.1 PL1.2.2 DOK 1 I can use my senses to describe and explain the properties of material objects. Interactive whiteboard –Solids, liquids and gases Song: “Matter is All Around” I can use appropriate scientific tools to measure and record objects and materials. Compare and contrast materials by color, size, shape, texture, flexibility and magnetism I can observe and make predictions about the properties of material objects. SC-P-STM-S-4 Students will classify water and other matter using one or more physical properties I can classify matter using one or more physical properties. Students will identify nutrients (protein, carbohydrates, fats), which are important in the growth and development of healthy bodies. I can identify nutrients that are important for my body to grow and be healthy. Students will describe the overall purpose of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans. I can describe the purpose of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans and how it relates to my health. Guest Speaker: Jackie Hodgens, Taylor Co. Health Department Create a Wellness plan which includes a balanced diet. Dec./Jan Rock Cycle SC-P-2.3.1A DOK 2 SC-P-2.3.1B SC-P-EU-U-1 Students will understand that people use a variety of earth materials for different purposes because of their different properties. All products that people use somehow come from the Earth. SC-P-EU-S-1 Students will use senses and scientific tools (e.g., hand lens/magnifier, metric ruler, balance, etc.) to observe, describe and classify earth materials (solid rocks, soils, water and air) using their physical properties SC-P-EU-S-2 Students will explore how earth materials are used for certain things because of their properties I can explain how people use a variety of earth materials for different uses. Interactive whiteboard chart – rocks interactive rock cycle http://www.learner.org/interact ives/rockcycle/diagram2.html I can use scientific tools to observe, describe and classify rocks and minerals using their physical properties. I can explore earth materials for different properties. I can explain the difference between rocks, minerals, and soil. Song: Rock Cycle to tune of row, row your boat In your lab group, write your own poem, rhyme, song/rap, or skit about the rock cycle. Investigate and draw Mach Rocks Create igneous rocks out of peanut brittle I can explain the various types of Create sedimentary rocks out of rocks that make up the rock clay cycle. Create metamorphic rock using paper and crayons Jan/Feb Fossils Geological Time Biological Change SC-P-3.5.1 DOK 2 SC-P-BC-U-1 Students will understand that fossils found in Earth materials indicate that organisms and environmental conditions may have been different in the past. SC-P-BC-S-1 Students will identify and describe evidence of organisms that no longer exist (fossils) SC-P-BC-S-2 Students will examine fossils/representations of fossils and make comparisons between I can infer how fossils found in the earth indicate that organisms and environmental conditions may have changed over time. I can identify and describe organisms that no longer exist as fossils. I can make comparisons between organisms that lived long ago and organisms that are Using a track design by student create an animal that would have made the track and draw a picture of what animal would look like and what life would have been like for that animal. Compare and contrast fossils Create a fossil using plaster of Paris Interactive dino dig http://paleobiology.si.edu/dinos organisms that lived long ago and organisms of today (e.g., compare a fern to a fossil of a fern-like plant) SC-P-BC-S-3 Students will make inferences about the basic environments represented by fossils found in earth materials (e.g., fossils of fish skeletons represent an aquatic environment) February Water Cycle/Weather SC-P-1.1.3 DOK2 SC-EP-2.3.2 DOK 2 SC-P-BC-S-5 Students will compare fossils, plants and animals from similar environments in different geographic locations SC-P-STM-U-4 Students will understand that water can be a liquid, solid, or gas and can go back and forth from one form to another. SC-P-STM-S-3 Students will investigate the physical properties of water as a solid, liquid and gas SC-P-STM-S-4 Students will classify water and other matter using one or more physical properties SC-P-EU-U-2 Students will understand that some events in nature have a repeating pattern. Weather changes from day to day, but things such as temperature or precipitation tend to be similar (high, medium or low) in the same months every year. SC-P-EU-S-3 Students will observe weather conditions and record weather data over time using appropriate tools (e.g., thermometer, wind vane, rain gauge, etc.) alive today. aurs/interactives/dig/main.html I can infer about the basic environment fossils were found in. I can compare fossils, plants, and animals from their geographical locations. I can explain how water can exist in three states of matter. Hands on activity to teach each of the weather instrument I can investigate the physical properties of water. Set up weather station with instruments Collect data I can classify water using one or more physical properties. Graphing Weather over period of time I can identify repeating patterns in changes of weather from day to day. I can observe and record weather conditions using weather instruments over time. I can use weather data to describe weather conditions and make simple predictions based on patterns observed. March Sun/Moon/Earth SC-EP-2.3.3 DOK 2 SC-EP-2.3.4A DOK 2 SC-EP-2.3.4B SC-EP-2.3.5 SC-P-EU-S-4 Students will use weather data to describe weather conditions and make simple predictions based on patterns observed (e.g., daily, weekly, seasonal patterns) SC-P-EU-U-3 Students will understand that the sun, moon and stars appear to move slowly across the sky at different speeds and we can see patterns in their movement with careful observation. SC-P-EU-U-4 Students will understand that the sun can only be seen in the daytime. The moon can sometimes be seen during the day and sometimes be seen at night and its shape changes in a predictable pattern. SC-P-EU-U-5 Students will understand that observable interactions of the sun, moon and the Earth can be used to identify the apparent pattern of their movement. SC-P-EU-S-5 Students will observe the locations and real or apparent movements of the sun and the moon SC-P-EU-S-6 Students will investigate evidence of interaction between the sun and the Earth (e.g., shadows, position of sun relative to horizon) to support inferences about movements in the Earth/Sun system I can explain how the sun, moon, and stars appear to move slowly across the sky. http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/k s2bitesize/science/physical_proc esses/light_shadows/play.shtml I can explain the patterns I have observed from the movement of the sun, moon, and stars. Beach balls to represent sun, moon and earth Sun, moon and earth interactive http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/s cienceclips/ages/9_10/earth_su n_moon.shtml http://www.forgefx.com/casest udies/prenticehall/ph/eclipse/ec I can explain how the interaction lipses.htm of the sun, moon, and the Earth can be used to identify apparent Chart the moon cycle patterns of movement. http://www.google.com/search I can observe the locations and ?q=interactive+phases+of+the+ real or apparent movement of moon&sourceid=ie7&rls=com.m the sun and moon. icrosoft:en-us:IESearchBox&ie=&oe=&rlz= I can explain how the interaction between the sun and the earth causes shadows. http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.c gi?it=swf::800::600::/sites/dl/fre e/0072482621/78778/Lunar_Na v.swf::Lunar%20Phases%20Inter active I can explain why the sun only appears in the daytime and why the moon can be seen both in the daytime and nighttime. Moon challenge Game http://www.sciencenetlinks.com /interactives/moon/moon_chall enge/moon_challenge.html April Electricity and Magnetism Energy Transformation Waves Motion and Forces SC-EP-4.6.3 DOK 2 SC-EP-1.2.1 DOK 3 SC-EP-4.6.4 DOK 2 SC-P-ET-U-5 Students will understand that electricity can only flow when it has a closed path (circuit) to follow. Closed electric circuits can produce light and sound. SC-P-ET-S-5 Students will demonstrate open and closed circuits using batteries, bulbs and wires and analyze models of basic electrical circuits in order to determine whether a simple circuit is open or closed I can explain how energy flowing through a closed circuit can produce light and sound. Create electrical circuit I can construct an open and closed circuit using scientific tools. Create series circuits I can analyze models of basic electrical circuits the energy flow within the circuit. SC-P-ET-S-7 Students will explore a variety of models (e.g., food chains, webs, circuit diagrams) to infer whether the representation is complete or only part of the actual event/object SC-P-MF-U-5 Students will understand that magnetism is a force that can make some things move without touching them. I can explore circuit diagrams to infer whether or not the circuit is complete. SC-P-MF-S-6 Students will observe interactions of magnets with other magnets and with other matter (e.g., magnets have a force that can make some things move without touching them; larger size of a magnet does not have to mean it has greater force) in order to make generalizations about the behavior of magnets I can ask questions about energy and gather information to answer my questions. SC-P-MF-S-8 Students will ask questions about I can explain that magnetism is a force of energy that repels or attracts other objects. Create parallel circuits Interactive learning circuits http://www.learningcircuits.co. uk/ motion, magnetism and sound and use a variety of print and non-print sources to gather and synthesize information SC-P-ET-U-4 Students will understand that light can be observed to determine how it travels and how it interacts with different materials (e.g. reflects, is absorbed, and passes through). May Forces and Motion Graphing SC-EP-1.2.2 SC-P-ET-S-6 Students will investigate light traveling in a straight line until striking an object by observing the shapes of the shadows that are produced SC-P-MF-U-1 Students will understand that things move in many different ways (e.g., fast and slow, back and forth, straight, zig zag, etc.). SC-P-MF-U-3 Students will understand that the position of an object can be described by locating it relative to another object or the background. SC-P-MF-U-2 Students will understand that forces (pushes or pulls) can cause objects to start moving, go faster, slow down, or change the direction they are going. I can explain how light can travel and interacts with different materials. I can investigate how light travels in a straight line until it strikes an object and then creates shadows. I can explain how things move in different ways. I can explain the location of an object relative position based on other objects or backgrounds. I can explain how forces can cause objects to start moving, increase speed, decrease speed or change directions. Interactive Forces and Motion
![Essential_Standards_Science__Vertical_planning_chart[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009840405_1-5fca88c128fc4d4d79a9b0edc8a40fb7-300x300.png)